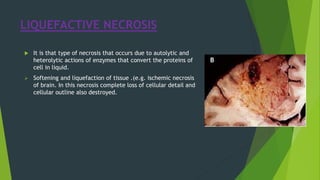
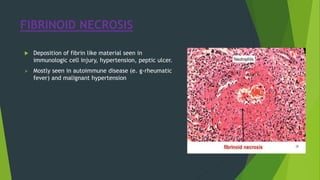
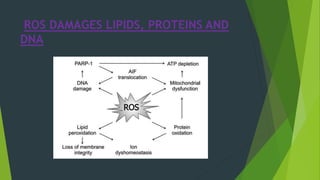
Necrosis is irreversible cell death characterized by cellular swelling, membrane rupture and loss of intracellular contents. It is initiated by factors like ATP depletion during ischemia. The main types of necrosis include coagulative, liquefactive, caseous, fat, fibrinoid and gangrenous necrosis which differ in their morphological appearance. Necrosis is regulated by signaling pathways involving kinases like RIPK1 and mediated by metabolic changes like ATP depletion, calcium and ROS accumulation. ROS can damage lipids, proteins, DNA and induce mitochondrial dysfunction, ultimately leading to necrotic cell death.


![NECROSIS
Necrosis is the morphological changes that follow cell
death in living tissue or organ. Those morphological
changes are called necrosis.
Necrotic cell death is characterized by cellular swelling,
plasma membrane rapture and the subsequent loss of the
intercellular contents. Necrotic cell death may be carried
out by a set of signal transduction pathway and execution
mechanism.
[RIPK1-receptor interacting protein kinase 1, TRAF2- TNF
receptor associated factor 2, PARP- Polly ADP ribose
polymerase, ROS- reactive oxygen species.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/necrosis-181125184038/85/Necrosis-3-320.jpg)










![NECROTIC CELL DEATH INDUCED BY
DEATH DOMAIN RECEPTOR
Mechanism of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)
induced necroptosis. Binding of TNF-α to its receptor
results in formation of Complex I. Activation of cIAP
and tartrate resistant acid phosphatase activates
downstream NF-κB signalling and subsequently
promote cell survival. Complex II acts as a switch
between apoptosis and necroptosis. Activation of
caspase-8 guides the cells to apoptosis. Inhibition of
caspase-8 leads to formation of a necrosome.
Membrane translocation of phosphorylated MLKL
disrupts cell membrane.
[DAMPs: damage associated molecular patterns; MLKL:
mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein, cIAP: calf
intestinal alkaline phosphatise; TRADD: tumor necrosis
factor receptor associated death domain; TRAF: TNFR-
associated factors; RIP1: receptor-interacting protein 1;
CYLD: cylindromatosis, NF-kB: nuclear factor kappa.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/necrosis-181125184038/85/Necrosis-16-320.jpg)



![REFERENCES
[1] Clarke, P.G. (1990) Anatomy and Embryology, 181, 195-213.
[2] Hengartner, M.O. (2000) Nature, 407, 770-776.
[3] Levine, B. and Klionsky, D.J. (2004) Dev. Cell, 6, 463-477.
[4] Festjens, N., Vanden Berghe, T. and Vandenabeele, P.
[5] Yoshida, H., Kong, Y.Y., Yoshida, R., Elia, A.J., Hakem, A.,
Hakem, R., Penninger, J.M. and Mak, T.W. (1998) Cell, 94,
739-750.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/necrosis-181125184038/85/Necrosis-21-320.jpg)
