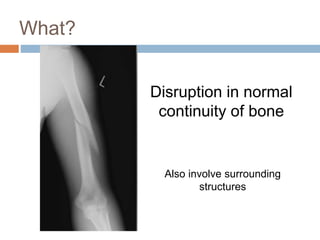
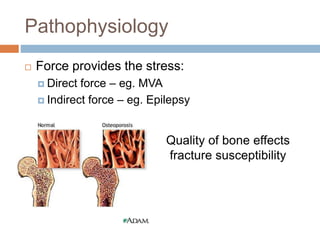
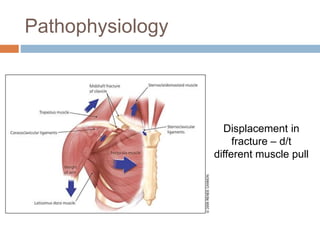
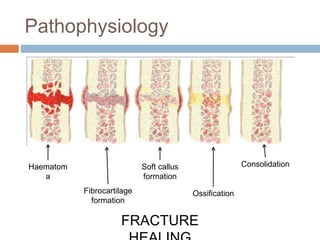
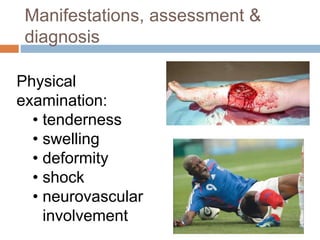
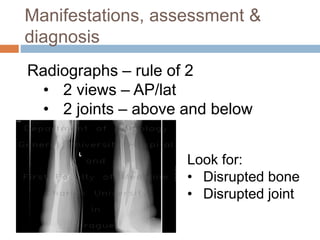
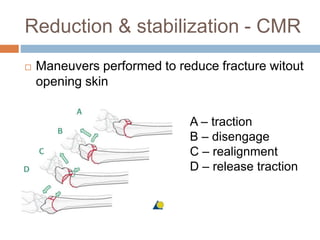
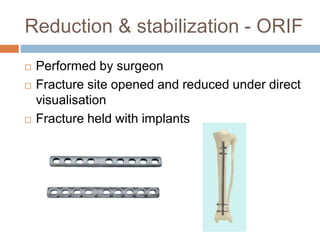
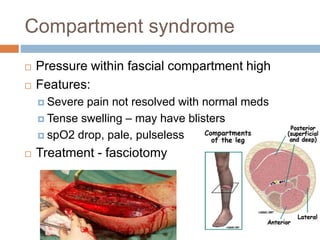
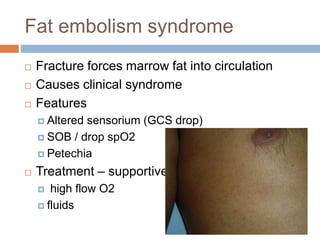
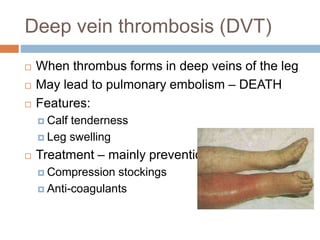
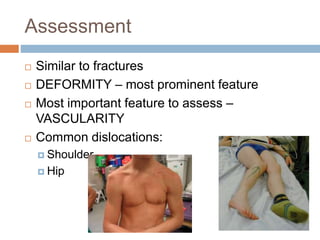
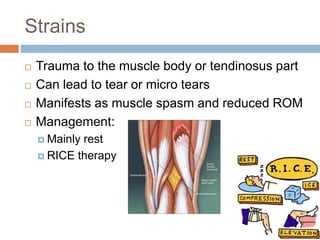
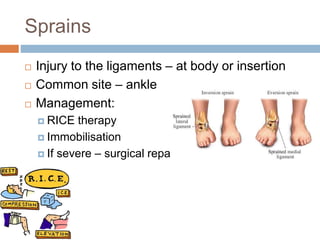
This document provides an overview of musculoskeletal trauma, including fractures, dislocations, and soft tissue injuries. It describes the pathophysiology, manifestations, assessment, diagnosis and management of fractures. Fractures occur when there is a disruption in normal bone continuity and involve surrounding structures. They are caused by mechanical overload that provides a force greater than the bone can absorb. The document outlines the stages of fracture healing and complications to monitor for, such as compartment syndrome. It also reviews the reduction and stabilization techniques of closed manipulation, open reduction internal fixation, external fixation and traction. Dislocations and soft tissue injuries like strains and sprains are also summarized.