Embed presentation

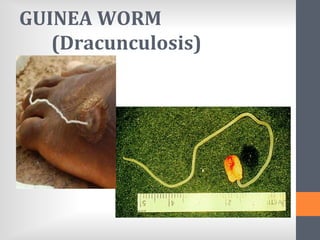
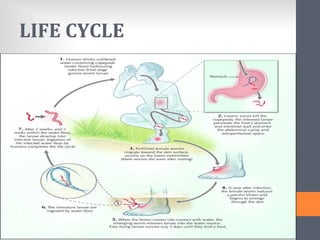
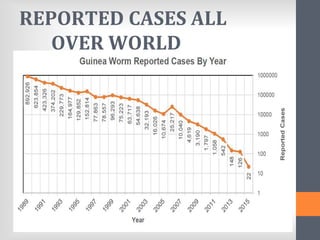
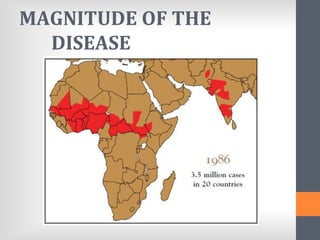
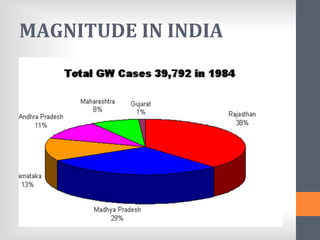

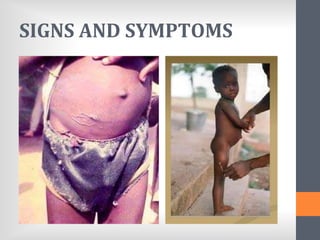
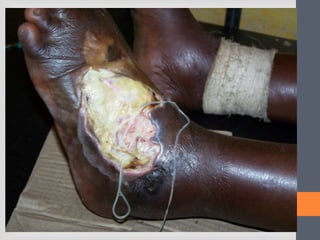




The document outlines India's National Guinea Worm Eradication Programme. It discusses the life cycle of Guinea worm (Dracunculiasis) and describes the programme which was implemented in 1984 to work with states, WHO, UNICEF and other organizations to provide health education, treat water sources, and conduct surveillance to eliminate cases of Guinea worm disease. Through these efforts, India was certified free of transmission by 2000 and the programme continues surveillance and education activities to prevent any future outbreaks.












