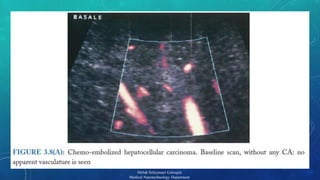
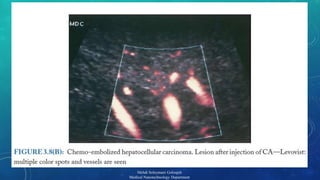
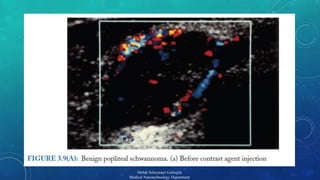
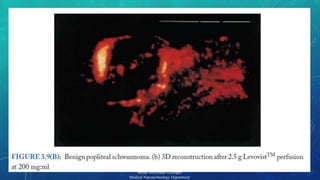
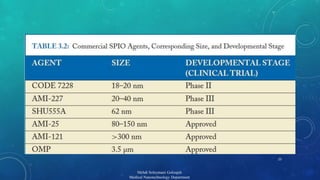
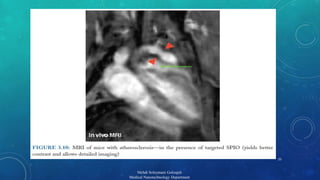
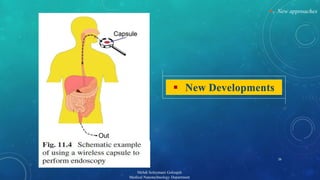
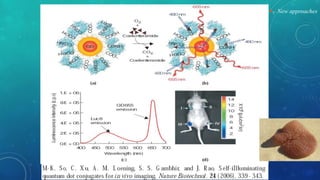
The document presents a comprehensive exploration of bionanoimaging, focusing on quantum dots (QDs) and their applications in medical imaging, particularly for cancer detection. It discusses the properties, classifications, and emerging technologies associated with QDs and ultrasound contrast agents. Future trends and innovative approaches in medical nanotechnology are also highlighted, emphasizing the ongoing advancements in imaging techniques.









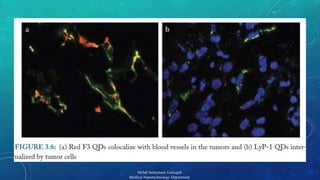
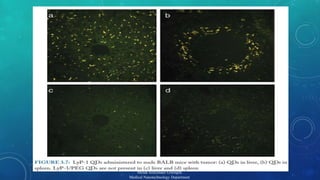
![ULTRASOUND CONTRAST AGENTS
Ultrasound is currently a well-established technology enabling real-time imaging of the
Mehdi Soleymani Goloujeh
Medical Nanotechnology Department
human body
Traditional ultrasound, however, has its own limitation including increase in
attenuation with increasing insonating frequency, yielding low resolution of thicker
structures, and thus prohibiting deeper scans
A possible solution to overcoming the issues of deep scans and achieving improved
resolution is the use of contrast agents (CA) for ultrasound imaging [25, 26]. The
ultrasound imaging contrast agents (UICA) can be classified into liposomes, polymeric
nanosomes, and these are further classified according to the type of ultrasound agent
encapsulated in them.
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bionanoimaging-141121070609-conversion-gate01/85/Bionanoimaging-16-320.jpg)