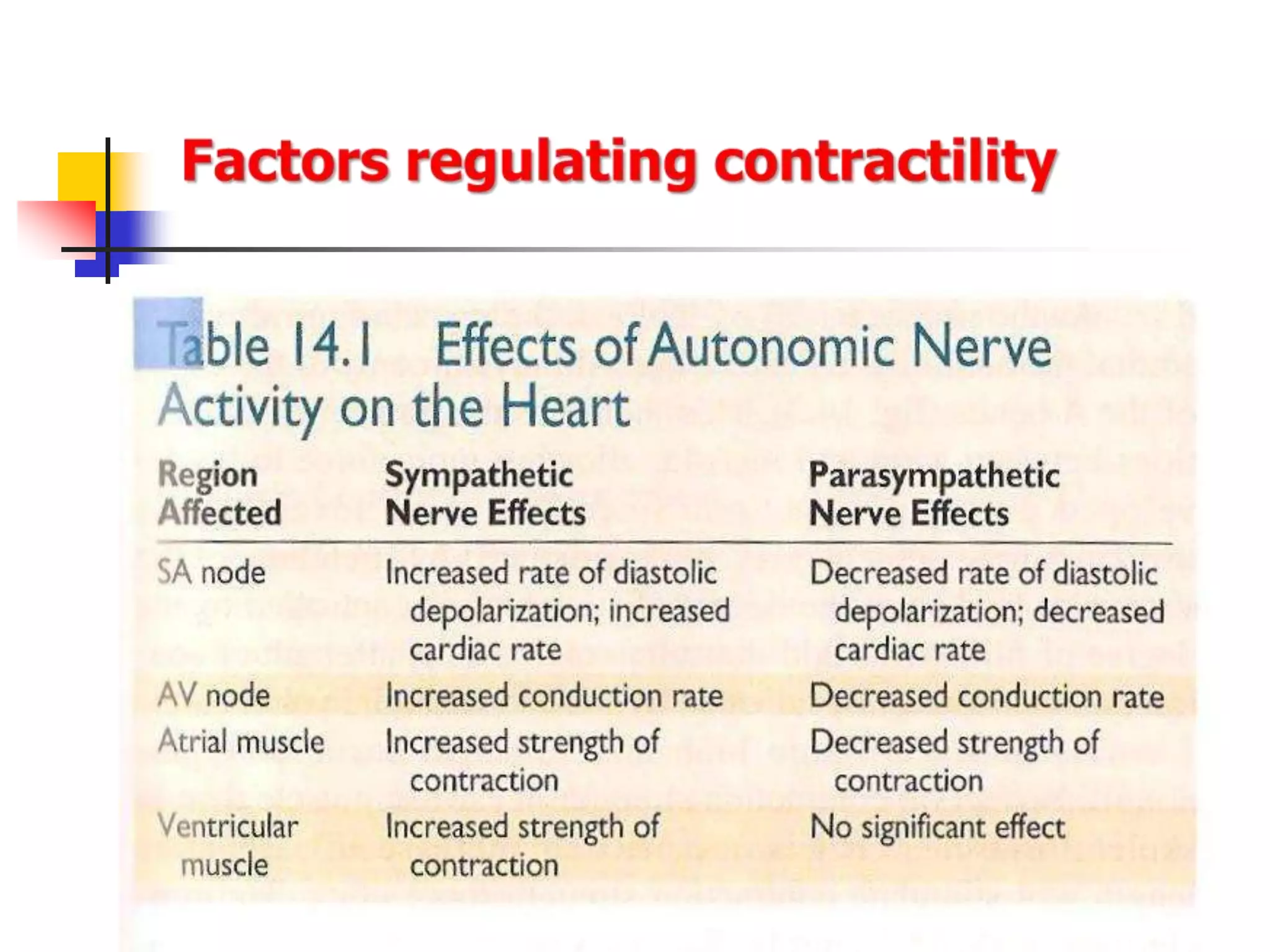
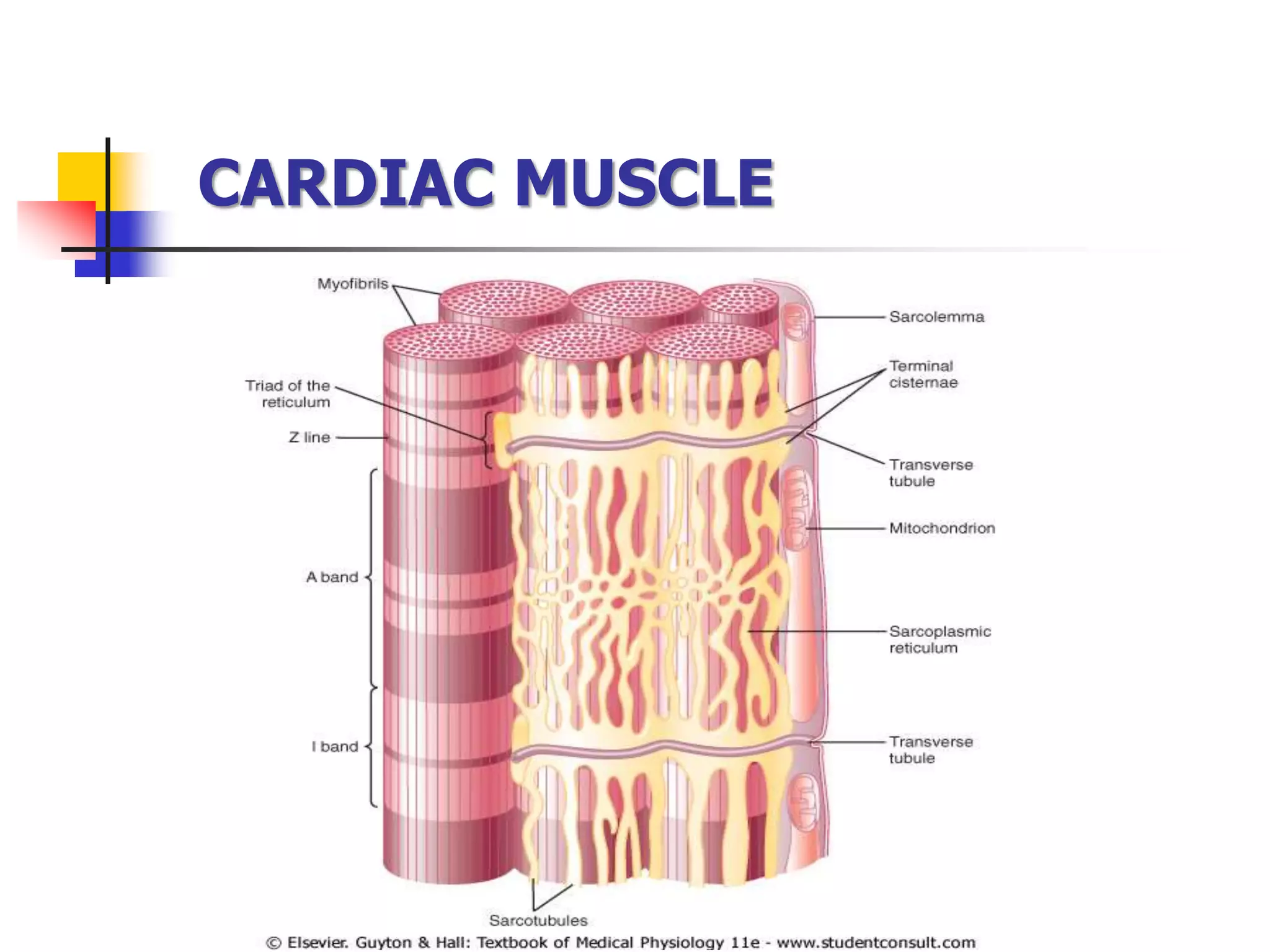
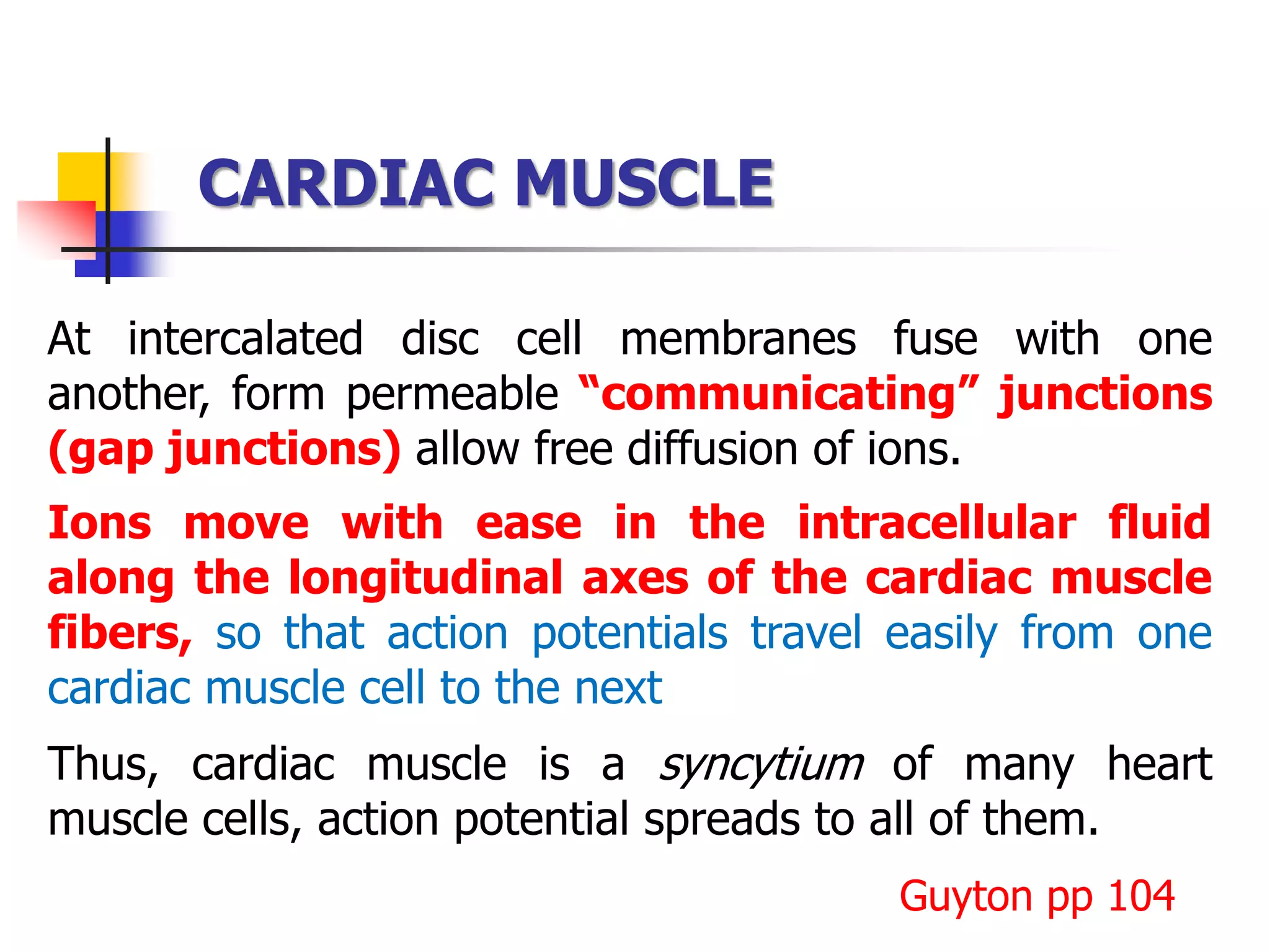
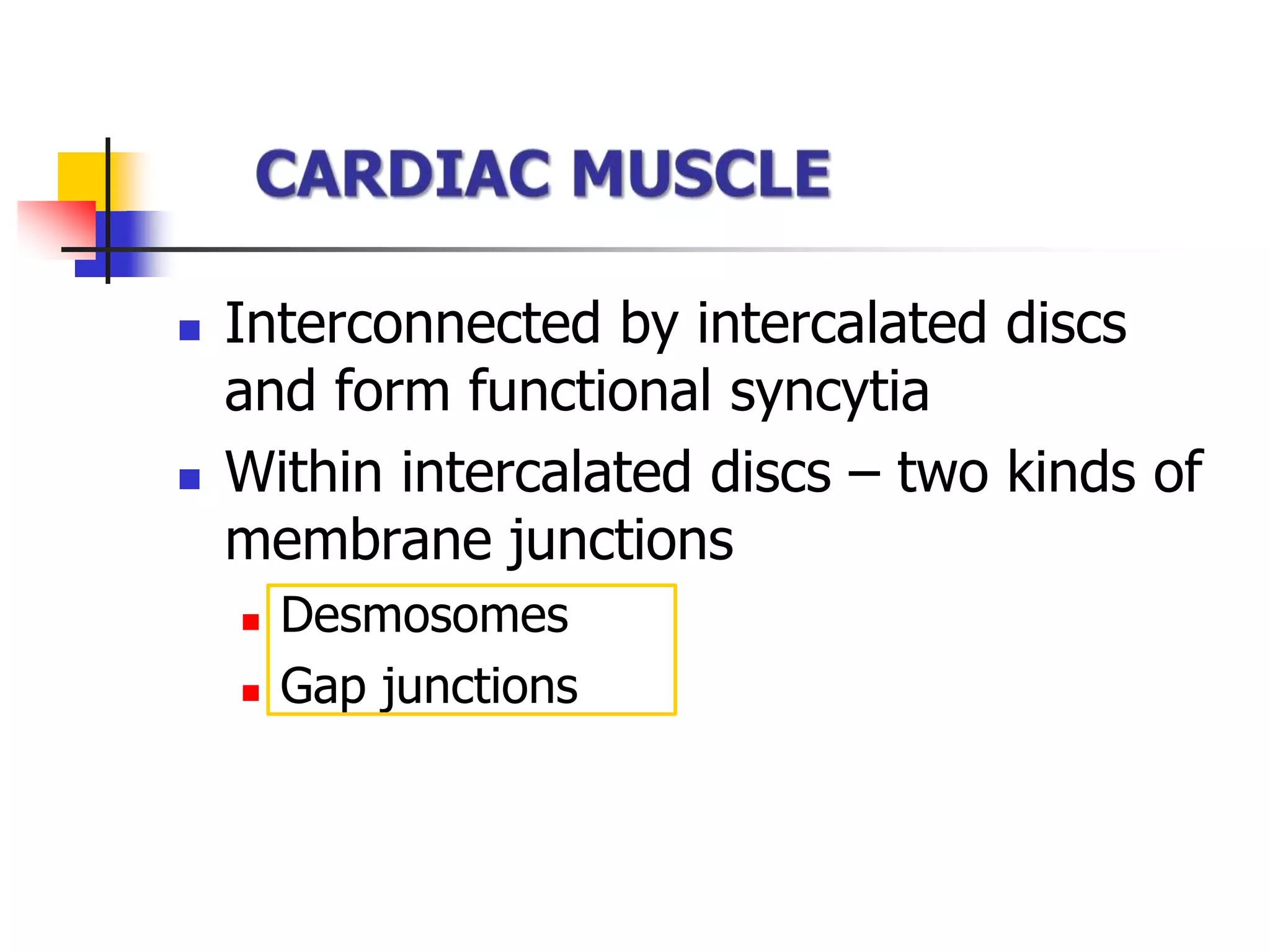
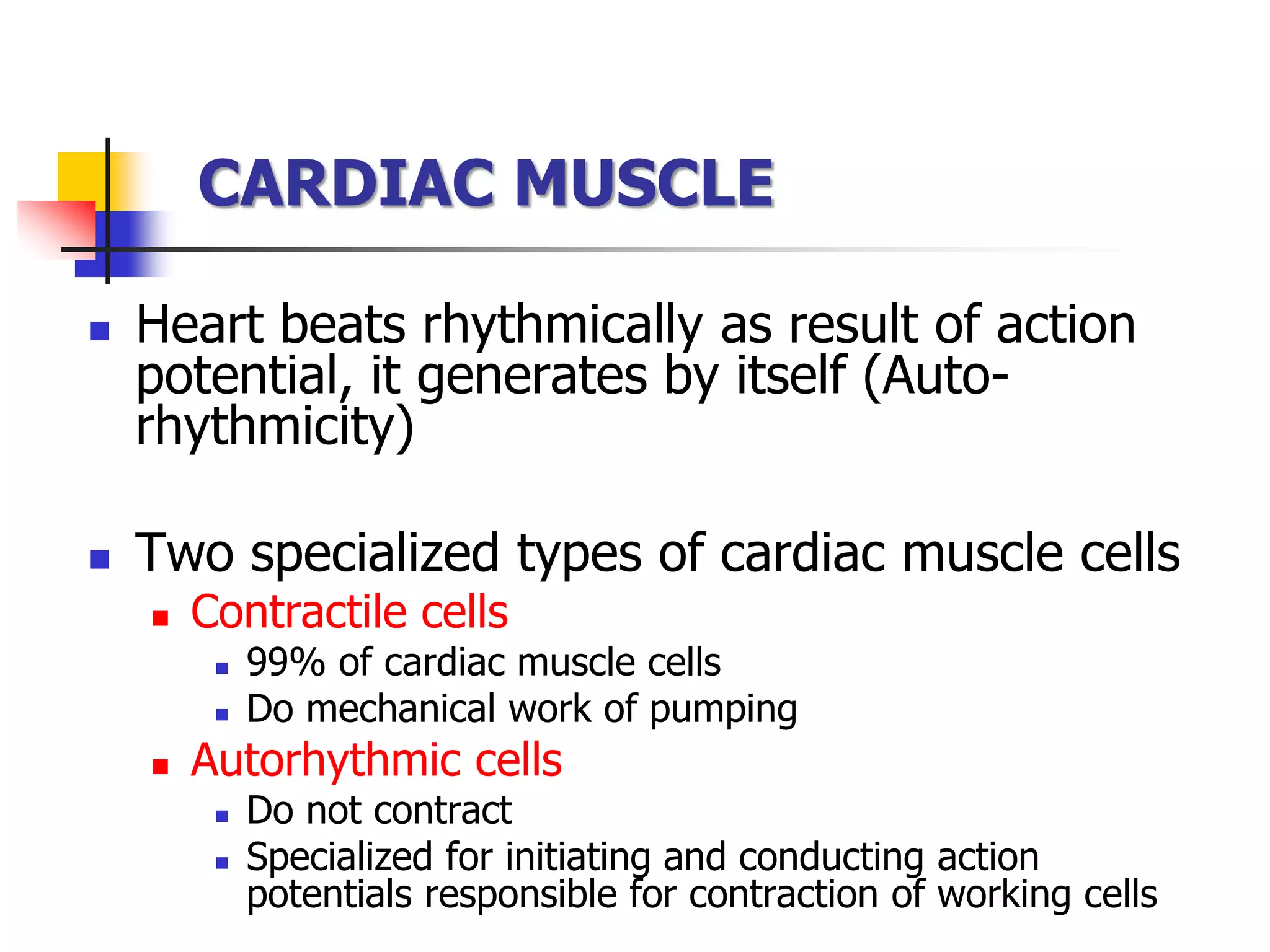
The document summarizes the structure and function of cardiac muscle. It discusses that cardiac muscle is composed of three types - atrial muscle, ventricular muscle, and specialized excitatory and conductive muscle. Cardiac muscle fibers are striated and interconnected via intercalated discs containing gap junctions. The discs allow electrical signals to easily spread between cells, making cardiac muscle a syncytium. Contraction is triggered by calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to an action potential. The heart possesses properties of automaticity, excitability, conductivity, contractility, and rhythmicity which allow it to contract rhythmically.







![Excitation-Contraction coupling
Excitation Contraction
[ Ca++
]i
(Action Potentials) (shortening)
Excitation-Contraction coupling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1cardiaccontractilitylecture-230304132502-dca9df7a/75/cardiac-ppt-13-2048.jpg)
![Excitation Contraction
[ Ca++
]i
(Action Potentials) (shortening)
Excitation of the heart is triggered by electrical impulse
rather than neural transmitters.
Contraction of the heart is triggered by elevation of
intracellular calcium influx.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1cardiaccontractilitylecture-230304132502-dca9df7a/75/cardiac-ppt-14-2048.jpg)