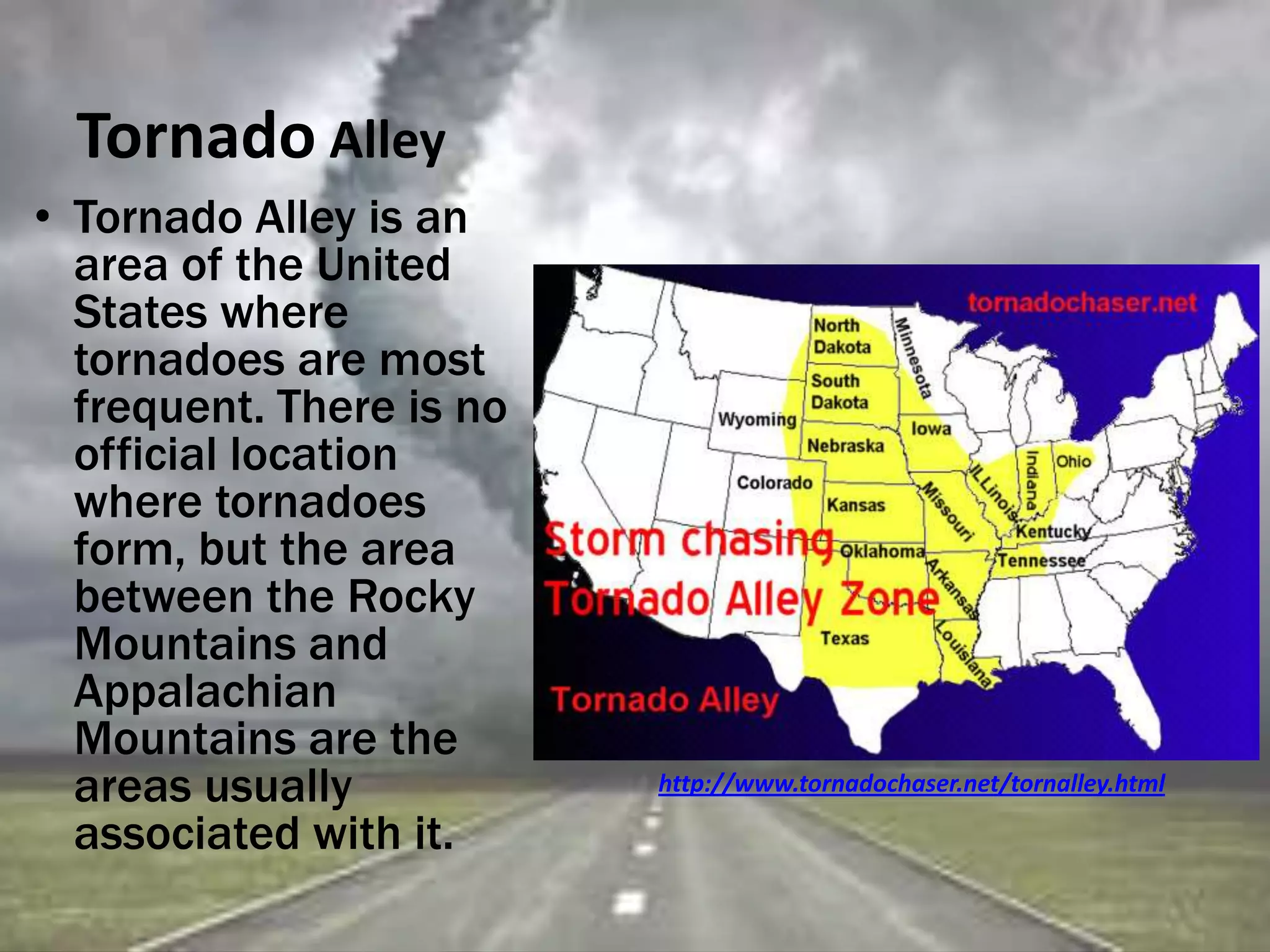
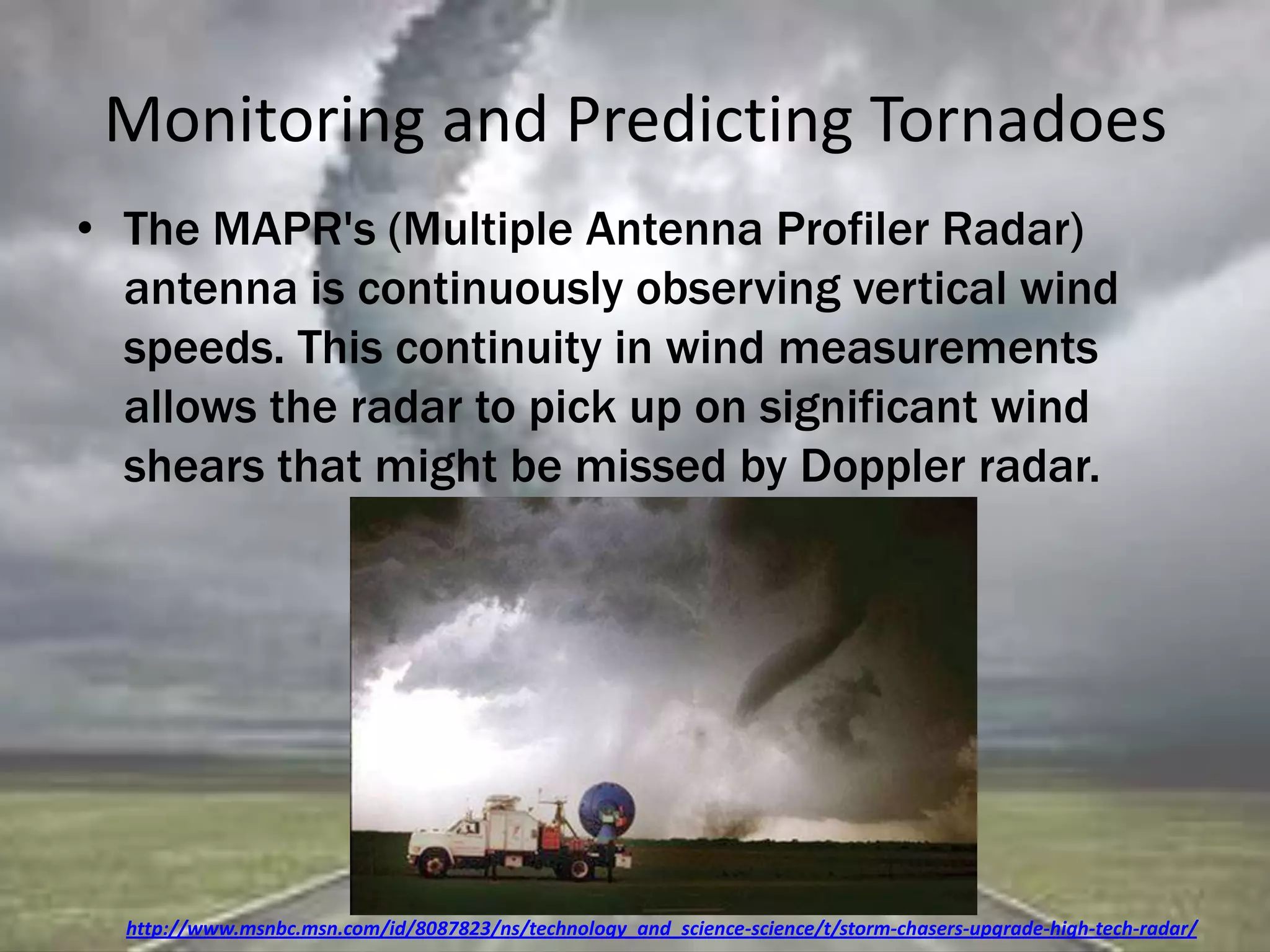
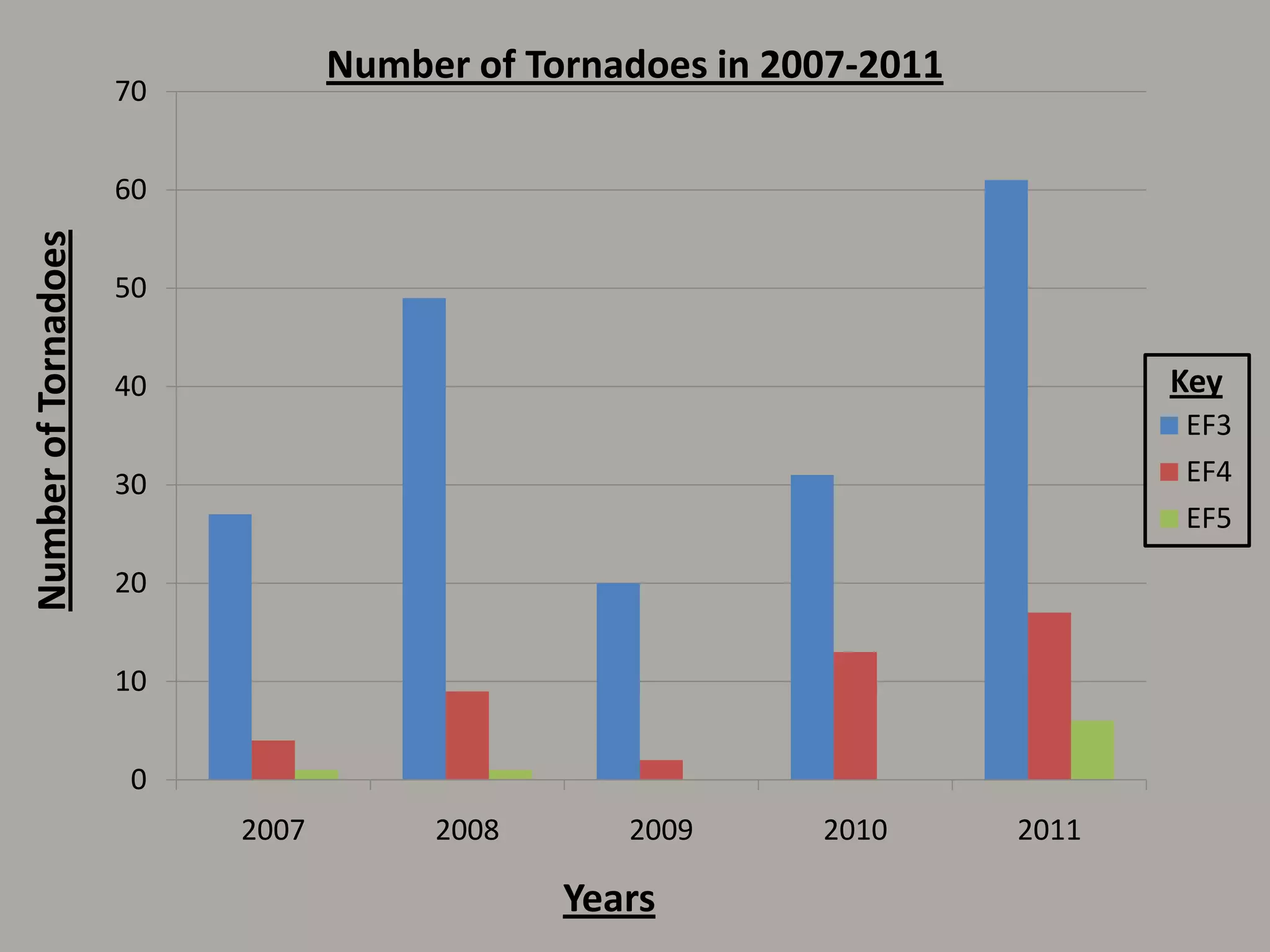
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that extends from a thunderstorm to the ground. Most tornadoes have wind speeds under 110 mph and dissipate after traveling a short distance. During storms, warm air rises while cold air sinks, causing the warm air to twist into a funnel-shaped spiral. Wall clouds are large cloud formations that often precede tornado formation. The deadliest tornadoes have caused hundreds of deaths and billions in damage, like the Joplin, Missouri tornado of 2011. Tornado Alley in the central US has the highest frequency of tornadoes. Doppler radar and other technologies help forecasters monitor conditions for potential tornado development.