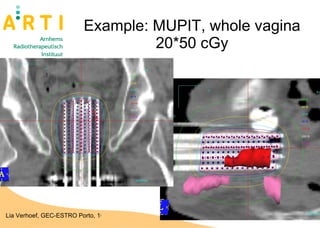
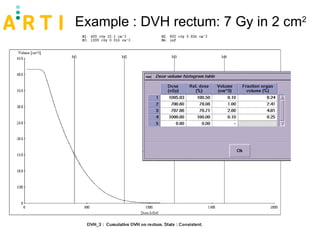
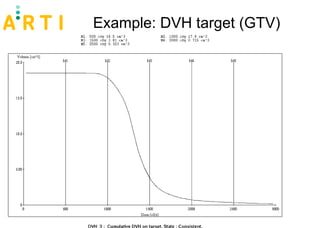
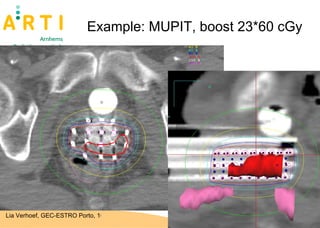
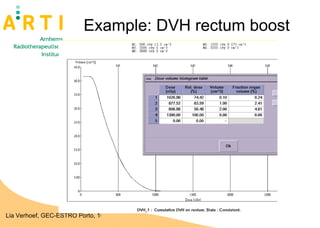
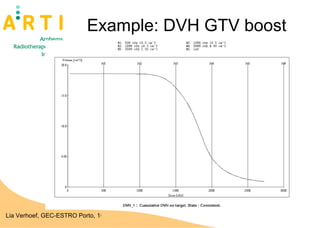
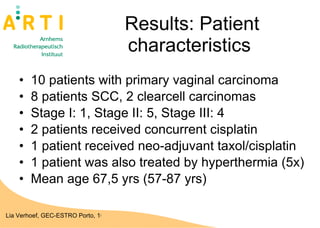
The document discusses a study evaluating the oncologic results and toxicity of MUPIT (Martinez Universal Perineal Template) implants for primary vaginal carcinoma. Ten patients with primary vaginal carcinoma underwent external beam radiotherapy followed by MUPIT brachytherapy. All patients completed treatment without complications and achieved a clinical complete response with no local or regional recurrences observed after a median follow-up of 55 months. However, there were some grade 2-4 toxicities observed, suggesting careful planning is needed to minimize toxicity when using the MUPIT procedure.