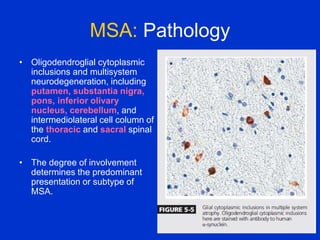
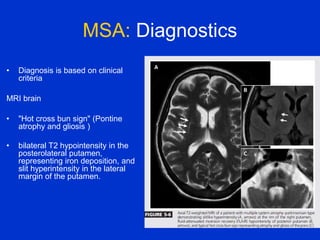
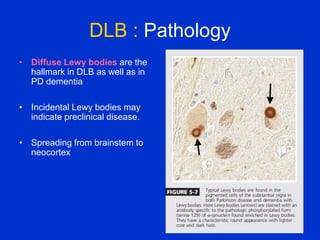
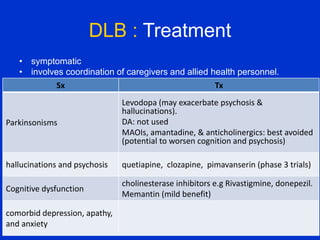
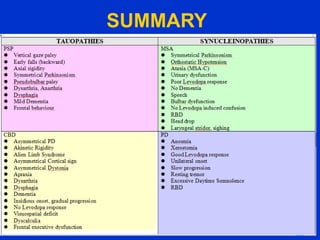
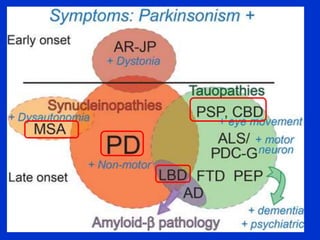
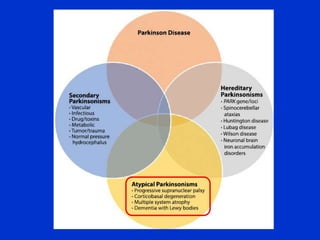
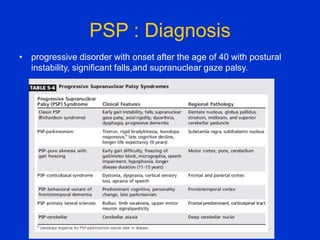
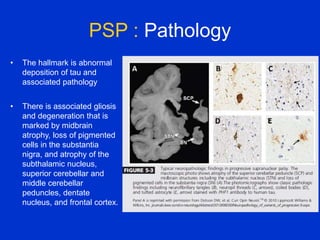
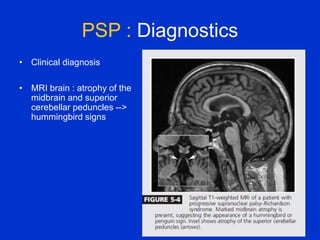
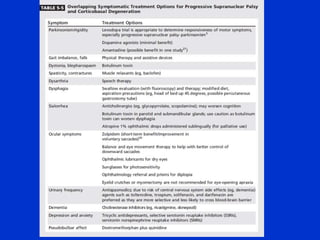
Parkinson plus syndrome refers to atypical Parkinsonism syndromes that are more challenging to diagnose than Parkinson's disease due to overlapping symptoms. The document discusses several Parkinson plus syndromes including progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration (CBD), multiple system atrophy (MSA), and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). It provides details on the epidemiology, clinical features, investigations, treatments, and prognosis of each condition. PSP is characterized by early falls and vertical gaze palsy. CBD presents with asymmetric rigidity and dystonia. MSA involves parkinsonism, cerebellar ataxia, and autonomic dysfunction. DLB involves early



























![MSA
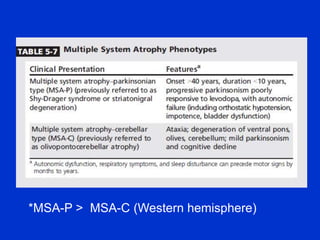
• Parkinsonism, cerebellar and pyramidal signs, and
autonomic dysfunction.
• Two clinical phenotypes are
– Parkinsonism (MSA parkinsonian type [MSA-P])
– Predominant cerebellar ataxia (MSAYcerebellar type [MSA-C])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parkinsonplussyndrome-191029155802/85/Parkinson-plus-syndrome-34-320.jpg)