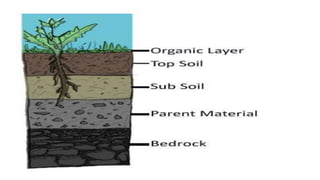
Soil is a mixture of minerals from rocks and organic material from living things that have died. It covers much of Earth's surface in layers, with topsoil near the surface containing more humus. Soil forms slowly over hundreds of years and provides nutrients and housing for plants and animals. Factors like wind, water, deforestation, and overgrazing can cause soil erosion, removing the nutrient-rich topsoil. Conservation efforts like afforestation, terrace farming, and building dams can help prevent soil erosion.