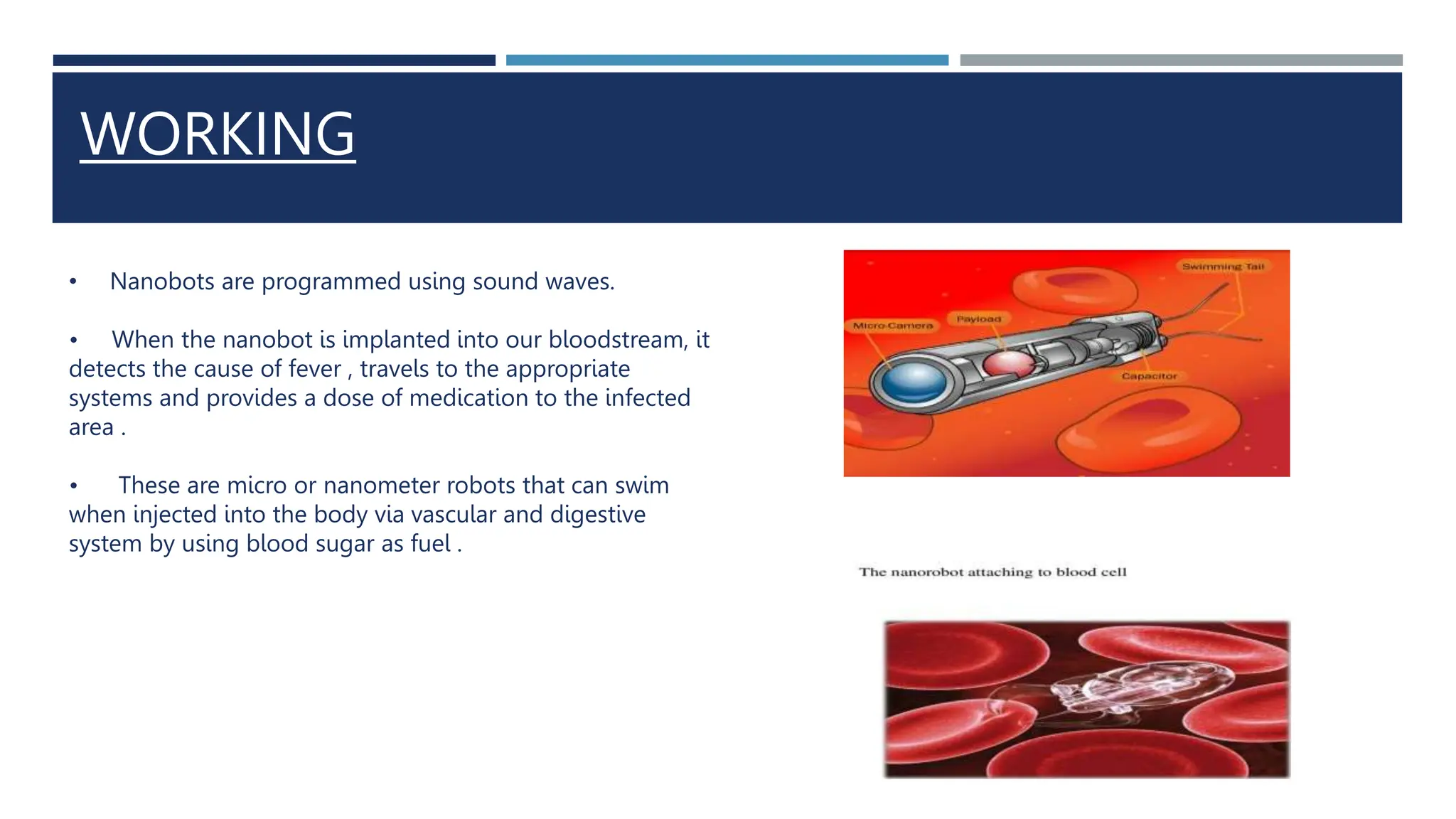
This document discusses nanorobotics, which involves creating robots between 1 and 100 nanometers in size called nanobots. Nanorobots could be programmed using sound waves and injected into the body to detect and treat illnesses like fevers and cancer. They would contain elements like carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Potential applications include breaking up blood cells, kidney stones, and arteriosclerosis. While nanorobotics could rapidly eliminate diseases, there are also disadvantages like a lack of knowledge and potential environmental hazards from disposal. Future areas of development include using nanobots to build faster computers and for controlled drug delivery.