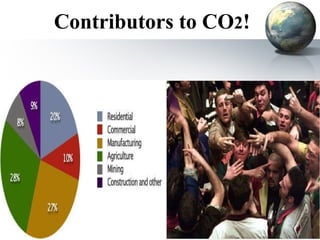
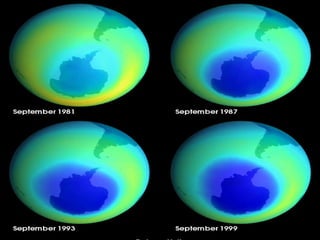
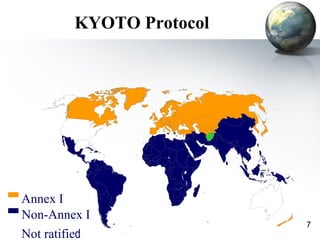
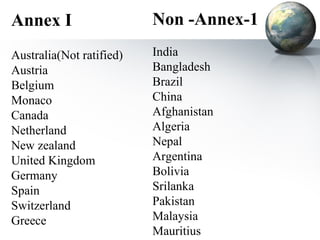
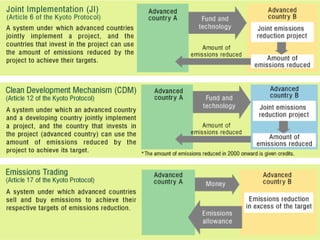
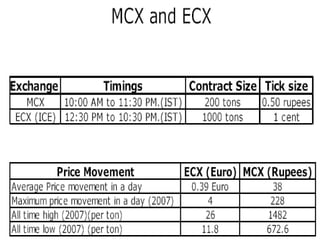
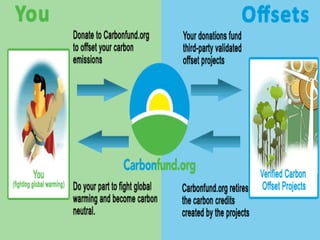
The document discusses carbon credits, which represent one ton of CO2 or equivalent greenhouse gas, regulated under the UNFCCC. It outlines the commitments of Annex I and non-Annex I countries under the Kyoto Protocol and highlights the carbon trading market, especially focusing on India's role in emissions trading and generation of carbon credits. Factors affecting carbon credit prices, including supply-demand dynamics and global economic conditions, are also examined.