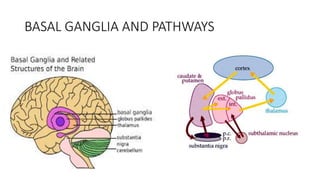
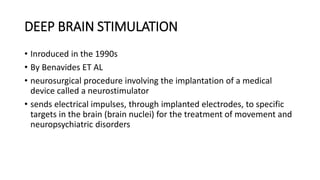
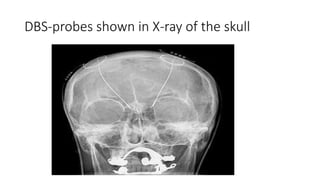
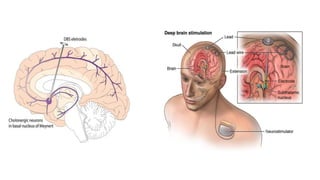
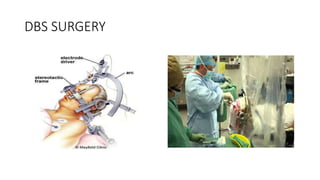
The basal ganglia are brain nuclei that coordinate movement and cognitive functions. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves surgically implanting electrodes into the basal ganglia to deliver electrical stimulation for treating movement and neuropsychiatric disorders like Parkinson's disease. DBS was introduced in the 1990s and works by inhibiting or activating target areas in the basal ganglia to disrupt pathological oscillations. Common targets for stimulation include the subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus. DBS improves motor symptoms in Parkinson's patients and allows for reductions in medication. Potential risks include infection, bleeding in the brain, and device-related complications.