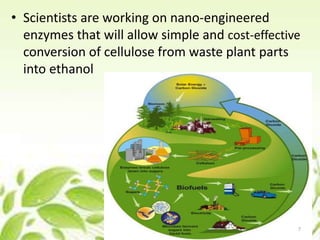
Nanotechnology plays a significant role in agriculture by enhancing crop biotechnology, improving fertilizer and pesticide delivery, and recycling agricultural waste. It offers innovative solutions such as nano-engineered enzymes for ethanol production, nanosensors for monitoring plant health, and biodegradable materials aimed at reducing environmental impact. The ongoing research in this field suggests that nanotechnology will drive substantial advancements in agricultural efficiency and sustainability.