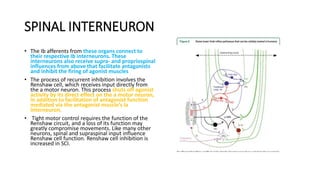
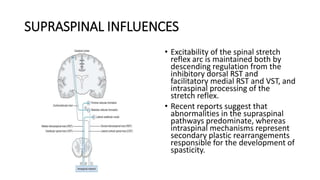
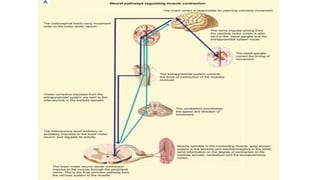
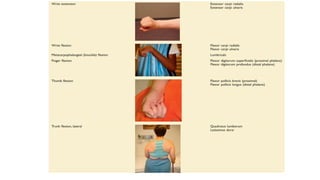
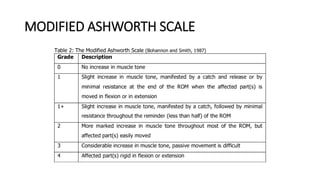
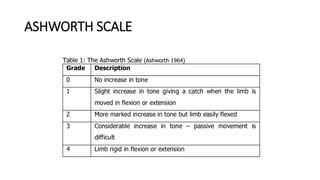
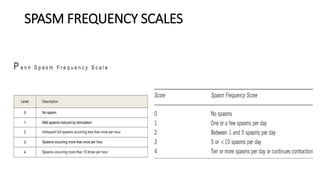
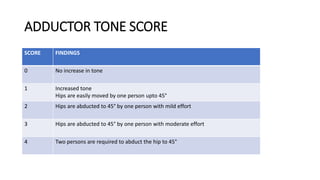
1) The document discusses spasticity, specifically the pathophysiology and assessment of spasticity. It covers topics like the stretch reflex, muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, spinal interneurons, and supraspinal influences on spasticity.
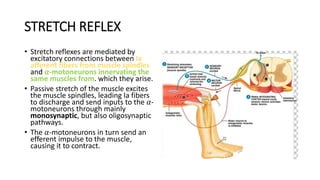
2) Key points include that spasticity is a velocity-dependent increase in muscle tone caused by hyperexcitability of the stretch reflex. It can be assessed by measuring the exaggeration of the stretch reflex at different velocities.
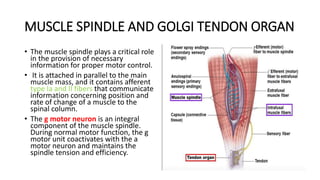
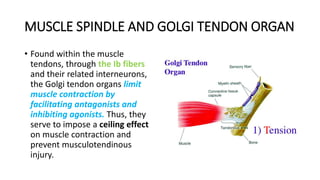
3) Spasticity is caused by abnormal processing in the spinal cord that leads to excessive reflex activation of motor neurons in response to input from muscle spindles. Supraspinal pathways like the reticulo