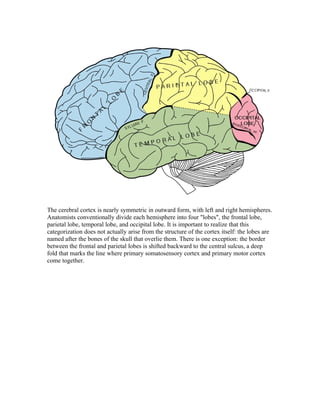
The human brain is the most complex organ and is greatly enlarged compared to other mammals. It contains billions of neurons connected by trillions of synapses. While protected by the skull, the brain is susceptible to damage from injuries, diseases, and toxins. The cerebral cortex is the largest part and is highly folded, with specialized regions involved in different functions like vision, motor control, and language. Communication between the left and right hemispheres occurs mainly through the corpus callosum.