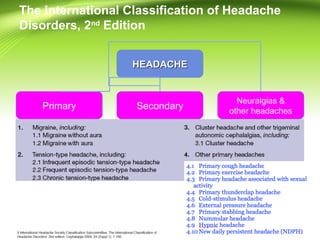
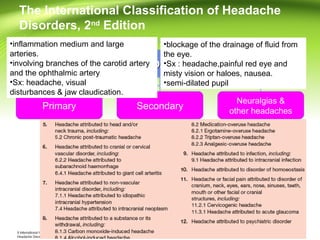
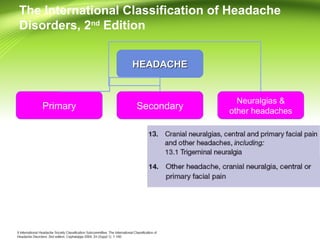
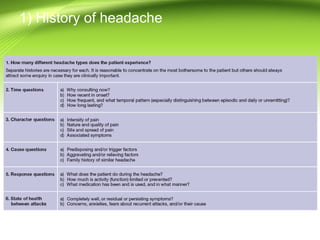
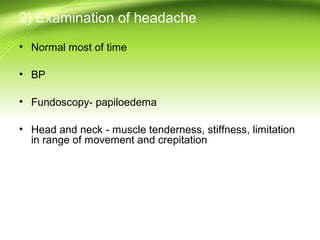
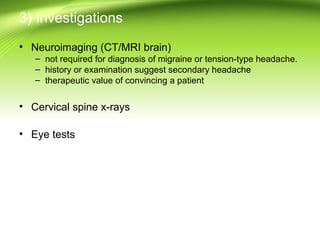
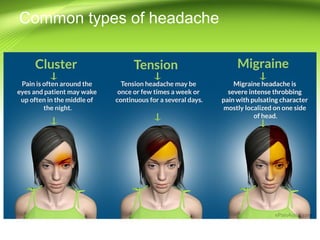
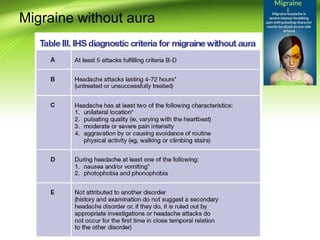
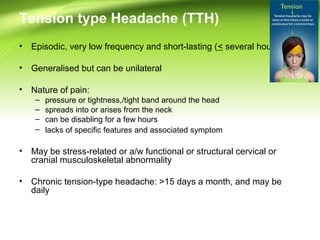
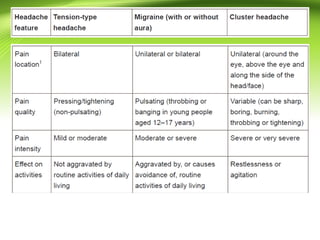
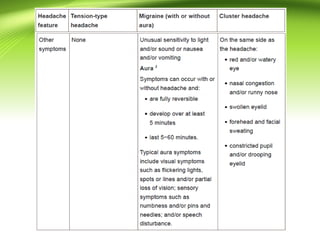
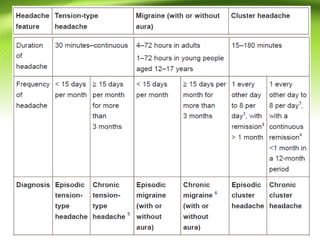
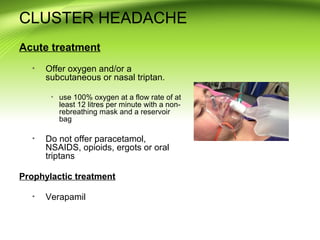
This document provides information on different types of headaches, including migraine, tension-type headache, cluster headache, and medication overuse headache. It discusses the classification, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of various headaches. For diagnosis, it emphasizes taking a thorough history and physical exam. It outlines red flags that warrant further investigation. Treatment involves acute and preventative medications. The focus is on a personalized approach and lifestyle modifications like keeping a headache diary.