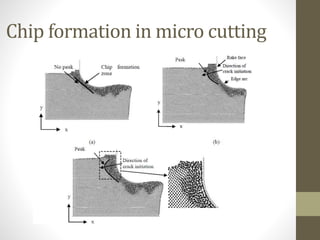
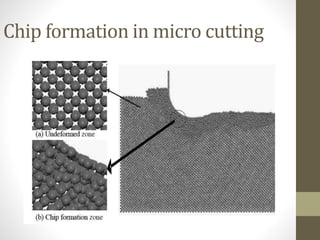
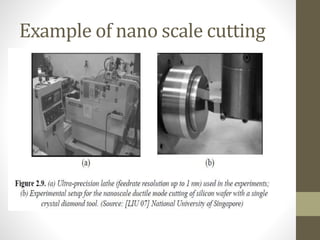
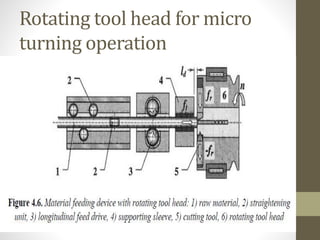
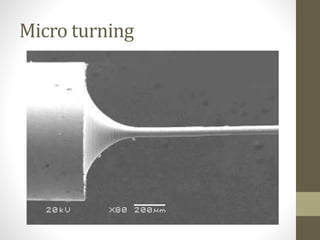
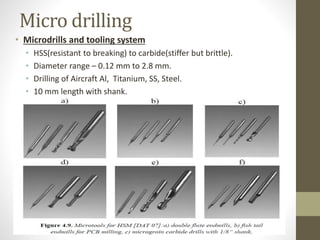
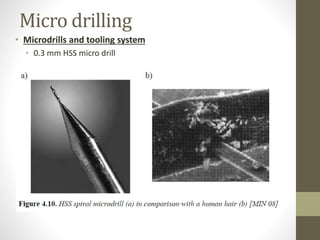
This document discusses micro and nano manufacturing techniques such as micro turning, micro drilling, and micro milling. Micro turning can produce mirror surfaces with less than 10 nm surface roughness and is used to machine hard materials without subsurface damage. Micro drills as small as 5-50 μm in diameter are used to drill holes in PCBs, inkjet printer nozzles, and other applications. Micro milling is capable of creating 3D features from a few microns to hundreds of microns in size and drilling holes tens of microns in size. Machine tools such as ultra-precision lathes, Swiss-type lathes, and spindles with speeds over 500,000 rpm are used to enable these micro manufacturing processes.

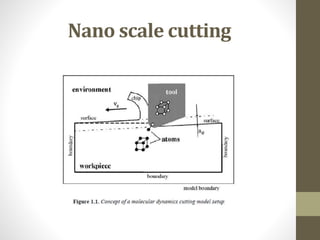
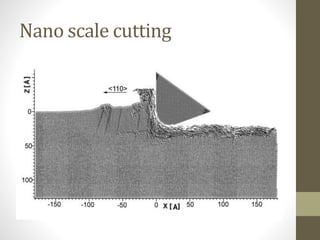
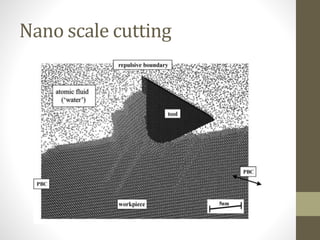
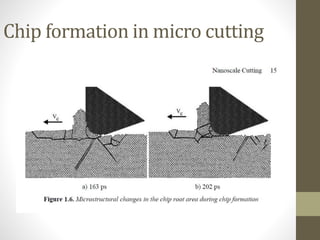

















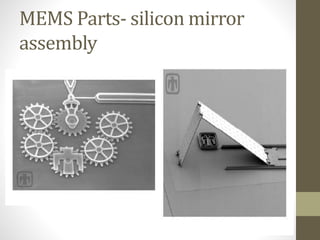

![Micro manufacturing example
• A mite measuring 500m long sits on a mirror array used for optical data switching.
• The mirror [flat in the left image, folded in the right] is positioned with a gear mechanism](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microandnano-parti-161116041415/85/Micro-and-nano-manufacturing-33-320.jpg)
