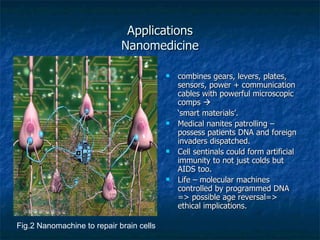
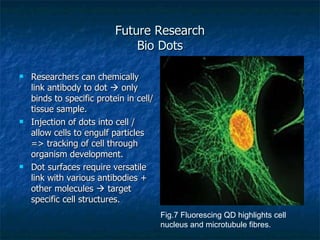
Bionanotechnology involves engineering and manufacturing at the atomic scale using biological precedents. It is a subset of nanotechnology that is closely related to biotechnology, allowing the design and manipulation of intricacies at the atomic scale. Potential applications include using nanomachines built to the nanoscale and programmed by DNA to repair brain cells, deliver drugs to target locations, or even reverse aging. However, molecular nanotechnology could also have dangerous military applications if used to create invisible molecular weapons. Future research focuses on areas like developing innovative drug delivery systems, using quantum dots to track cells, and creating implantable biomedical devices through multidisciplinary approaches.