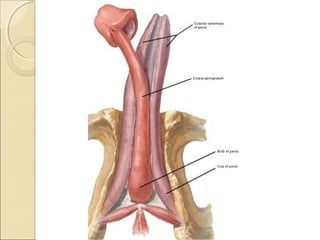
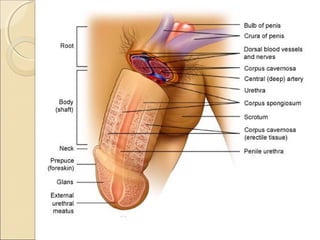
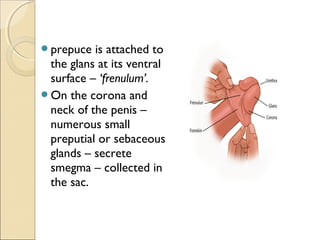
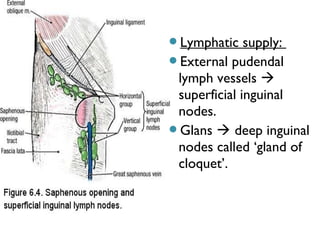
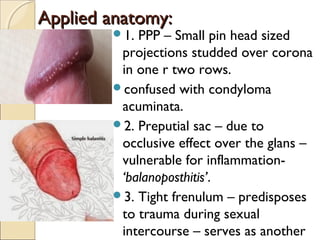
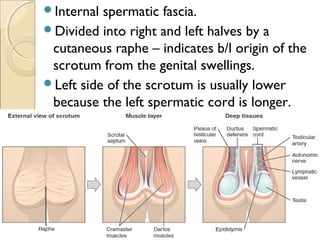
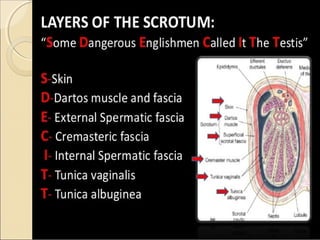
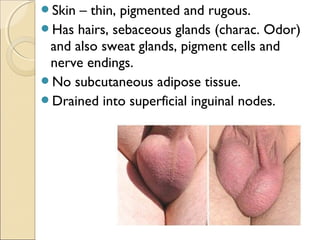
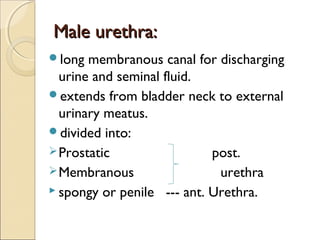
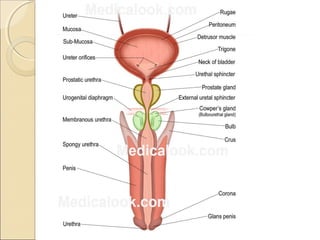
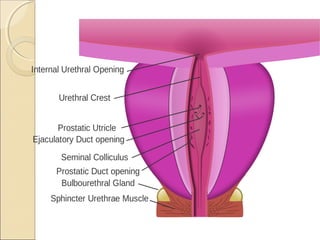
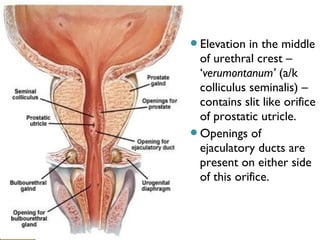
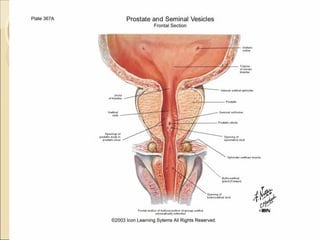
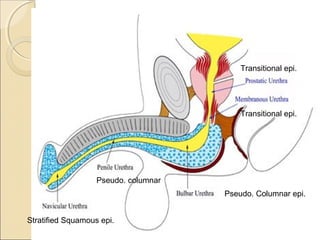
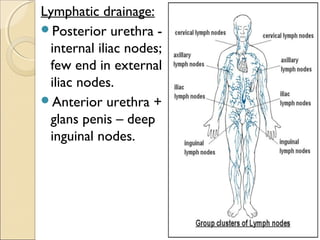
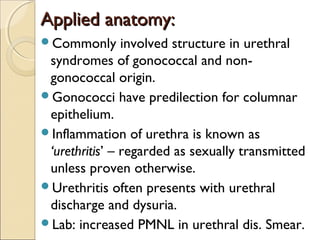
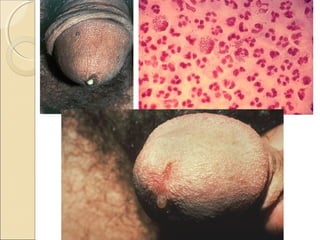
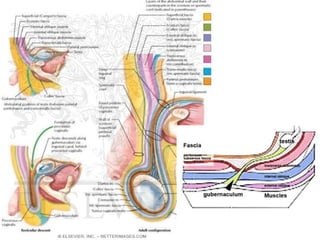
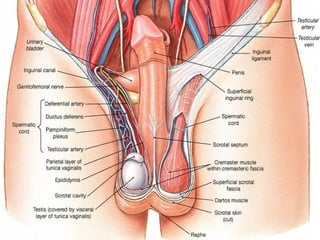
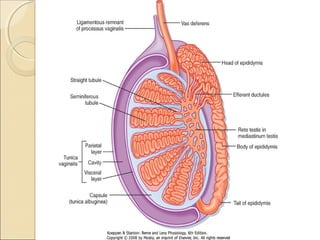
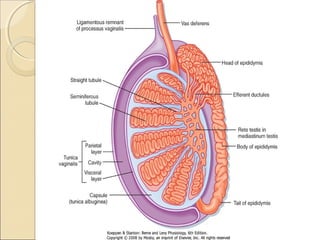
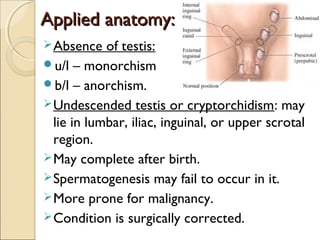
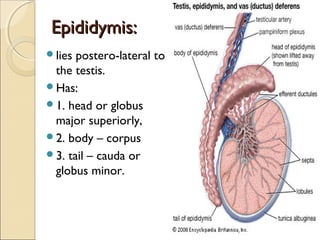
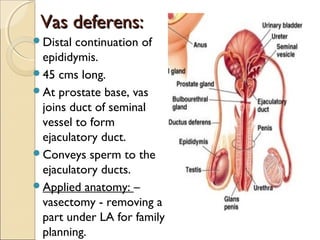
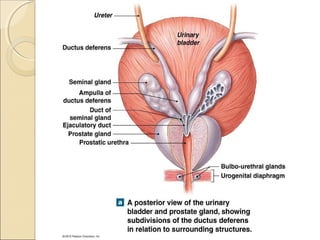
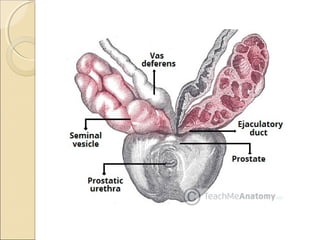
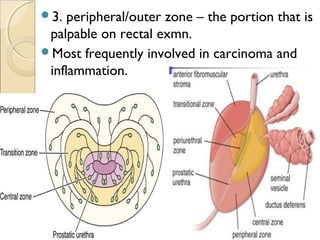
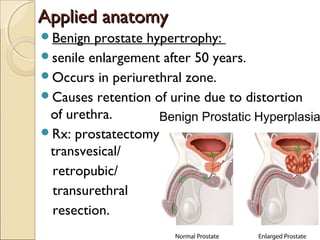
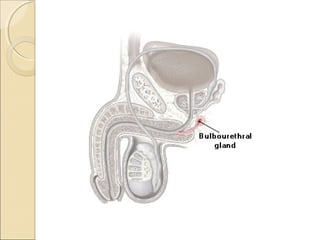
The male genital system includes both internal and external structures. The external genitalia are the penis and scrotum. The internal genitalia include the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, and urethra. The penis has three erectile tissues (corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum) and is covered in skin. The urethra pierces through the penis. The testes produce sperm and testosterone. During ejaculation, seminal fluid is secreted by the seminal vesicles and prostate to transport sperm through the urethra. Common clinical issues involving the male genital structures include inflammation, infections, tumors and congenital anomalies.