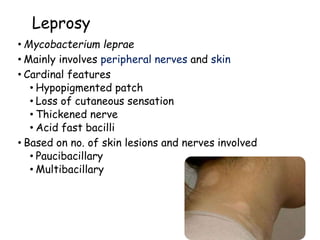
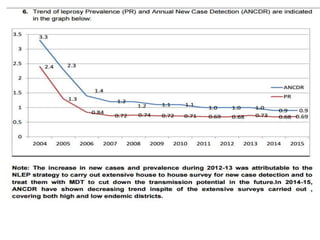
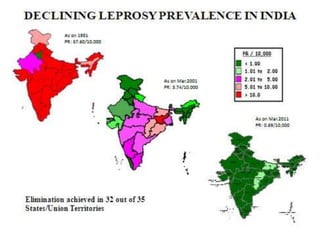
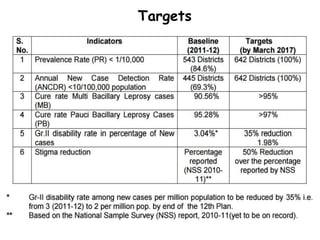
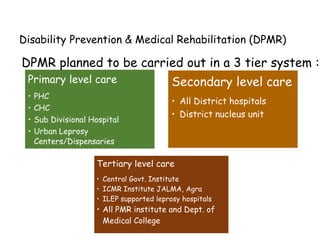
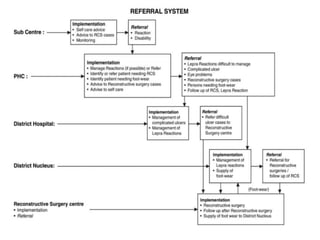
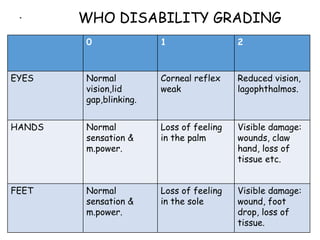
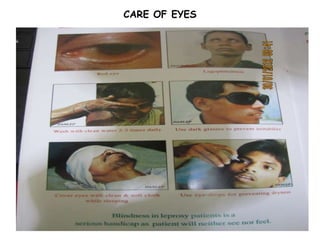
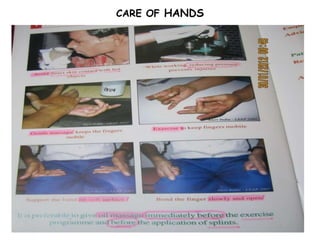
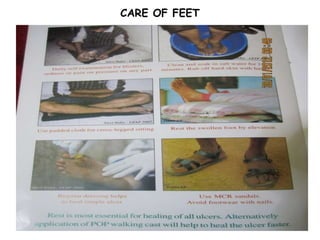
The document summarizes India's National Leprosy Eradication Programme. It discusses that leprosy is caused by Mycobacterium leprae bacteria and mainly affects the skin and peripheral nerves. The key milestones of the programme included introducing multi-drug therapy in 1982 and achieving elimination at the national level in 2005. The current strategies include integrating leprosy services into general healthcare, promoting early detection and complete treatment, involving ASHA workers, and reducing stigma through information campaigns. The goal is to continue driving down prevalence rates toward total eradication of the disease in India.