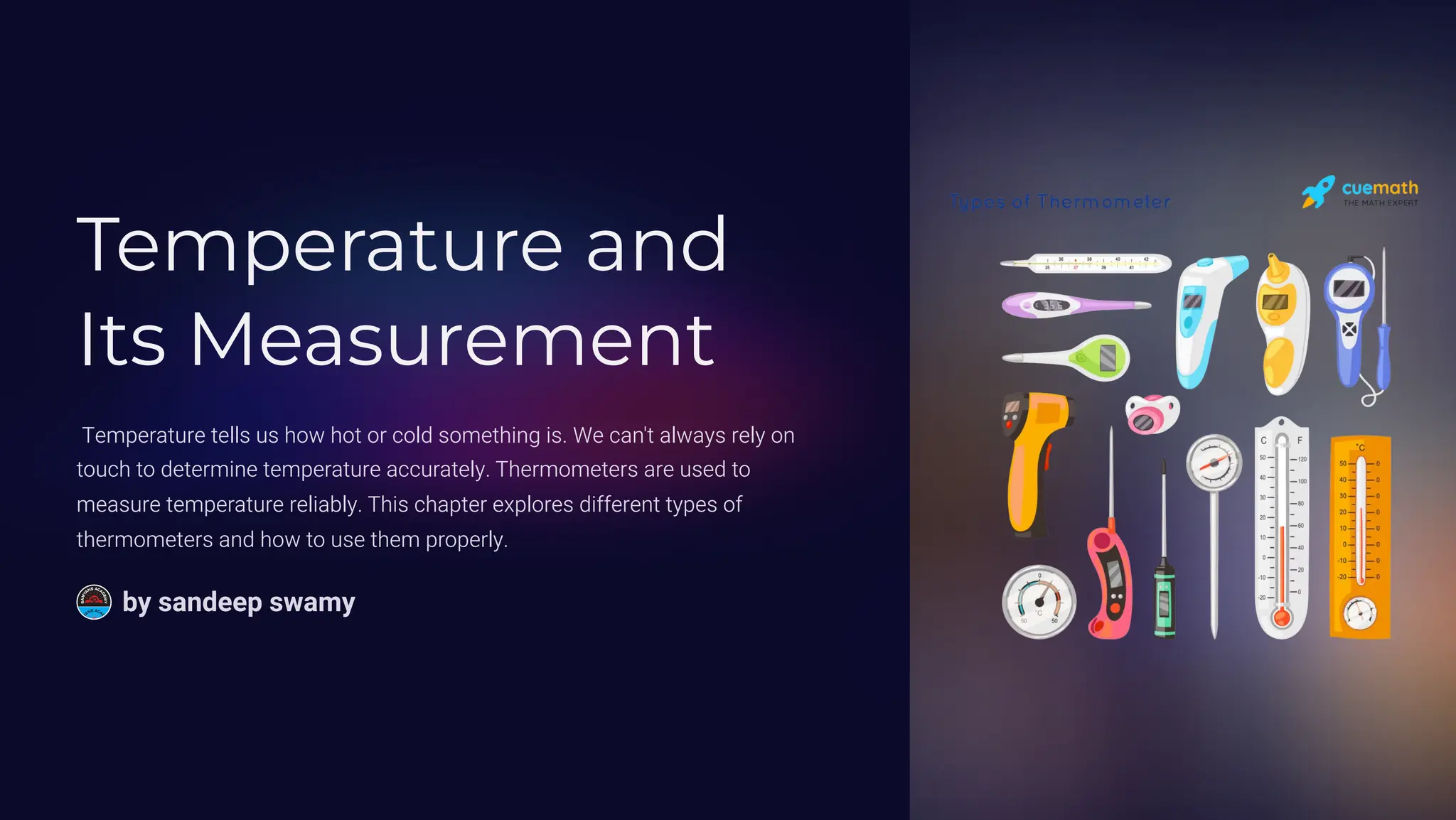
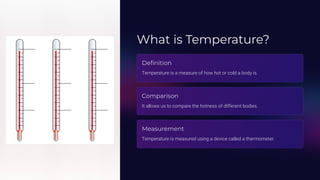
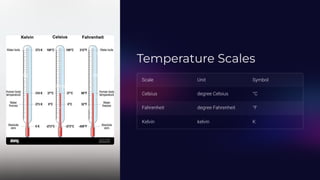
The document discusses the measurement of temperature, highlighting the importance of thermometers for accurate readings as our sense of touch can be misleading. It describes different types of thermometers, their applications, and provides guidelines for measuring body temperature properly. Additionally, it outlines temperature scales, variations, and the significance of precise temperature measurement in various fields such as scientific research and medical diagnosis.