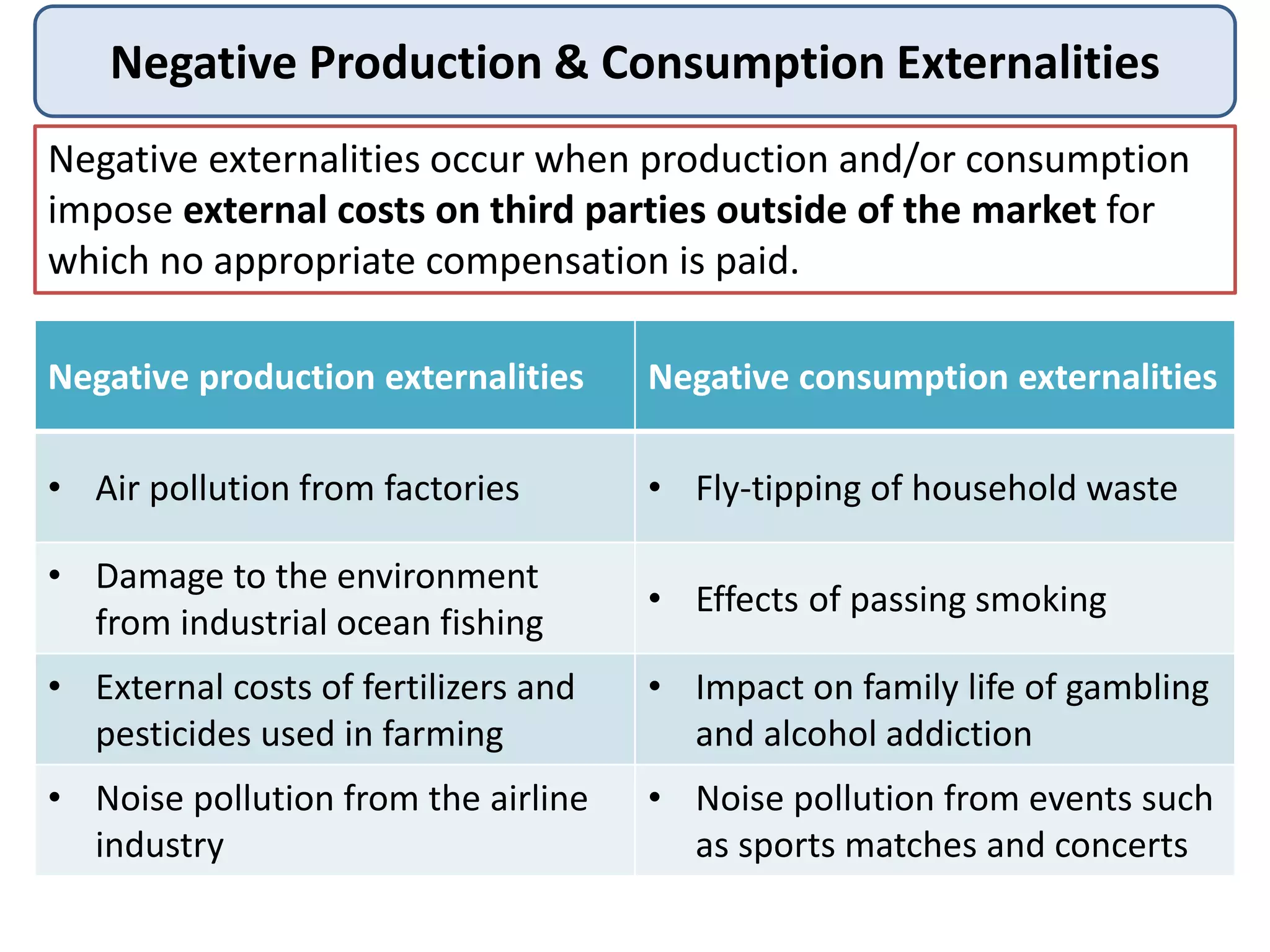
Negative externalities occur when production or consumption impose costs on third parties not involved in the market transaction. This leads to market failure as prices do not reflect the full social costs. Examples include pollution from factories imposing health costs, and noise pollution from events imposing costs of disruption. Taxes and regulations can help internalize these external costs and improve social welfare, but come with challenges of setting the right level and unintended consequences.