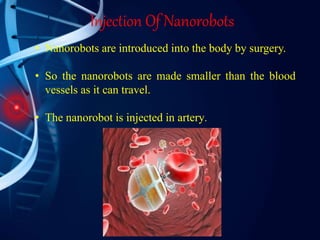
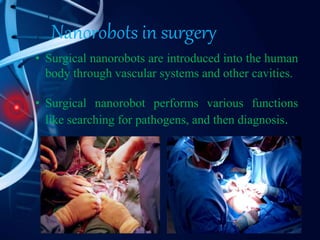
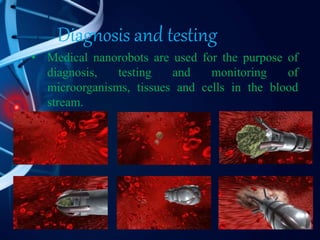
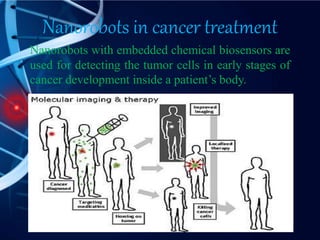
Nanorobots are tiny machines designed to perform specific tasks at the nanoscale level. They consist of sensors, propellers, molecular sorting rotors, and fins. Potential applications include using nanorobots for medical purposes like cancer detection and treatment, surgery, and gene therapy. While still in development, future nanorobots may be able to replicate themselves, communicate with each other, and self-repair. Advantages include high speed, low energy usage, and more precise medical treatment, though risks include high costs, cancer risks, and potential loss of control.