1) This document contains information about 4 pediatric radiology cases presented by Dr. Kirsten Ecklund from Boston Children's Hospital.
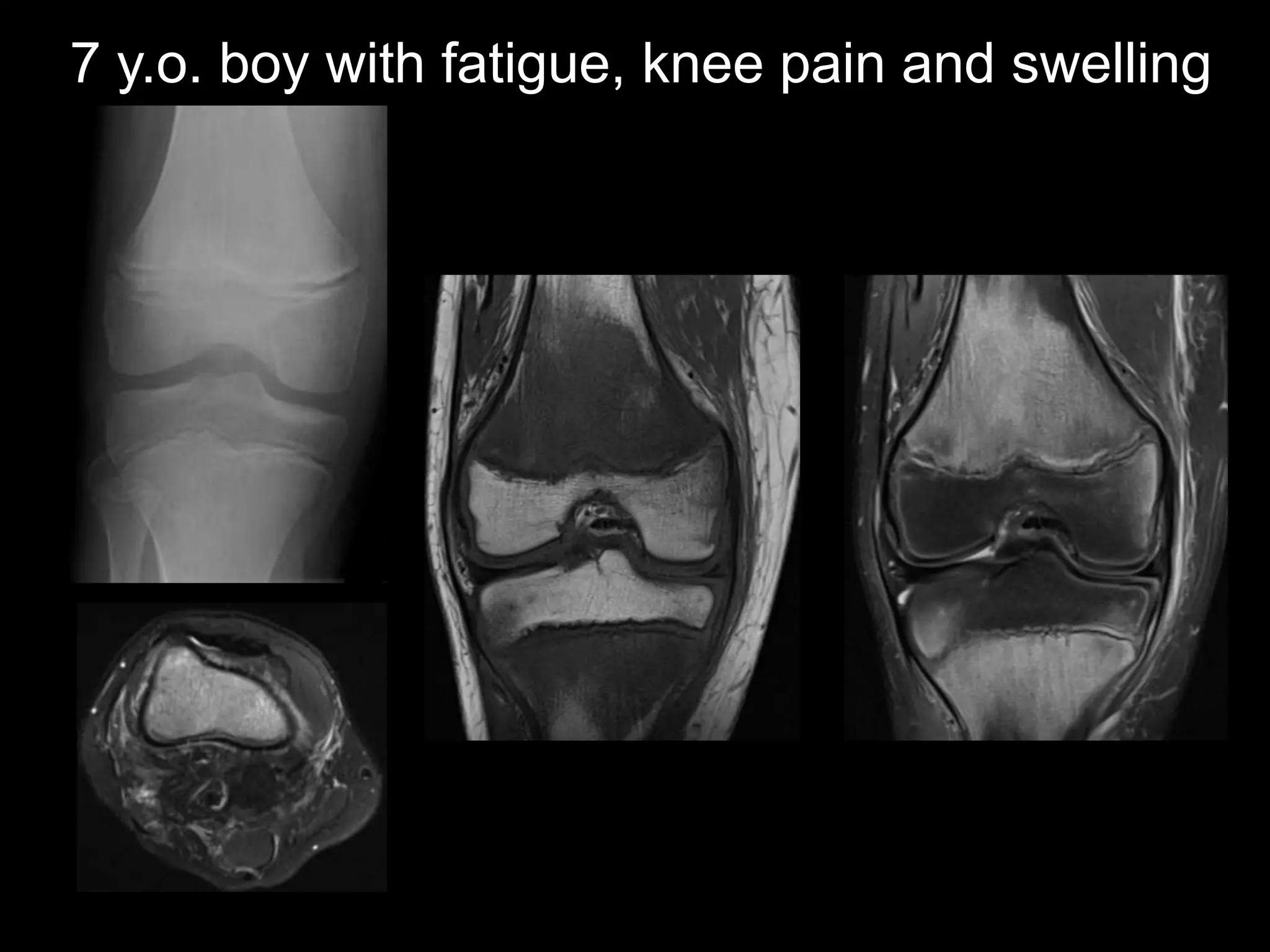
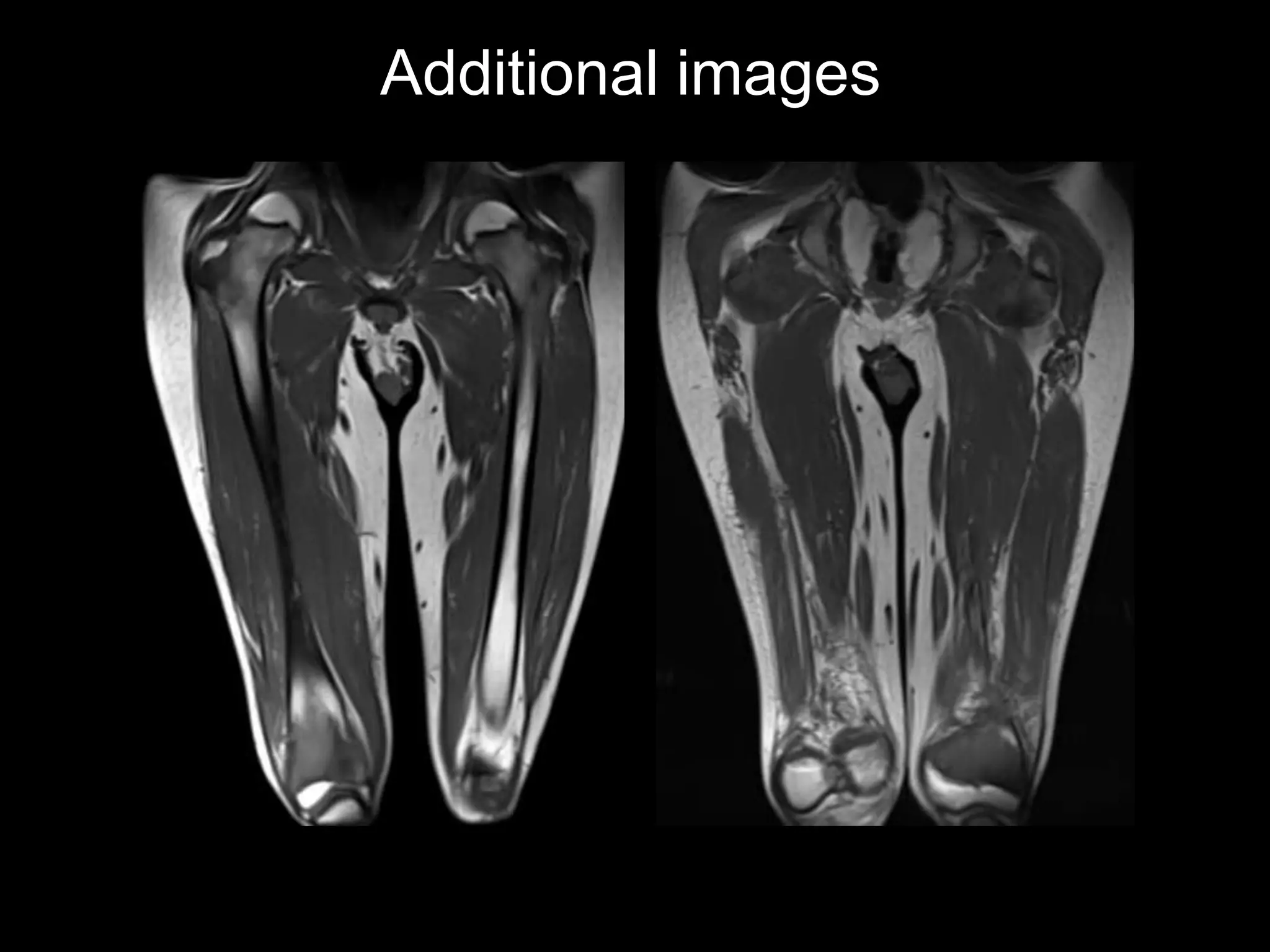
2) The first case discusses a 7-year-old boy with fatigue and knee pain who is diagnosed with scurvy, a vitamin C deficiency.
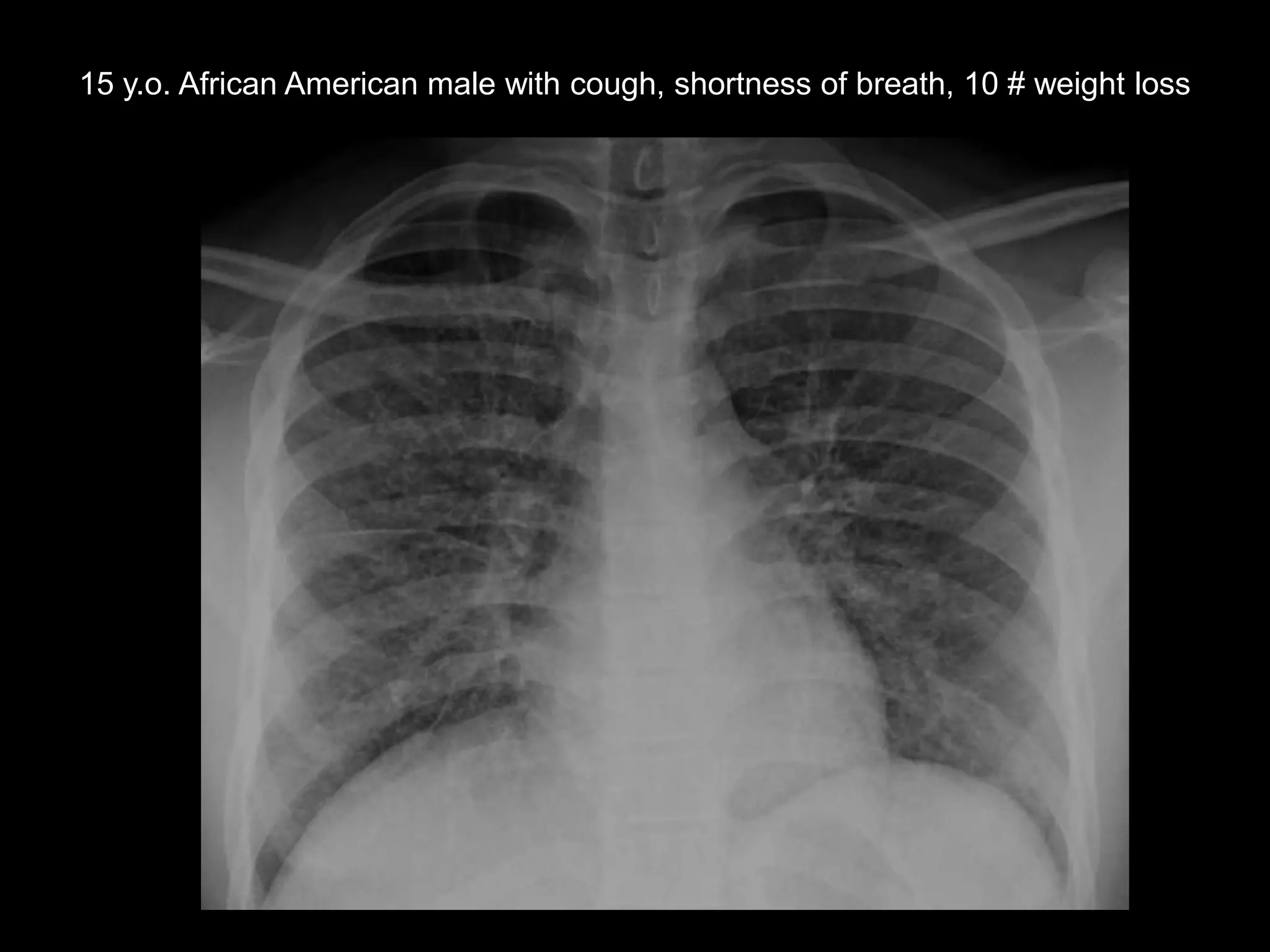
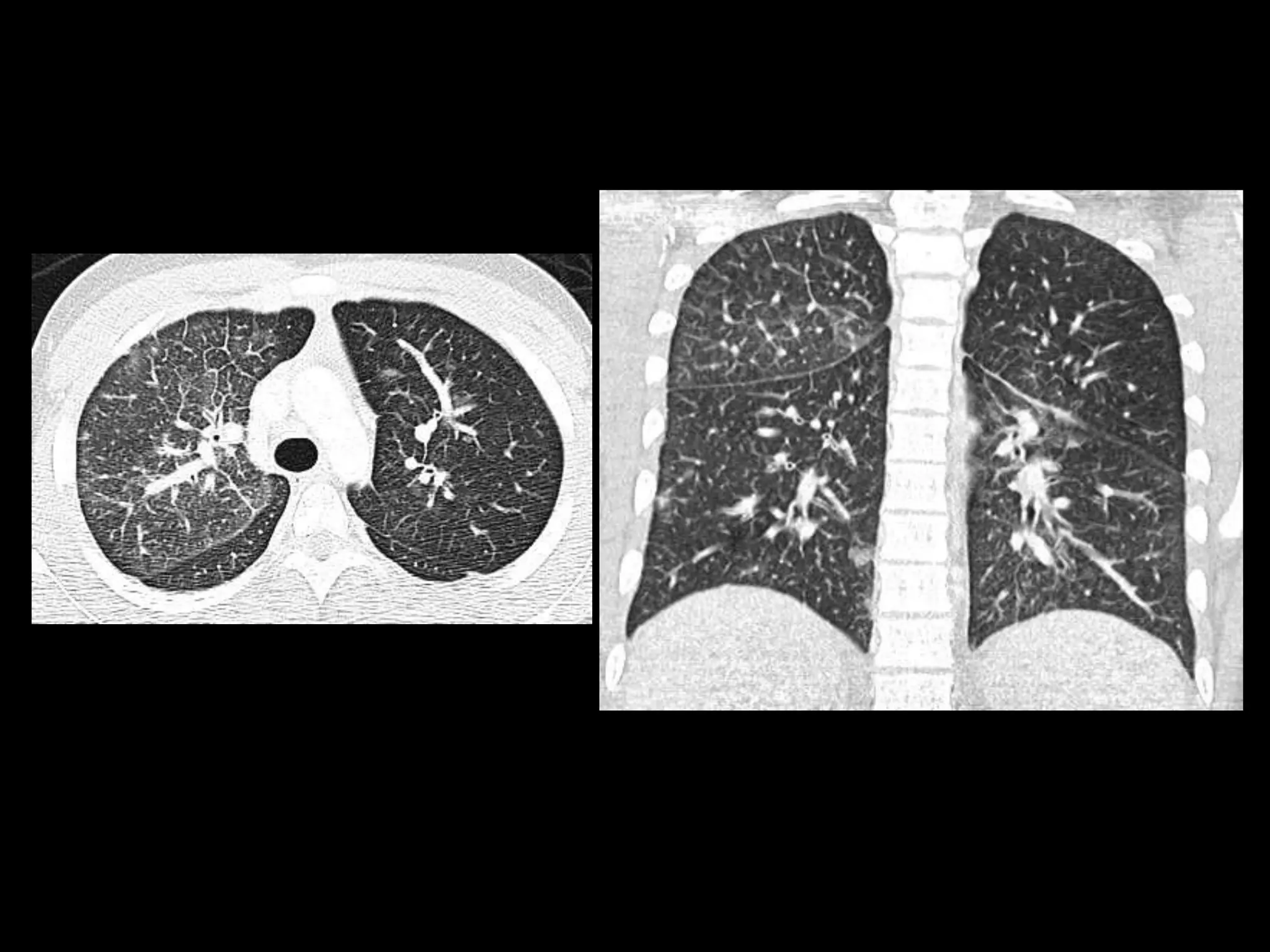
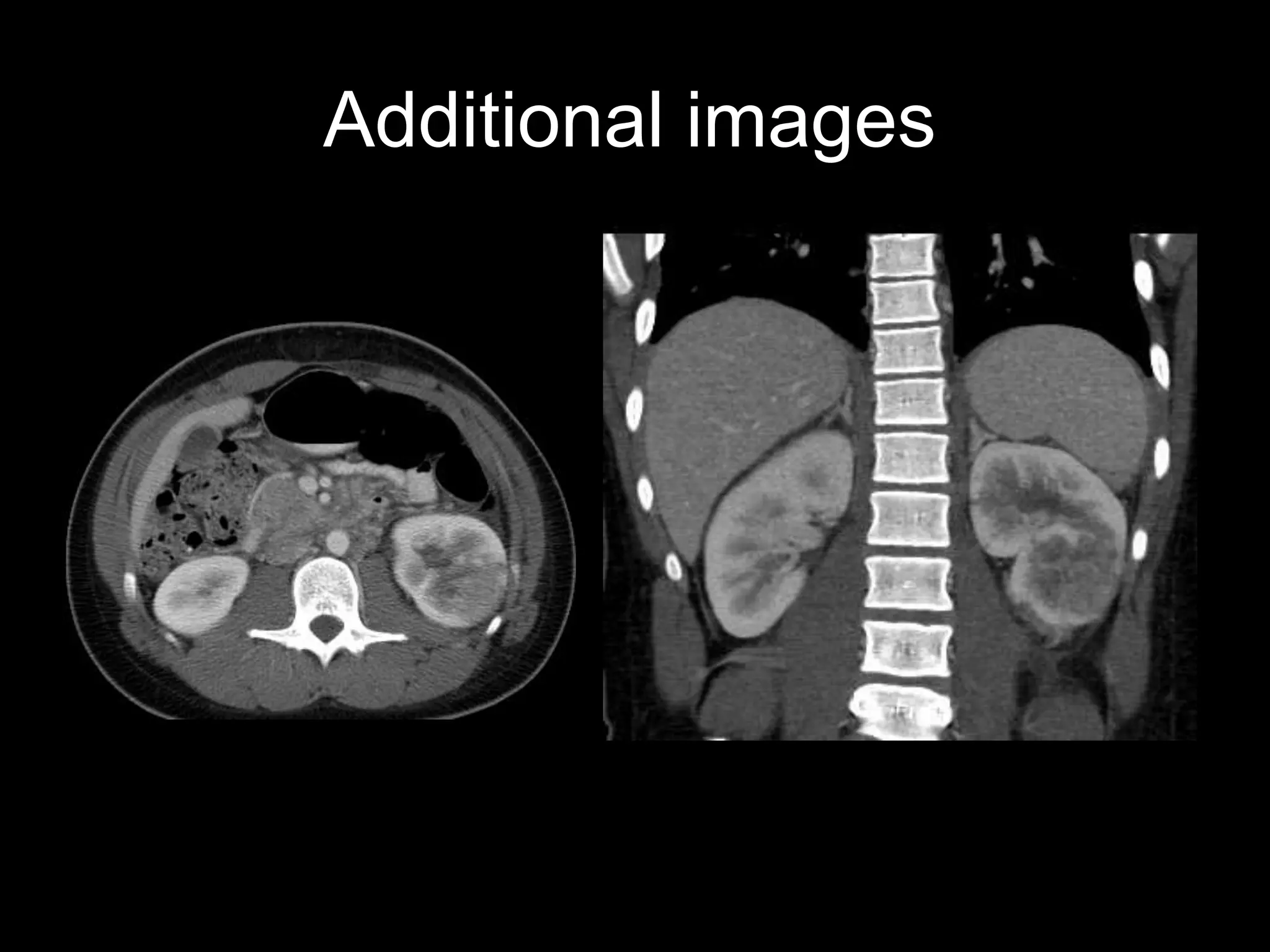
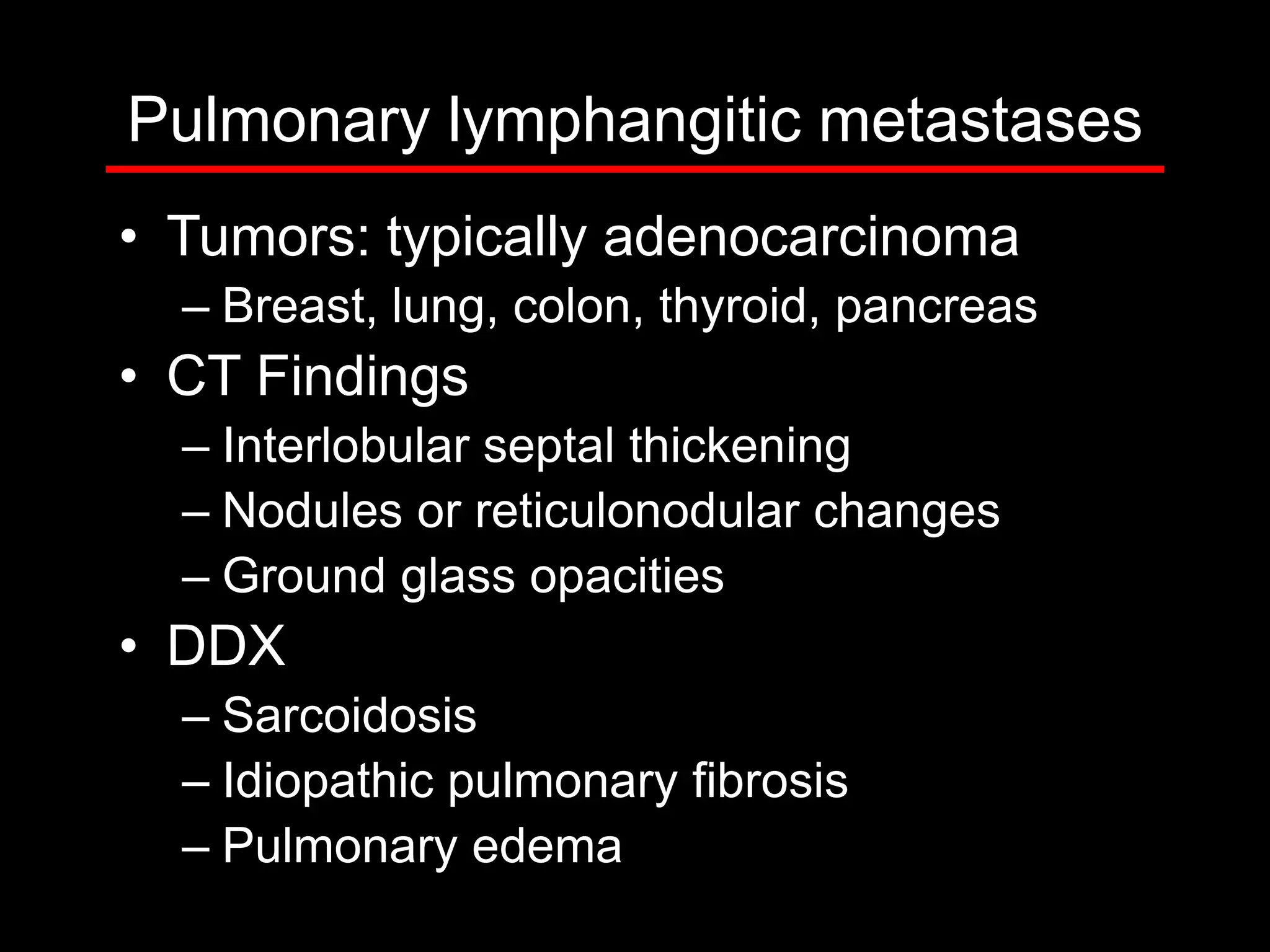
3) The second case involves a 15-year-old boy with cough and weight loss found to have metastatic renal medullary carcinoma to the lungs.
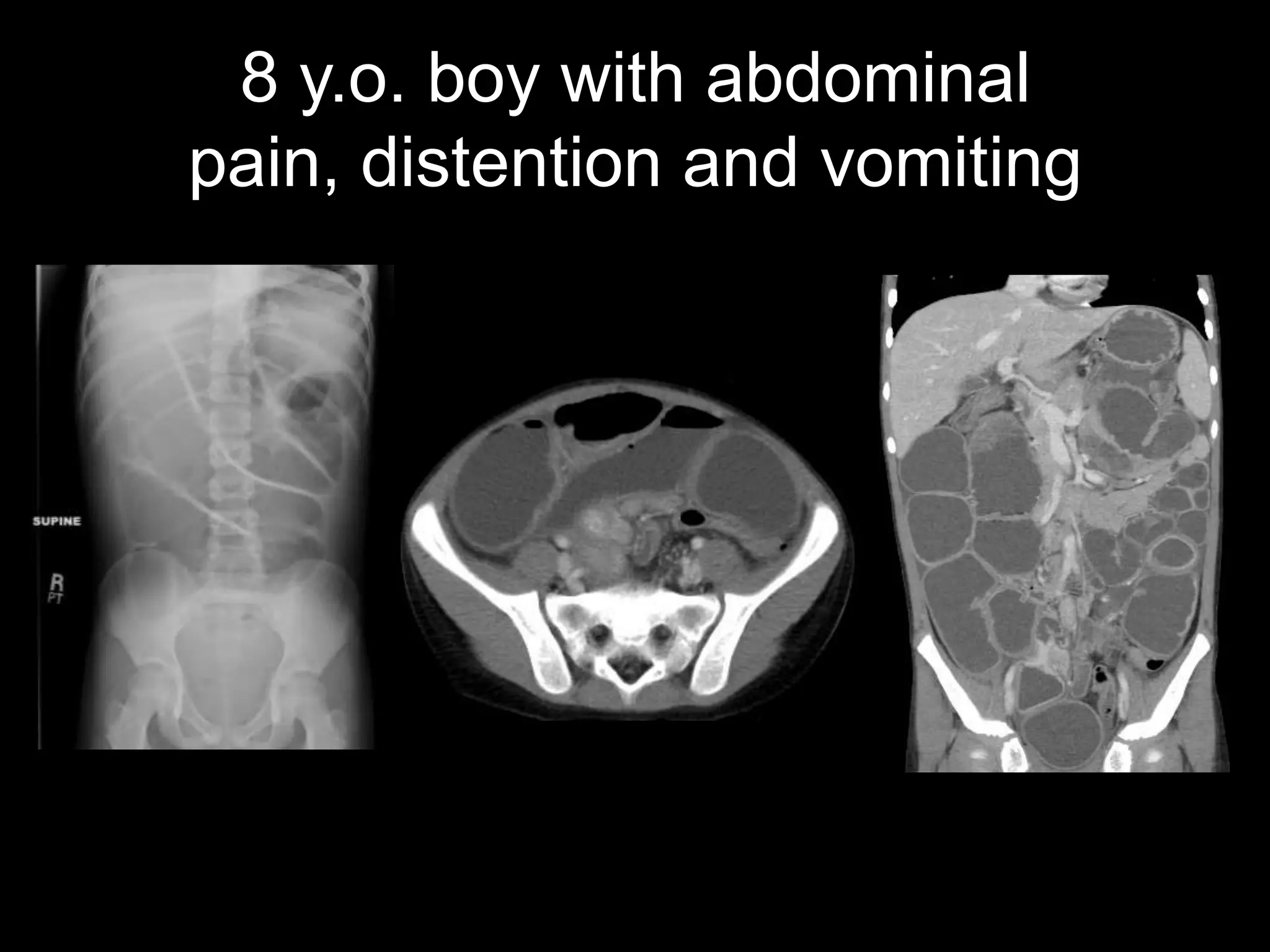
4) The third case is about an 8-year-old boy with abdominal pain found to have an inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor causing small bowel obstruction.
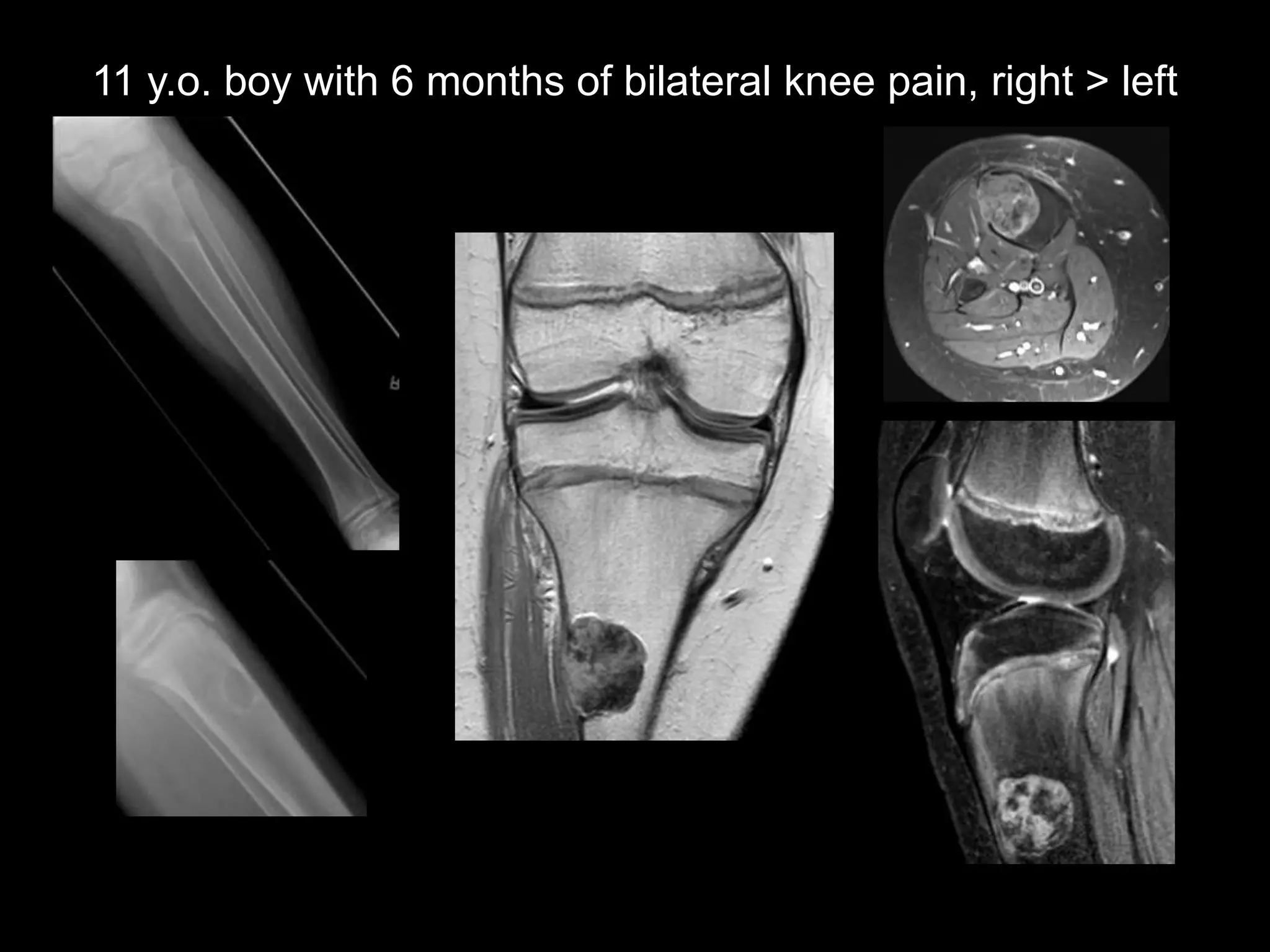
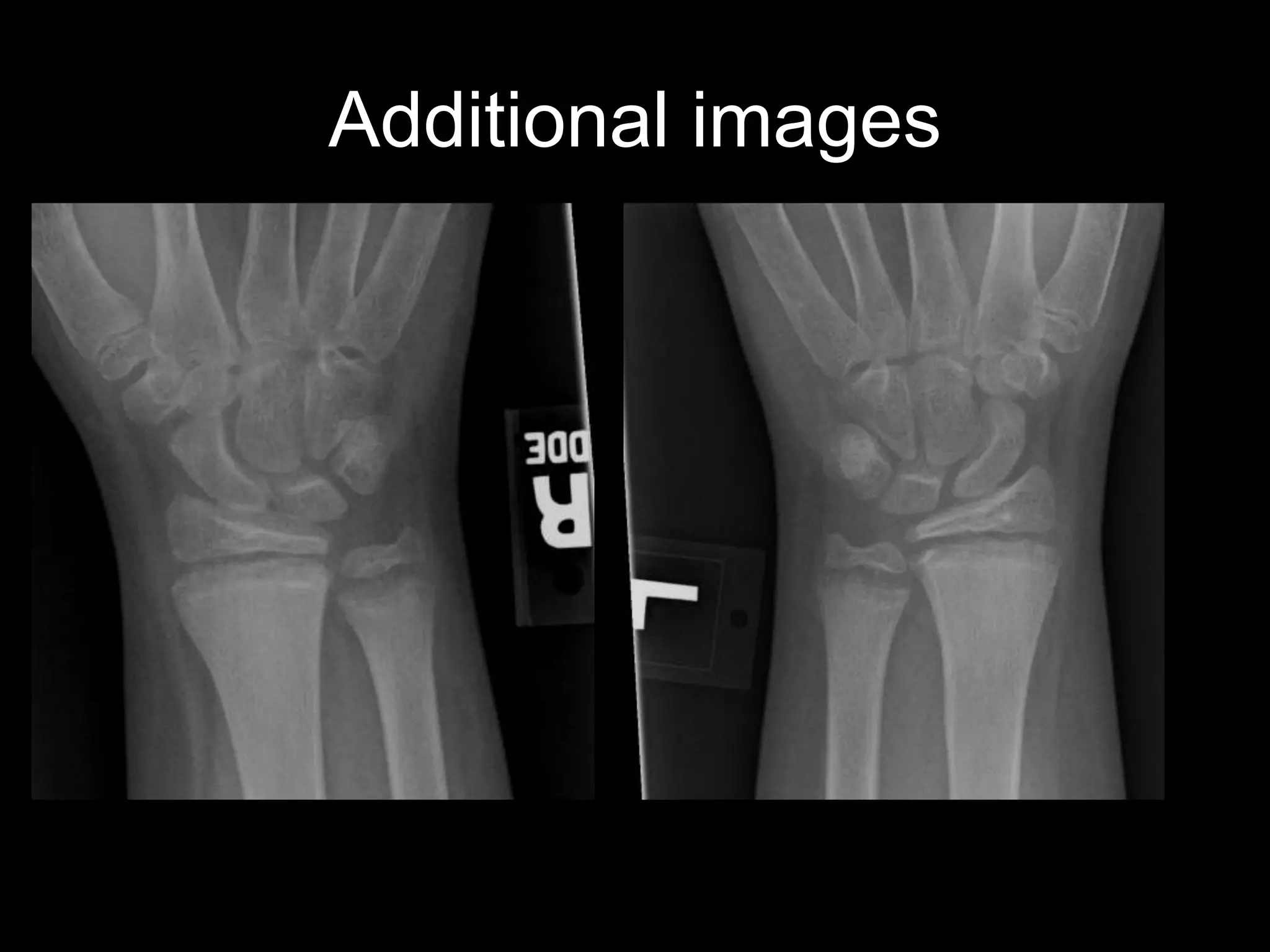
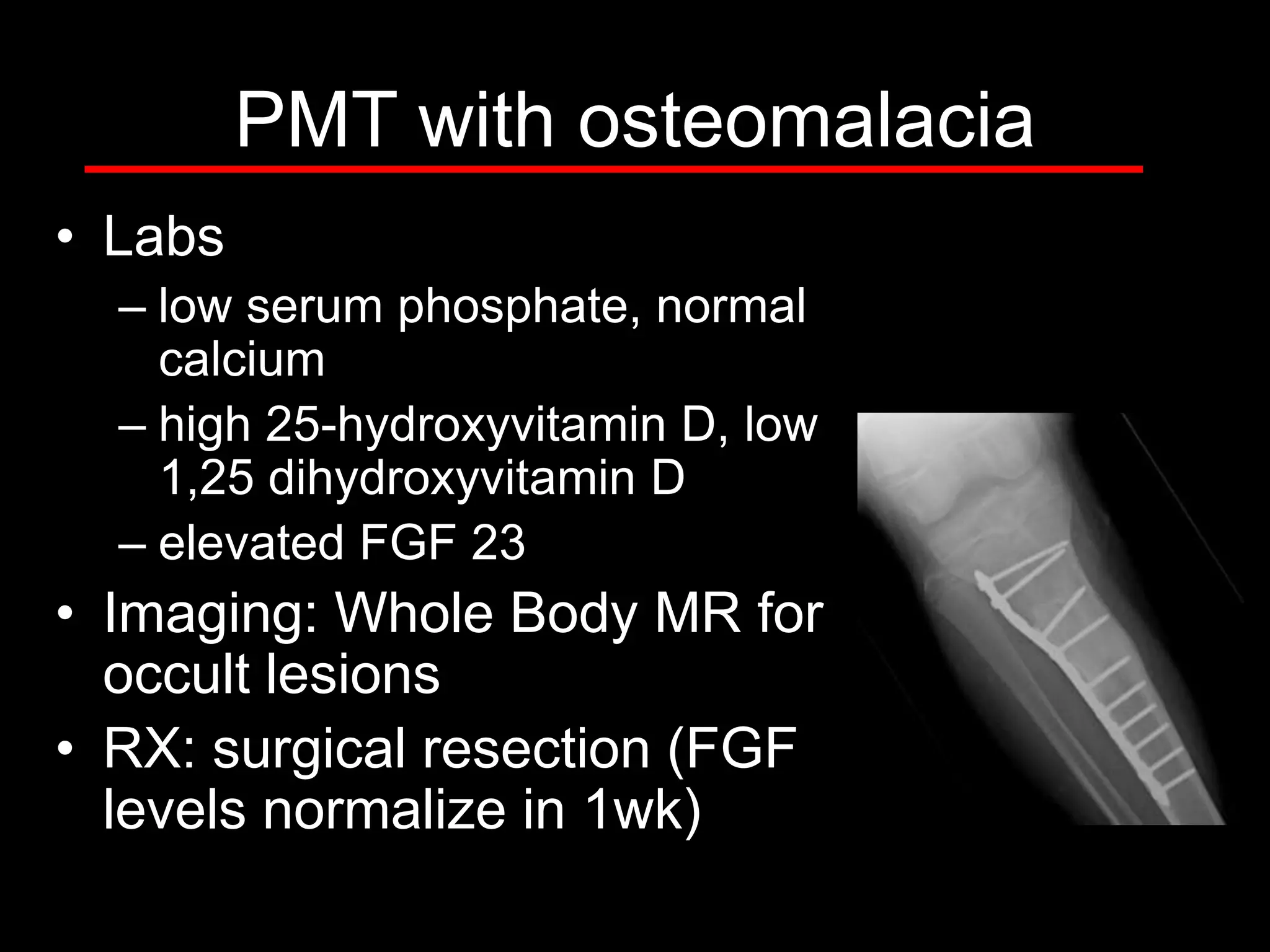
5) The fourth case discusses an 11-year-old boy