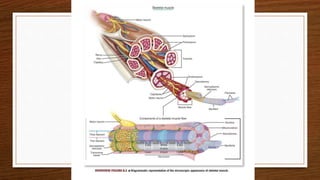
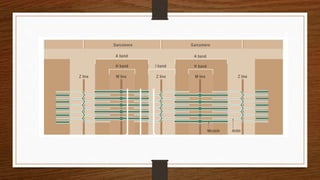
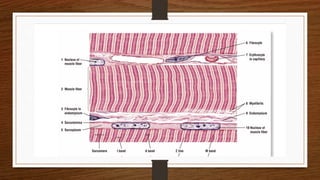
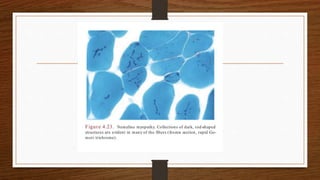
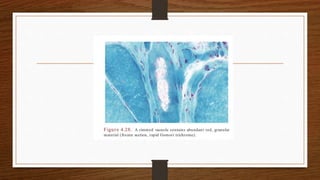
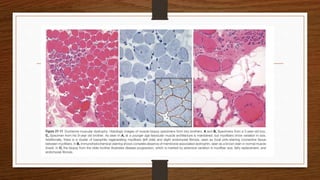
1. Muscle biopsy is used to diagnose neuromuscular diseases by examining muscle fiber histology and histochemistry under a microscope.
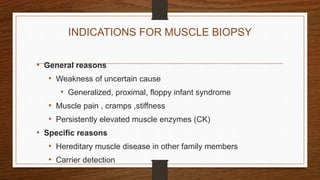
2. Indications for muscle biopsy include unexplained muscle weakness, elevated muscle enzymes, and suspected hereditary or inflammatory myopathies.
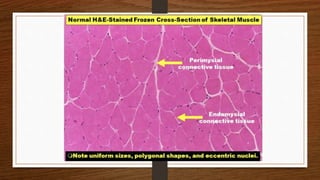
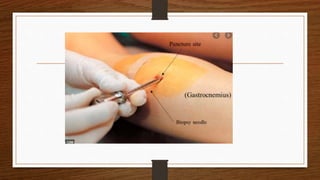
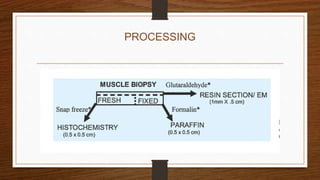
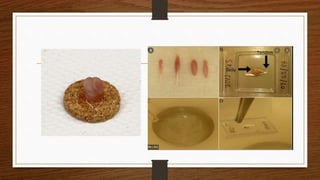
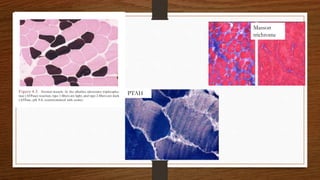
3. During the procedure, a small sample of muscle is removed using needle or open biopsy and processed with staining techniques to examine fiber characteristics.
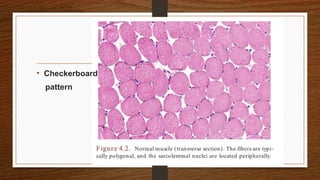
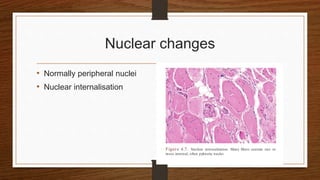
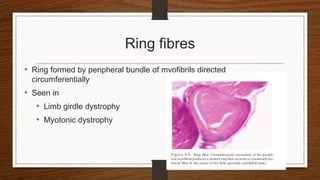
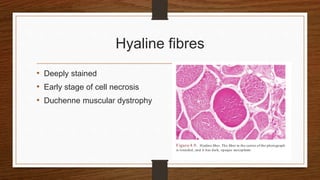
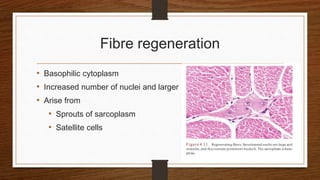
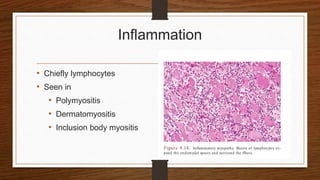
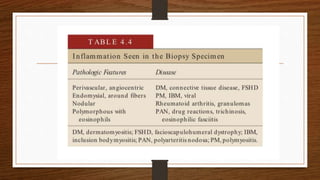
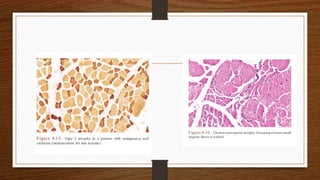
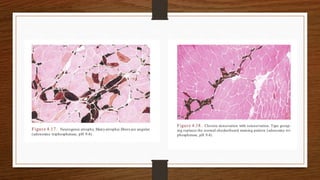
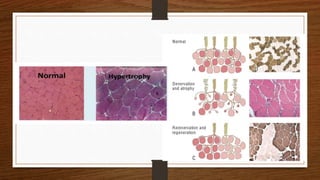
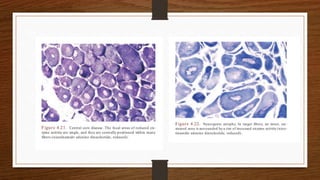
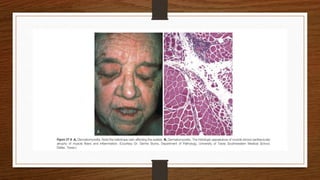
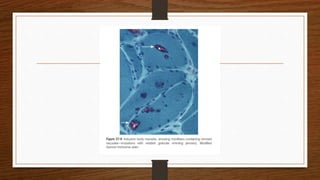
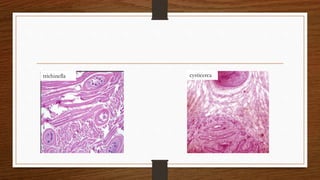
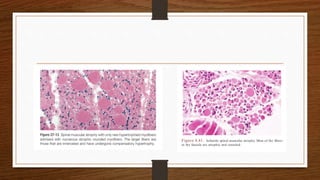
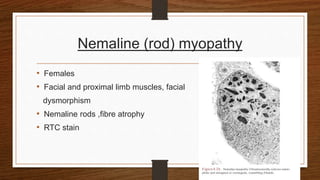
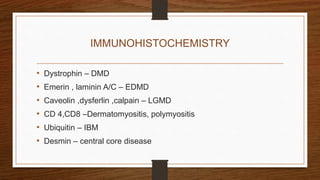
4. Common findings include fiber necrosis, regeneration, inflammation, fatty or fibrotic changes which can help identify diseases like muscular dystrophies, myositis, or metabolic myopathies.