The document discusses IPv4 and IPv6 addressing. It covers key topics such as:
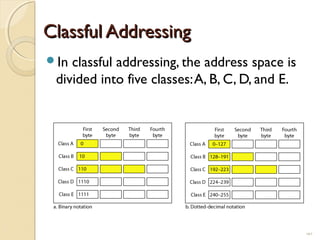
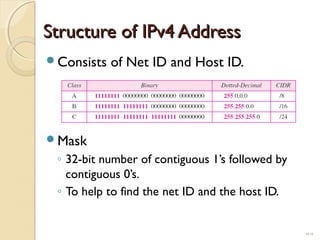
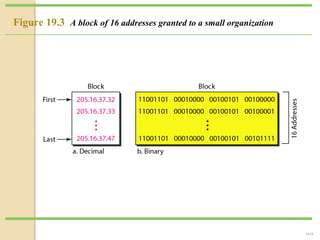
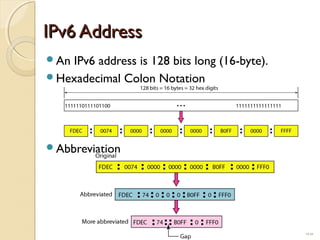
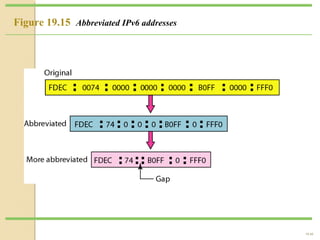
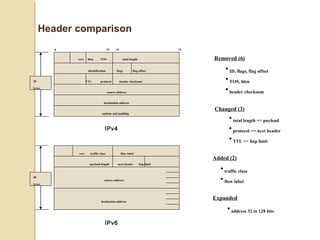
- IPv4 addresses are 32-bit and represented in dotted-decimal or binary notation. IPv6 addresses are 128-bit and represented in hexadecimal notation.
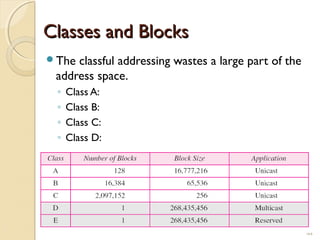
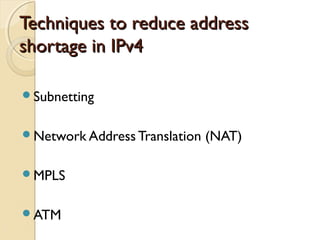
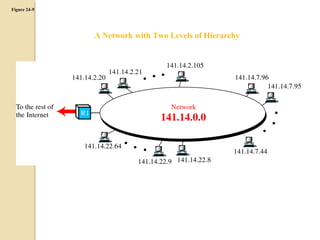
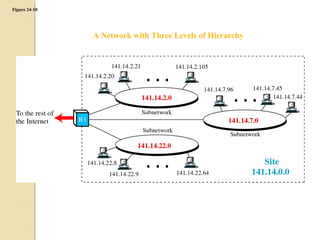
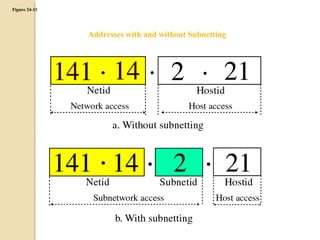
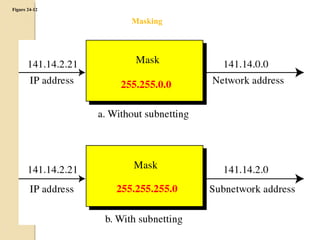
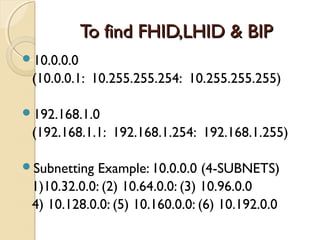
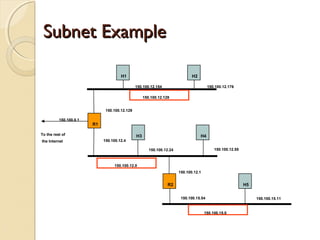
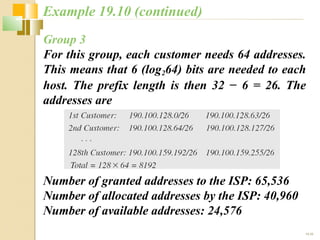
- Subnetting allows an IPv4 network to be divided into smaller sub-networks to reduce broadcast domains and improve performance.
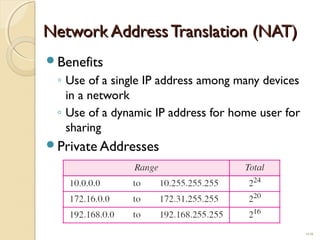
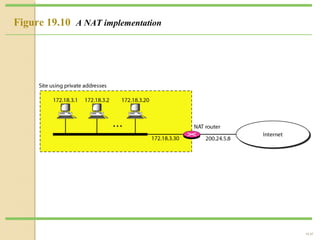
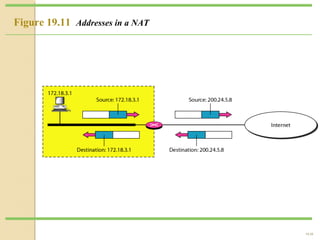
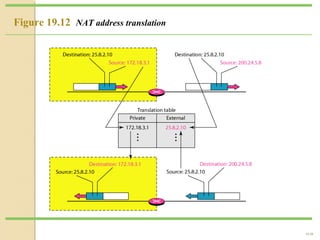
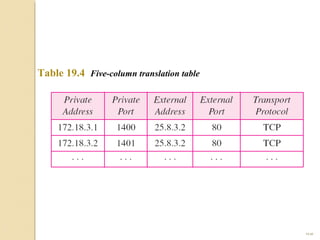
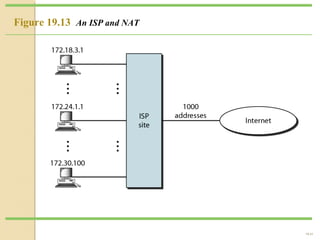
- Network Address Translation (NAT) allows private IP addresses to be translated to public IP addresses, conserving public address space.
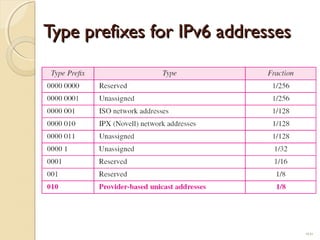
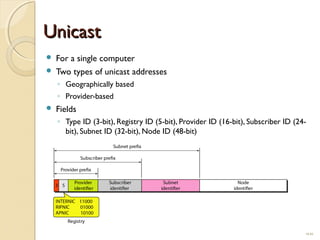
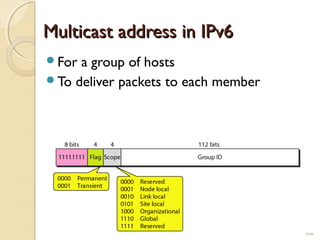
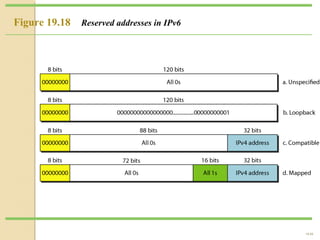
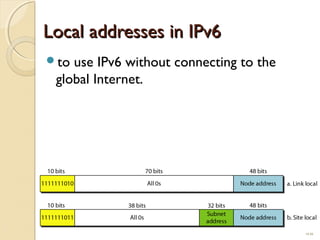
- IPv6 was developed to replace IPv4 due to the limited address space of 232 addresses in IPv4. IPv6 addresses issues each host a unique 128-bit address.