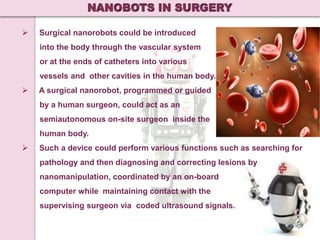
The document discusses the potential for nanorobots in medicine. It describes how nanorobots smaller than blood cells could be injected into the body to detect and treat medical issues. Researchers are working to design nanorobots that could treat conditions like cancer, repair damaged tissues, and more. While still in early stages of research, nanorobots may one day revolutionize healthcare by providing targeted treatment and curing currently incurable diseases with few side effects.