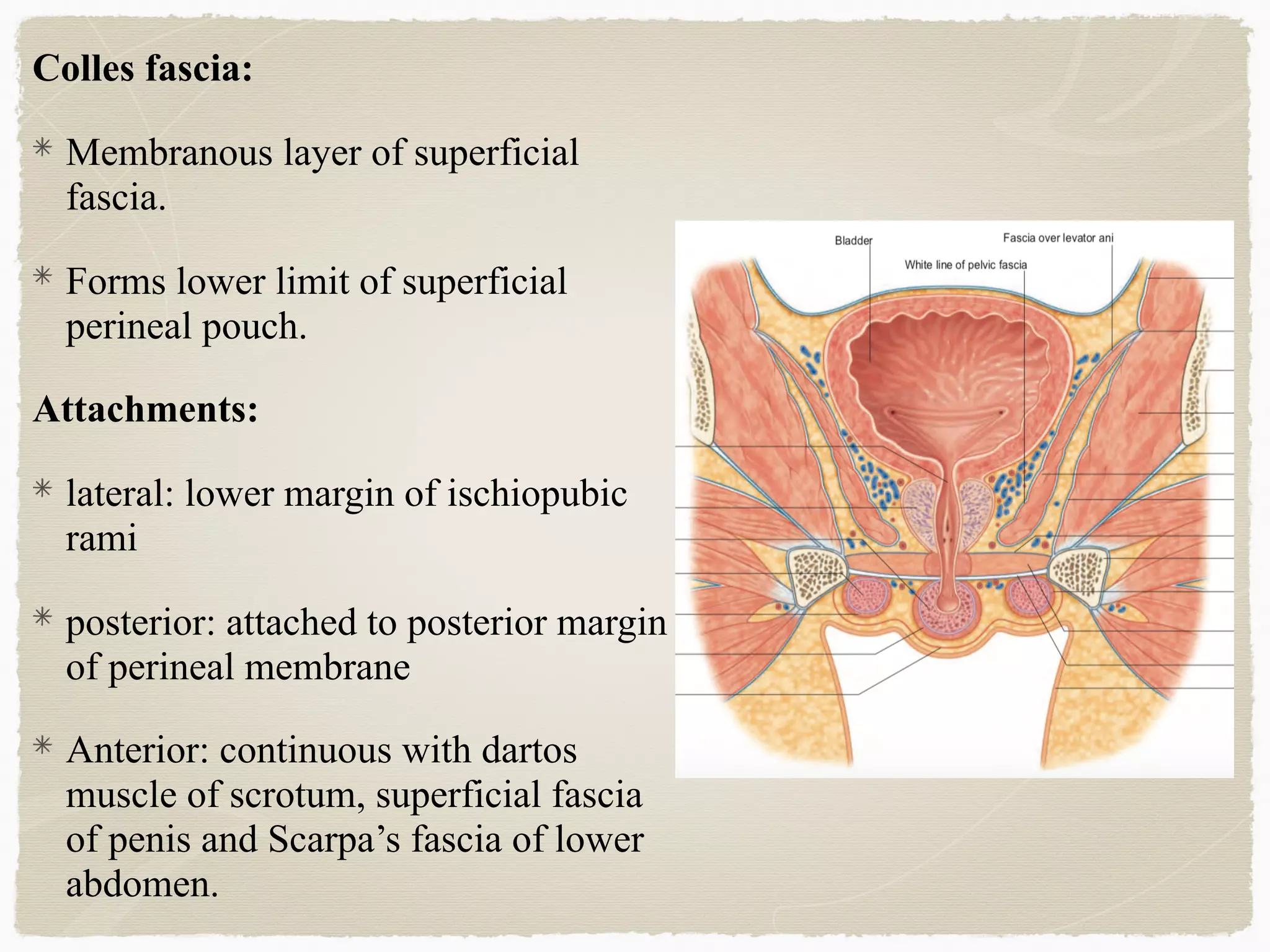
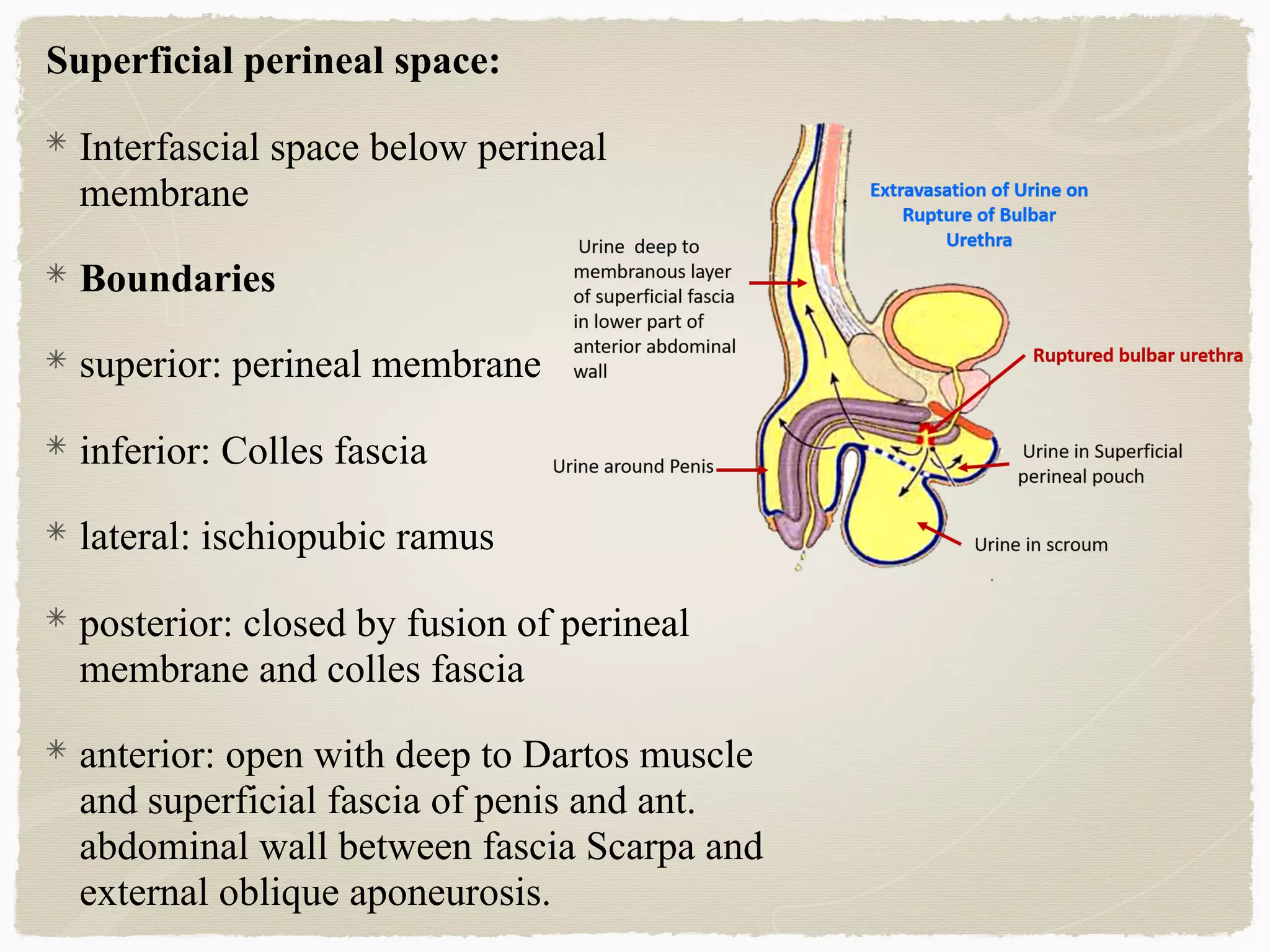
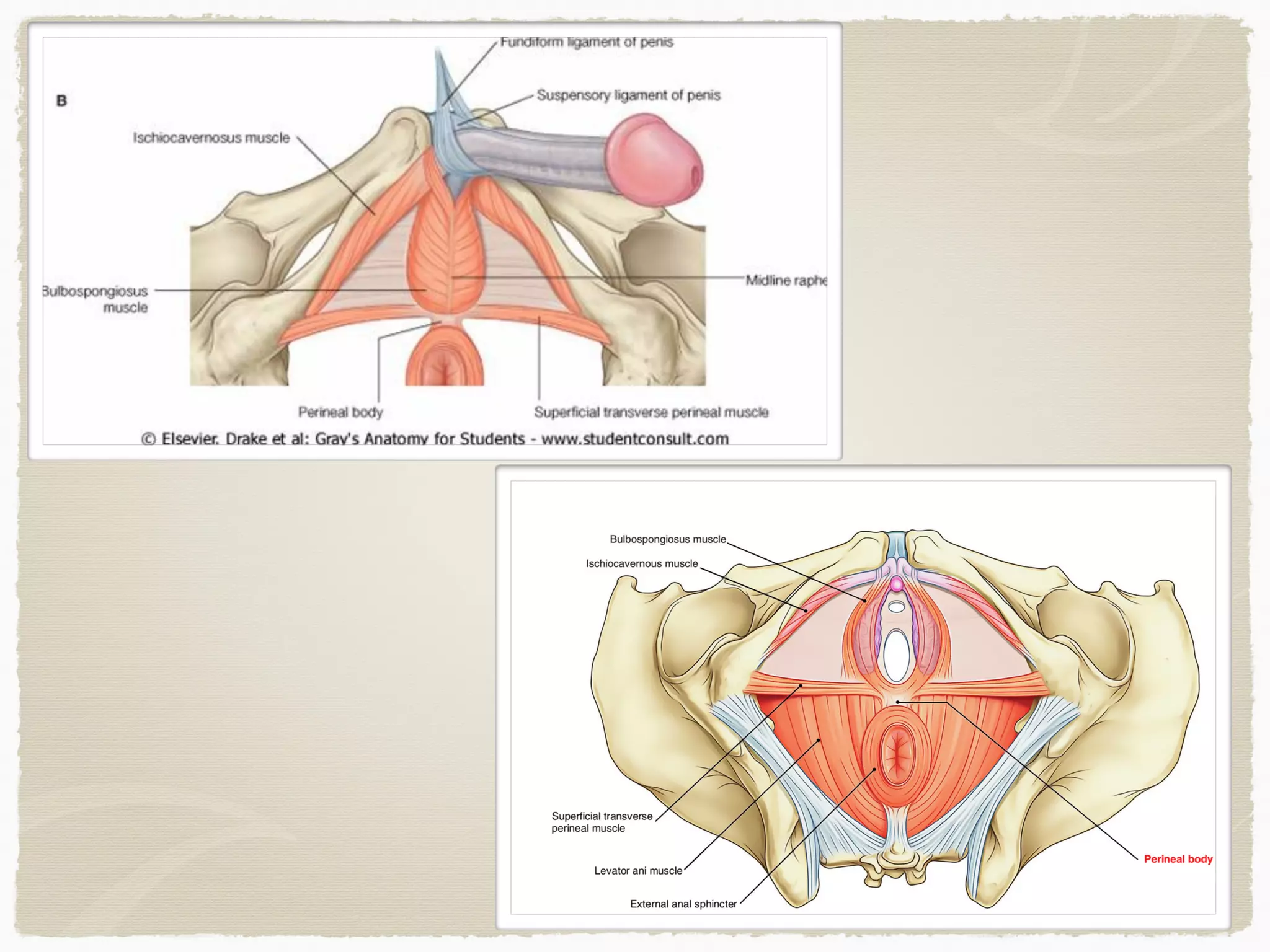
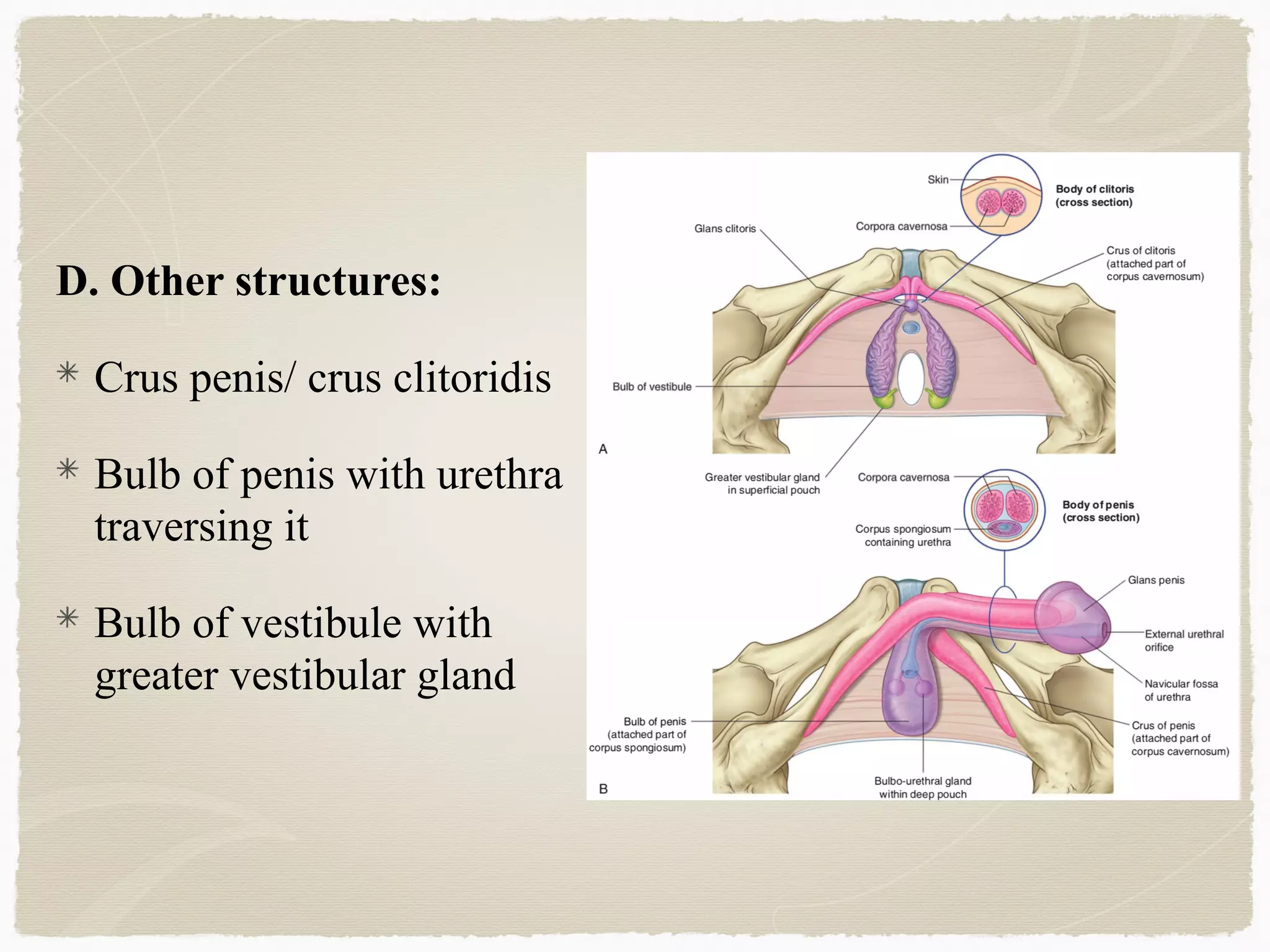
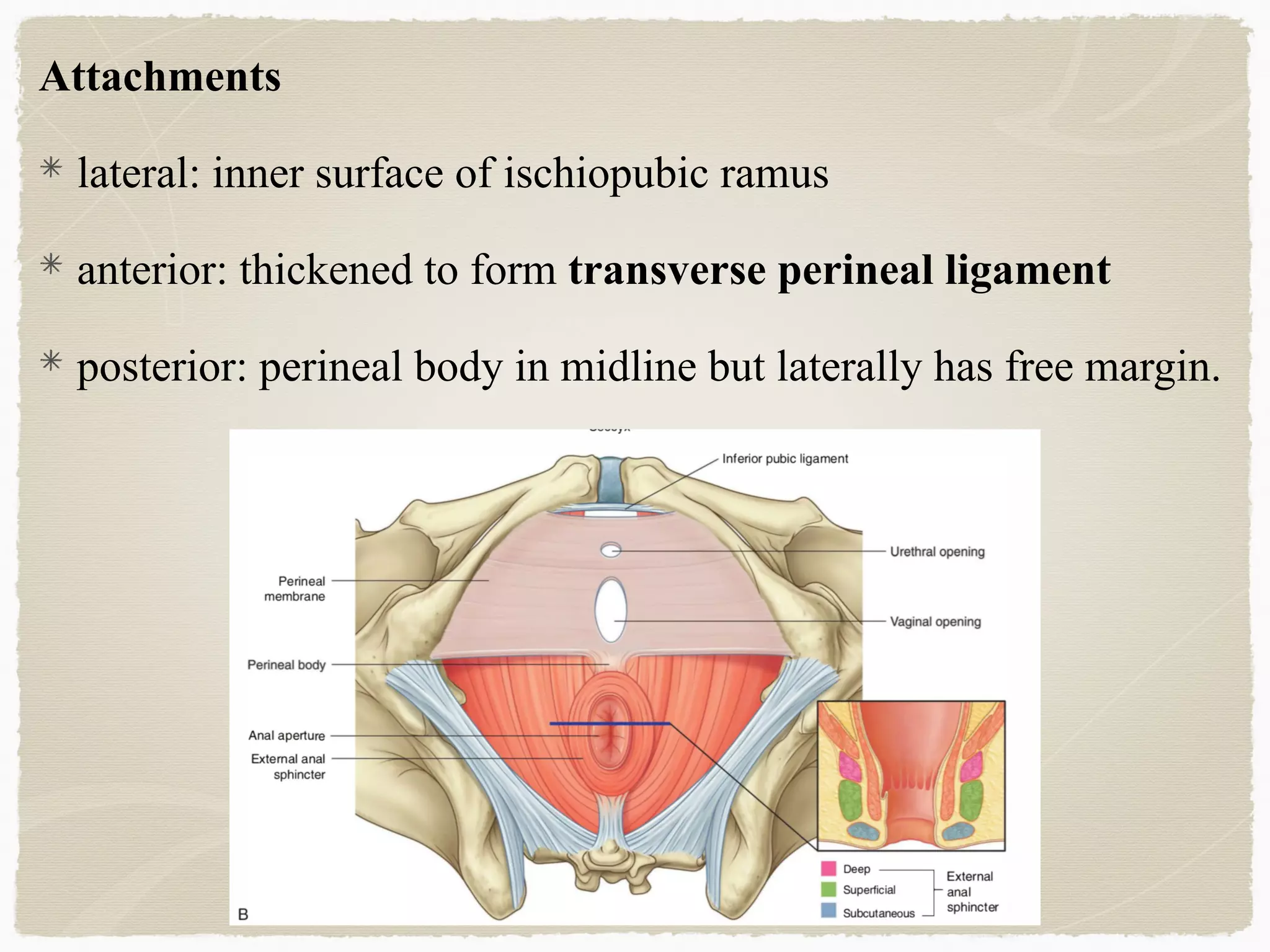
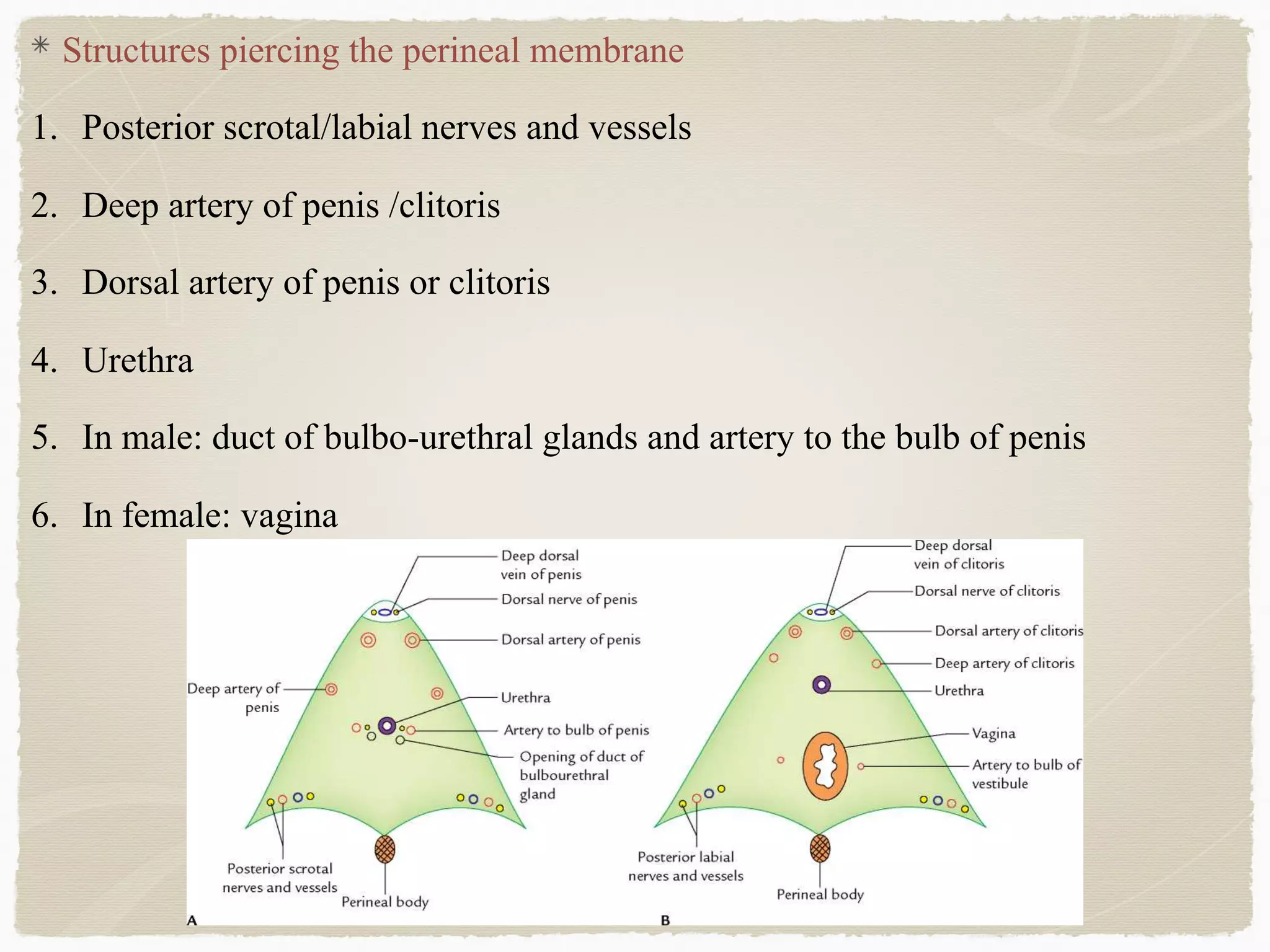
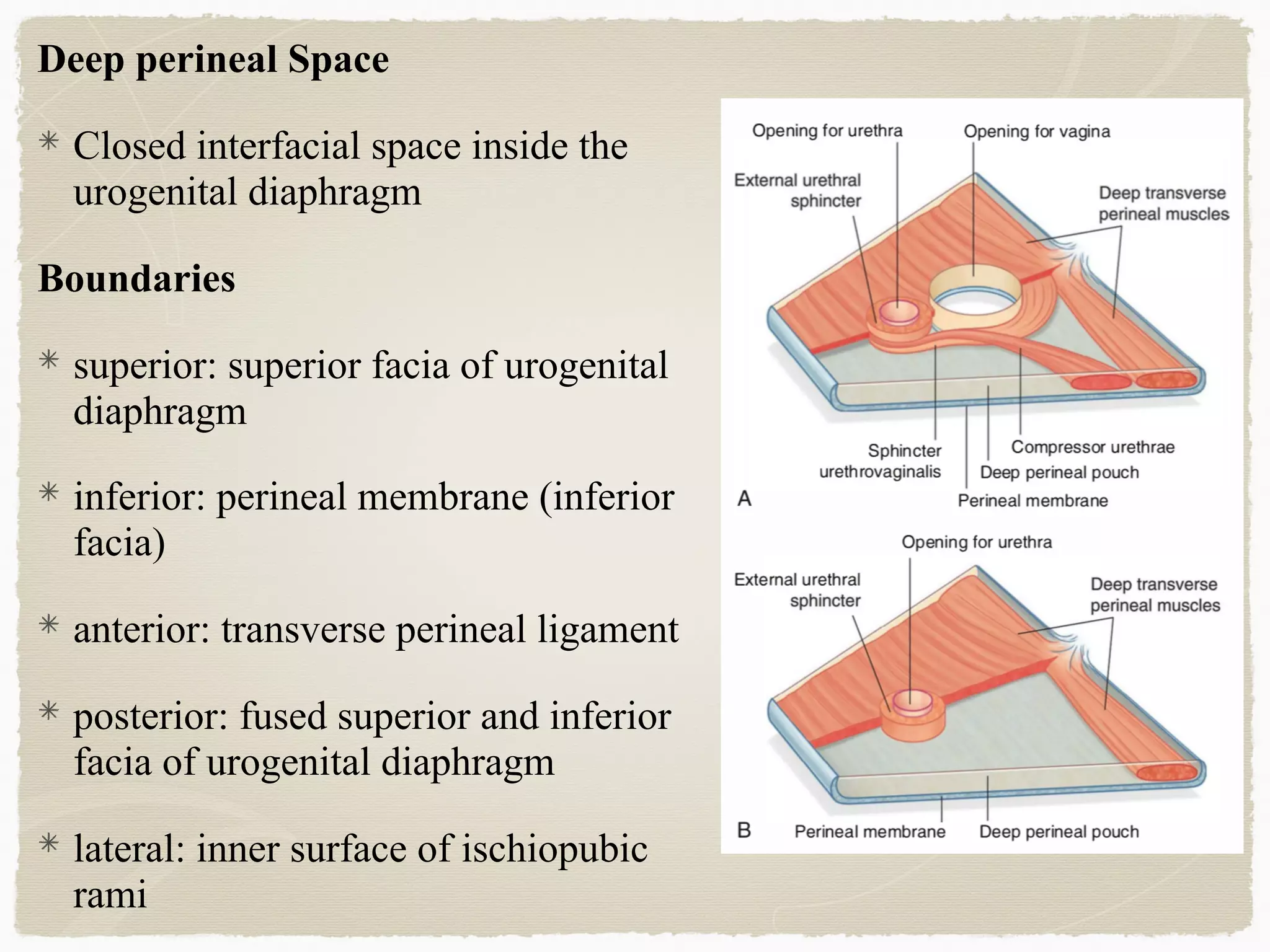
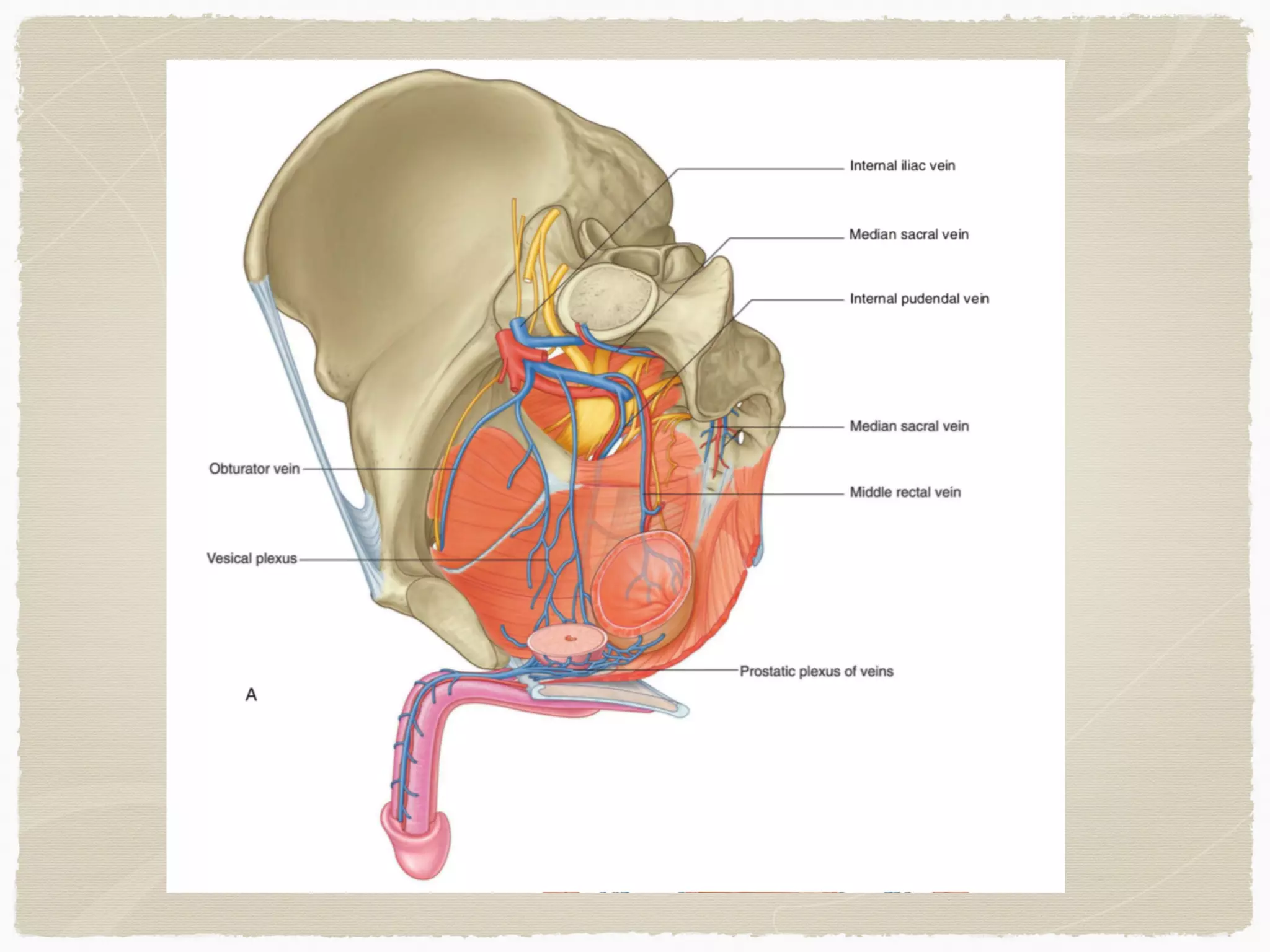
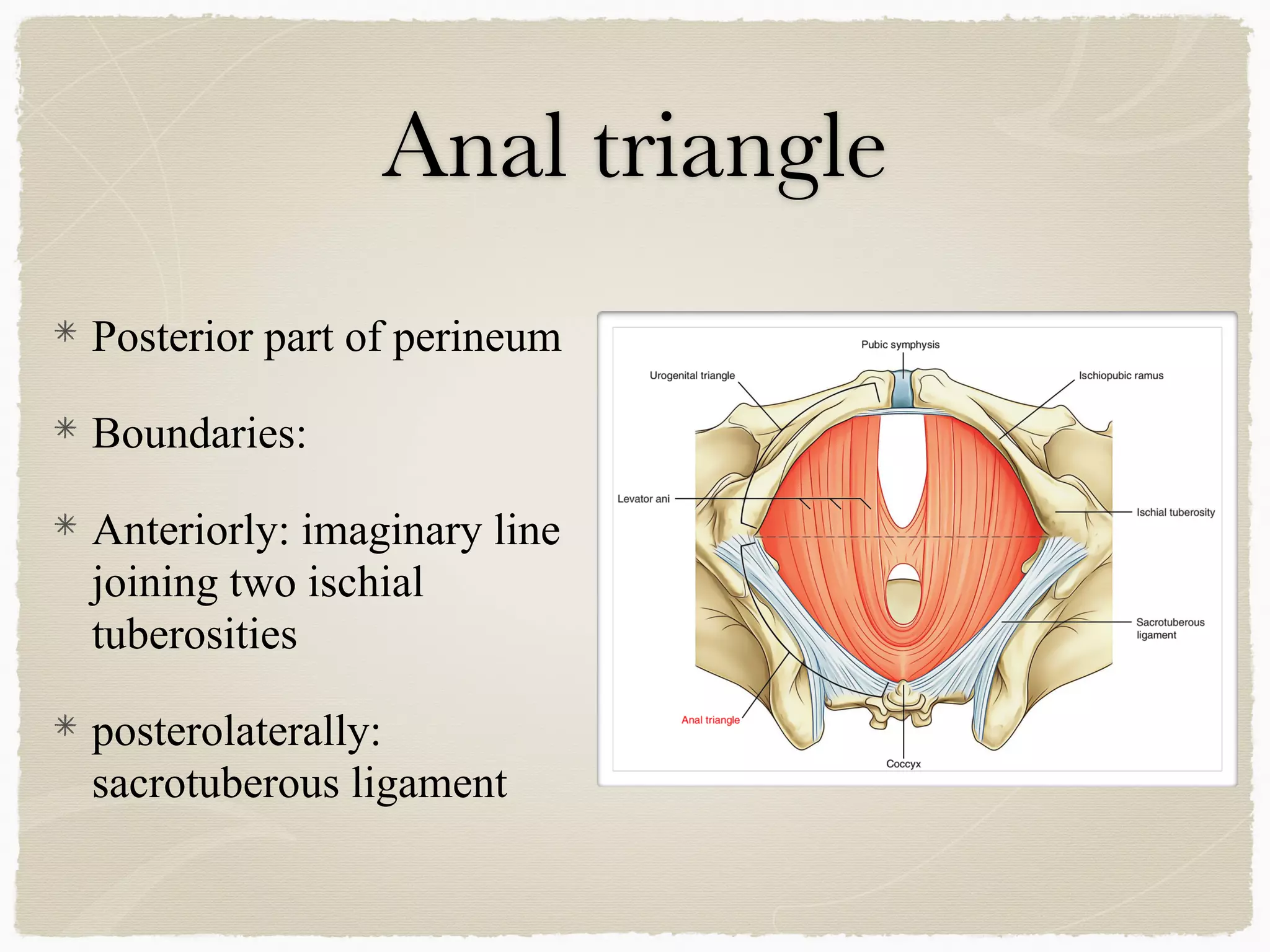
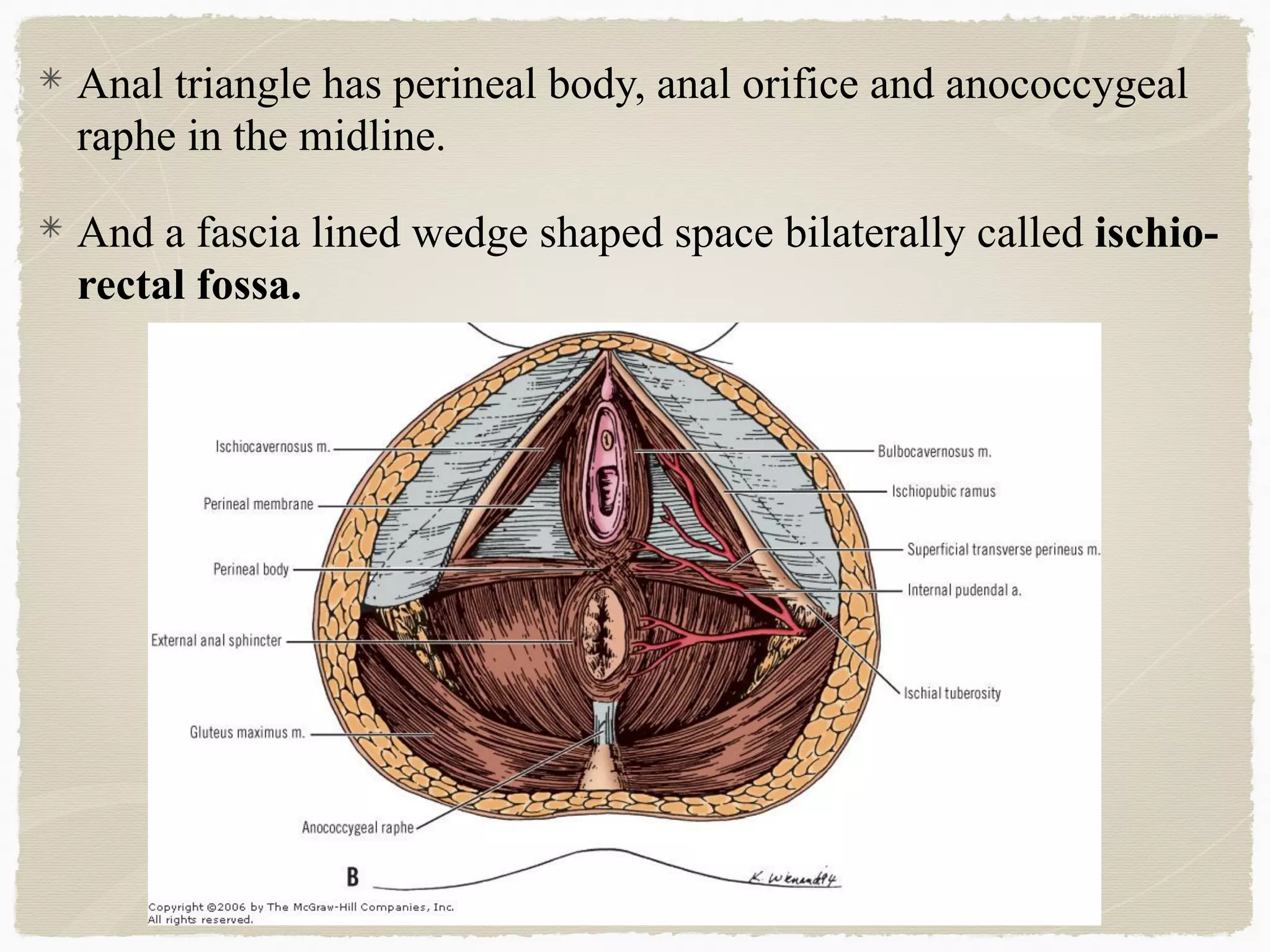
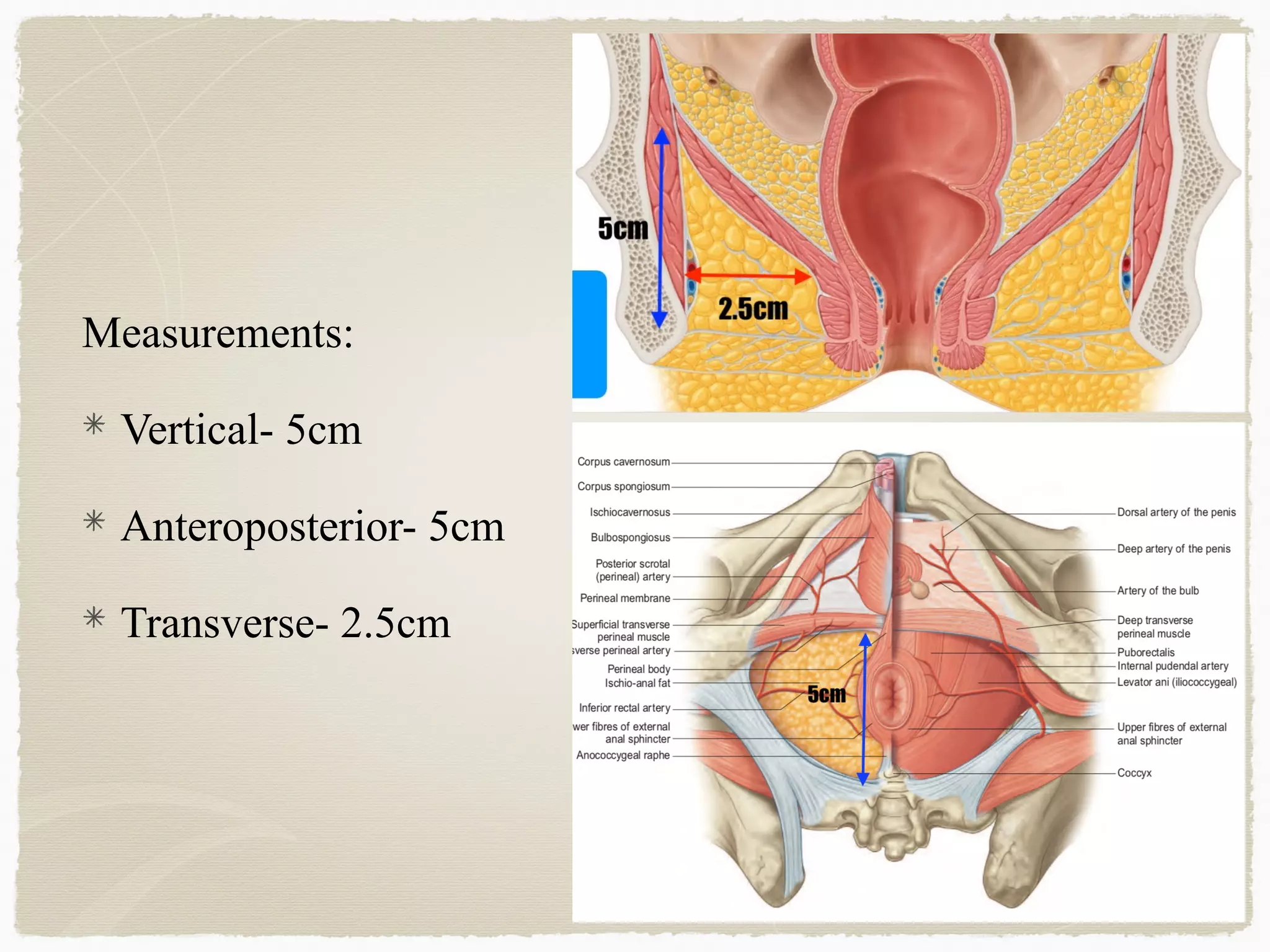
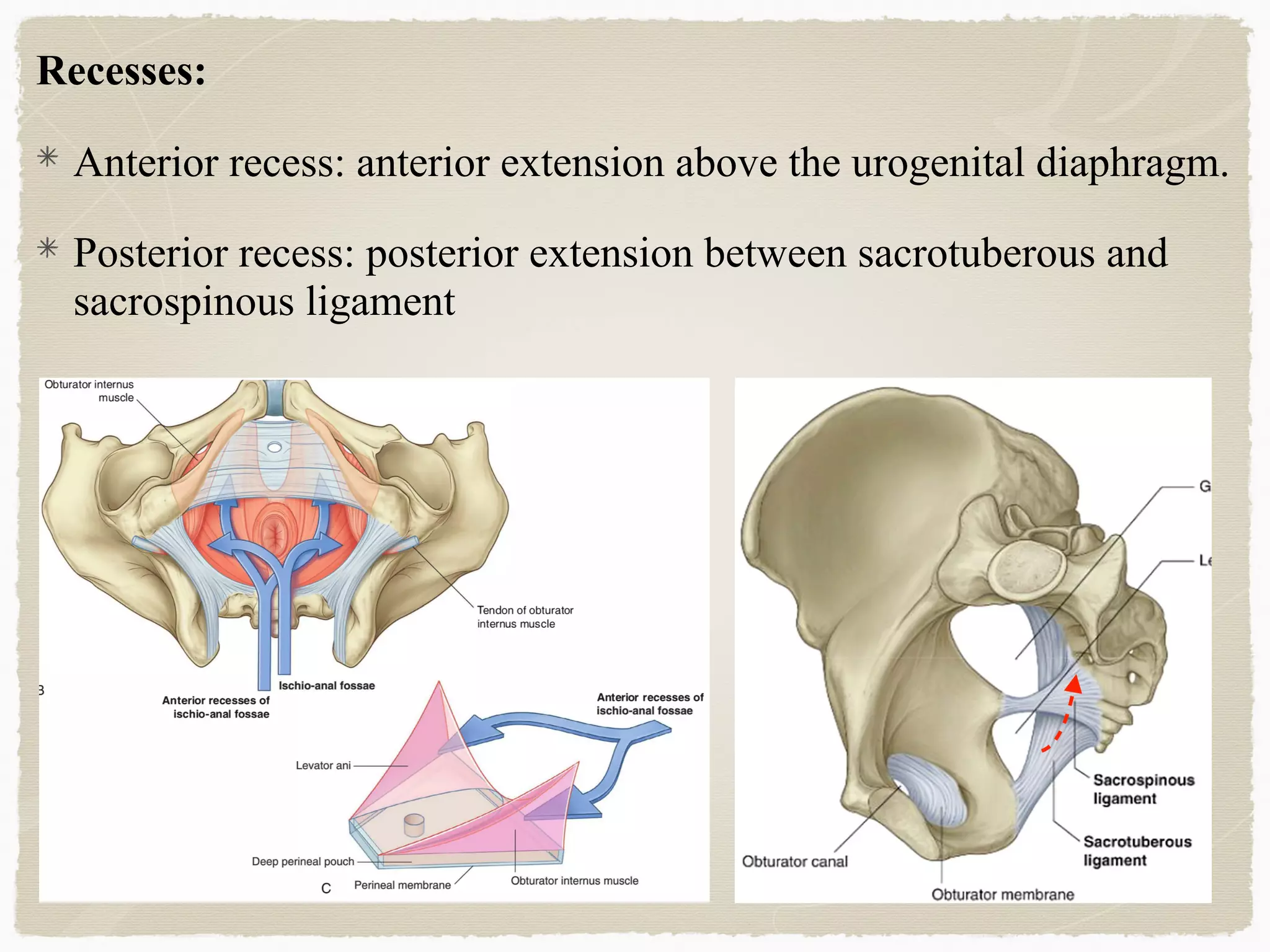
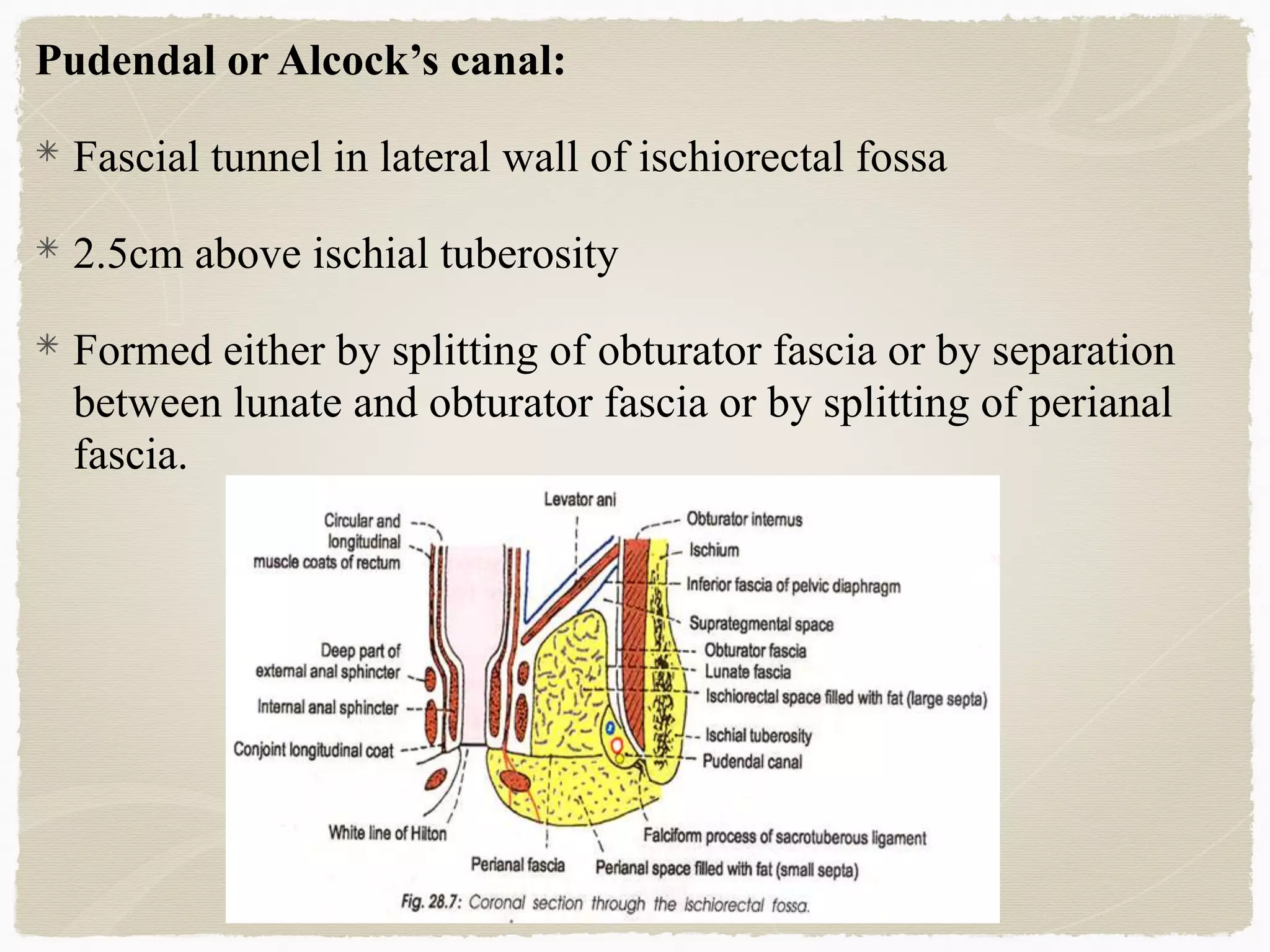
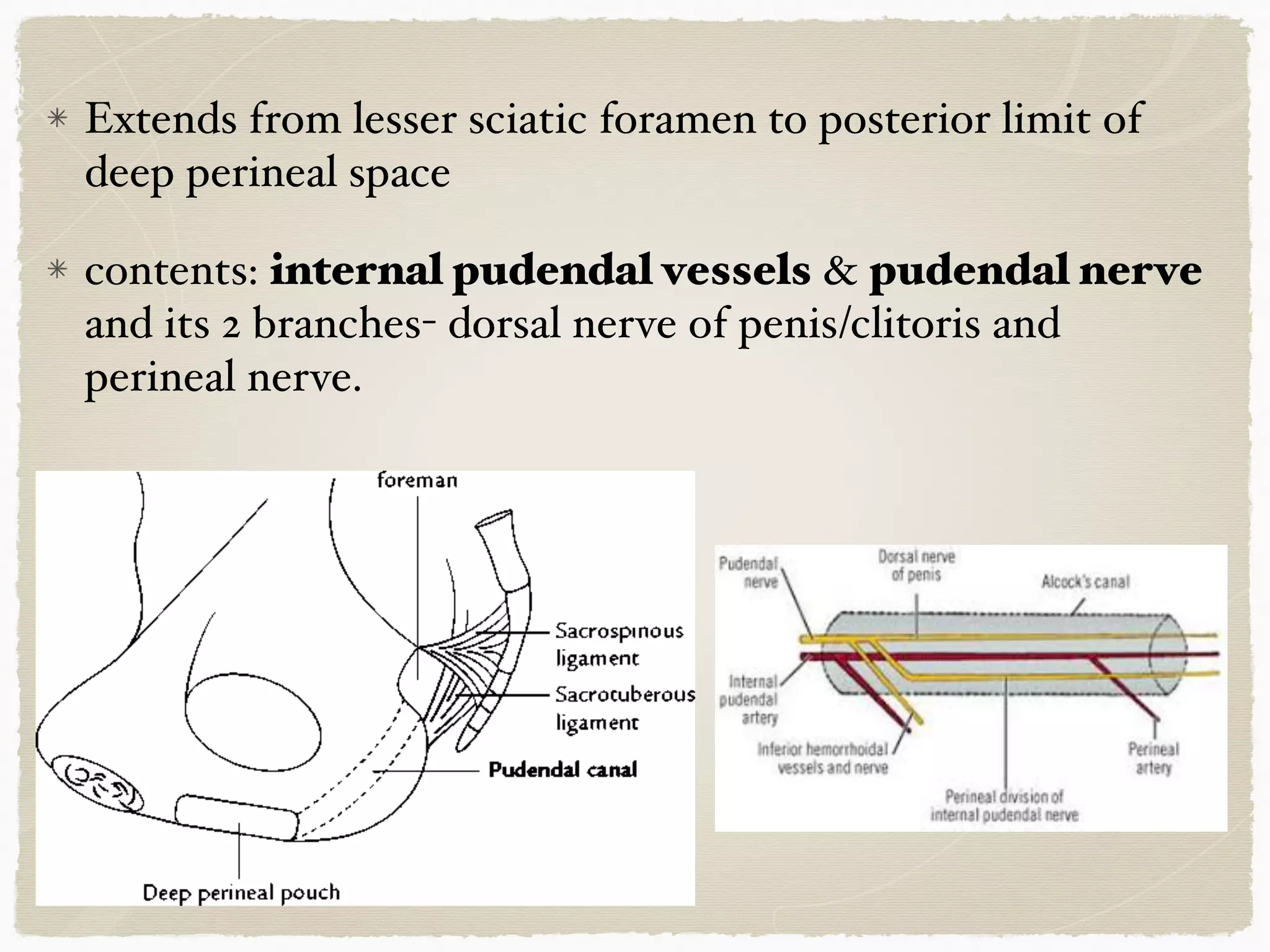
The perineum is the diamond-shaped region between the thighs and below the pelvic diaphragm. It is divided into the urogenital triangle anteriorly and the anal triangle posteriorly. The urogenital triangle contains the superficial and deep perineal spaces, separated by the perineal membrane. The superficial perineal space contains muscles like the bulbospongiosus and blood vessels, while the deep perineal space contains the sphincter urethrae muscle and membranous urethra. Posteriorly, the ischiorectal fossae are located lateral to the anal canal and contain fat, blood vessels and nerves like the pudendal nerve. Diseases