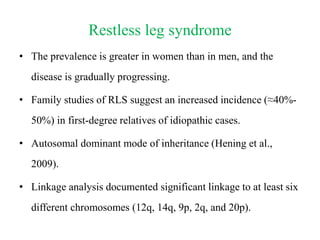
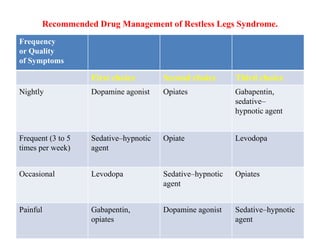
Restless leg syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disorder characterized by uncomfortable sensations in the legs and an irresistible urge to move them. It was first described in 1685 and termed RLS in 1945. RLS can be primary/idiopathic or secondary to conditions like iron deficiency, end-stage renal disease, and pregnancy. Diagnosis is based on clinical criteria including worsening symptoms at rest relieved by movement. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications and medications like dopaminergics, gabapentin, or opioids which provide symptom relief.