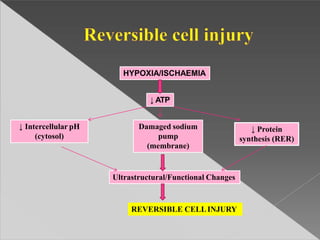
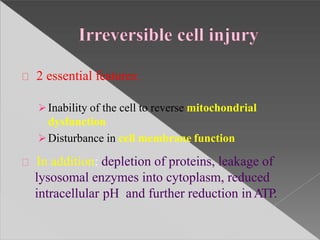
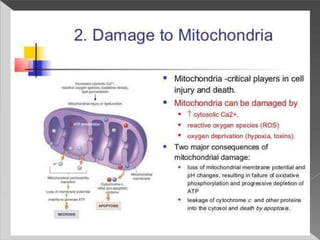
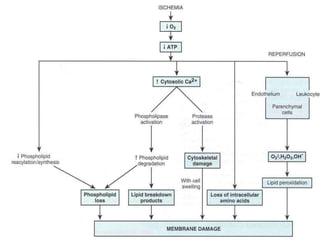
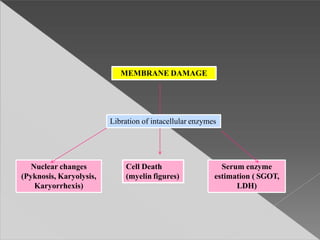
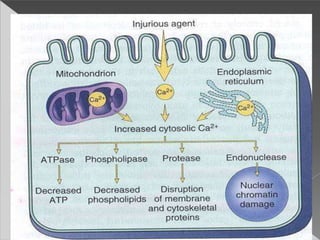
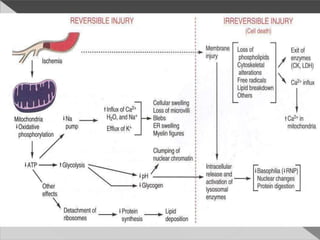
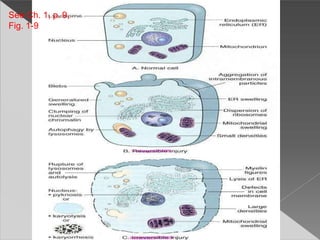
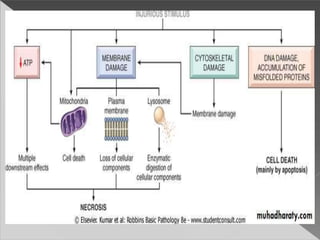
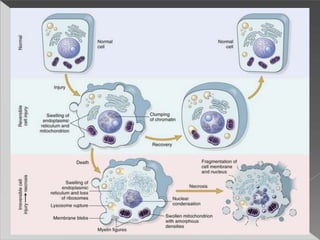
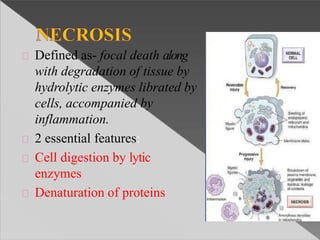
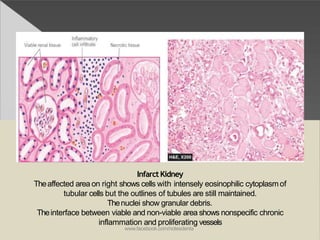
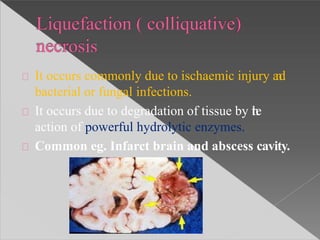
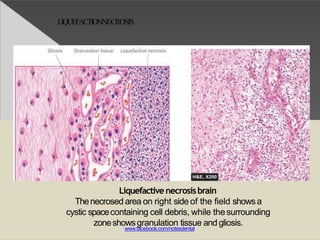
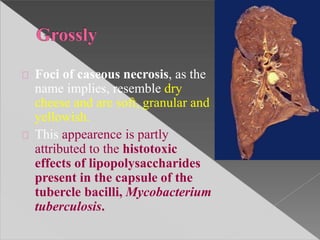
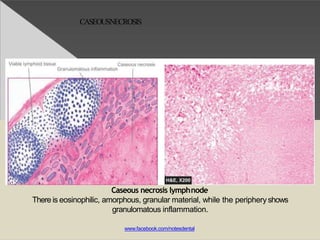
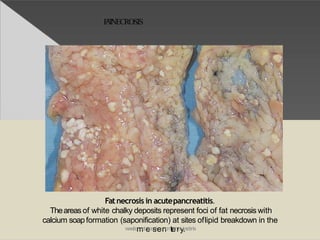
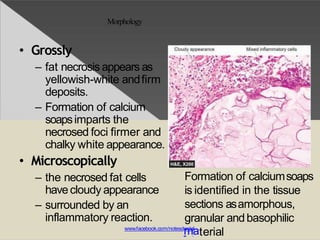
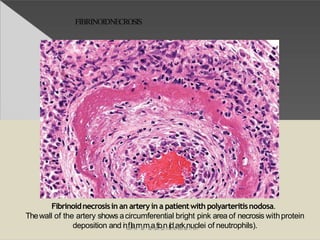
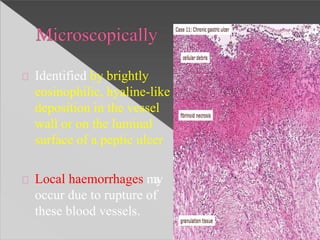
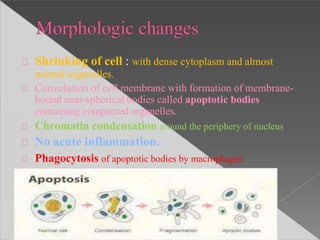
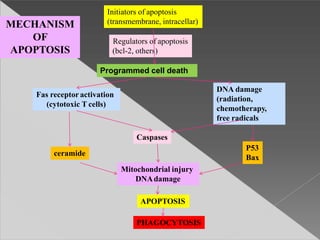
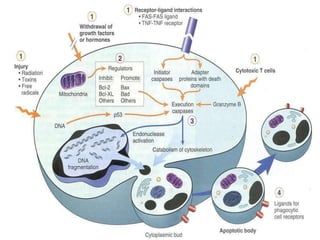
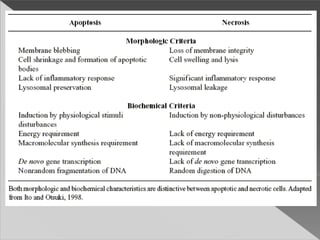
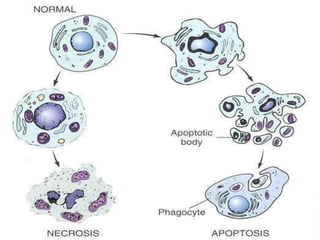
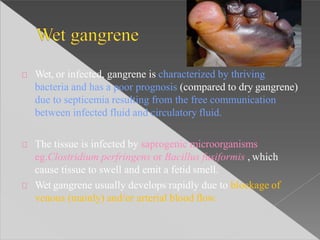
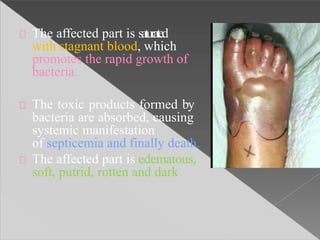
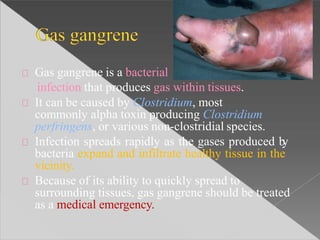
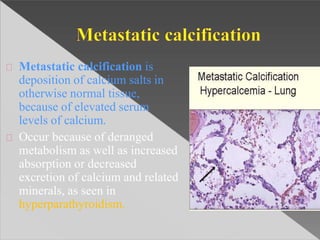
This document discusses cell death and necrosis. It begins by introducing cell injury and defining it as stresses that cells encounter internally and externally. There are two main types of cell death - necrosis and apoptosis. Necrosis is the irreversible cell injury and death that occurs when damage becomes too severe for the cell to recover. Apoptosis is programmed cell death that is important for normal physiology. The document further explores the mechanisms, morphology, and types of necrosis including coagulative, liquefactive, caseous, fat, and fibrinoid necrosis. It also discusses the mechanisms, initiators, regulators and roles of apoptosis. Gangrene is defined as a condition caused by critically insufficient blood supply that results in cell death.