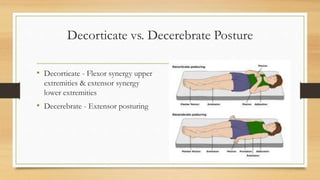
This document discusses muscle tone, including its physiology, characteristics of normal and abnormal tone, and approaches to managing tone issues. Muscle tone refers to a continuous low-level contraction that keeps muscles firm and ready to respond. It is important for posture, balance, and movement. Abnormal tone can include hypotonia (low tone) or hypertonia (high tone), and has various causes. Managing tone issues depends on whether it is low or high, and may involve positioning, stretching, splinting or other techniques. The Modified Ashworth Scale is used to assess levels of high muscle tone.