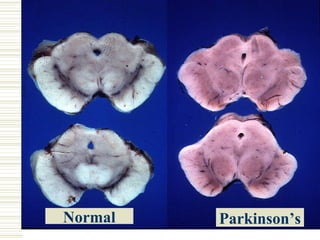
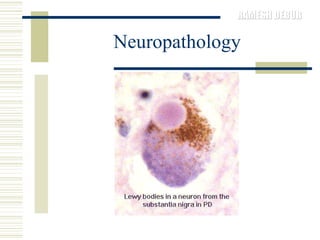
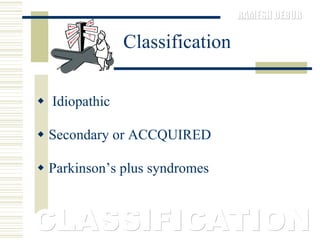
Parkinson's disease is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra region of the brain, which can lead to motor symptoms like bradykinesia, rigidity, tremors, and postural instability. It is usually classified as idiopathic or secondary/acquired. Diagnosis is based on the presence of motor symptoms and the absence of other conditions. Management involves medications to replace dopamine or stimulate receptors, as well as physical, occupational, and speech therapy to address mobility, activities of daily living, and communication difficulties.