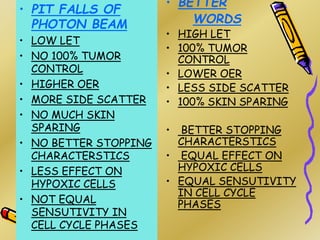
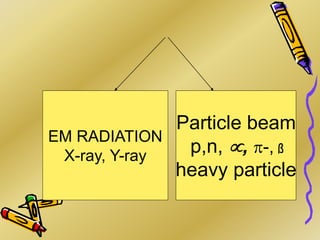
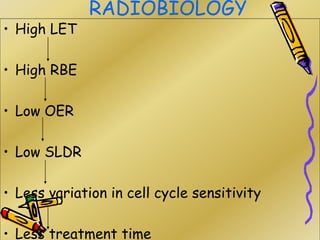
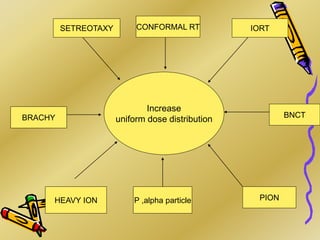
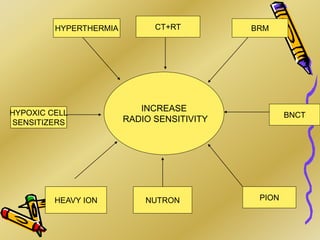
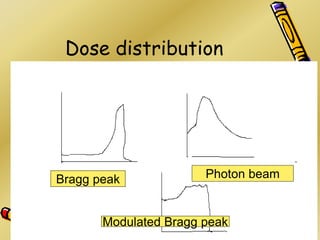
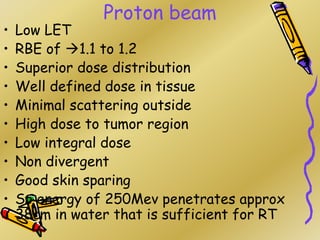
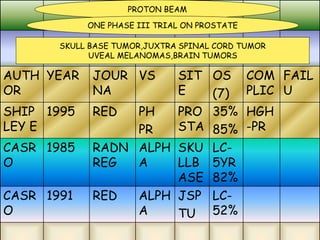
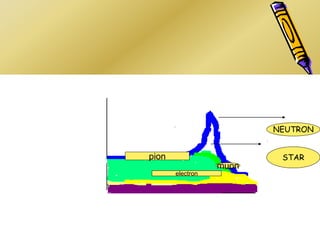
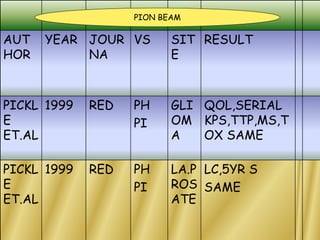
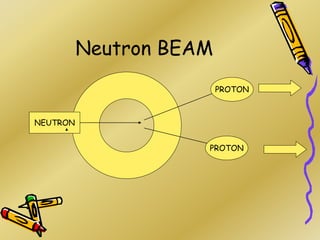
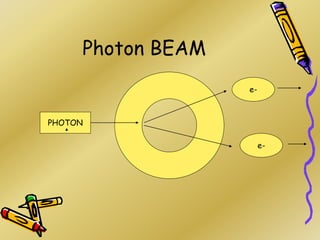
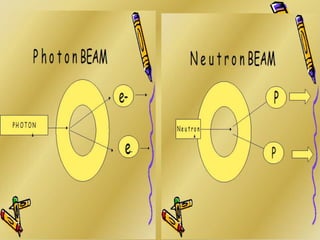
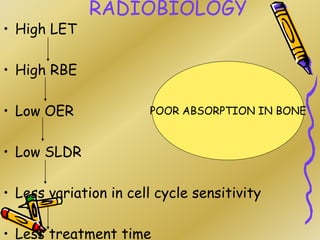
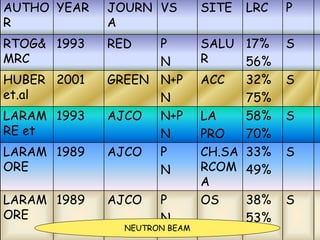
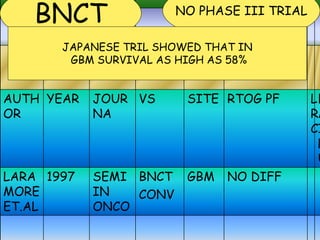
This document discusses various particle beams used in radiation therapy, including their properties and effectiveness. It states that proton beams have superior dose distribution compared to photon beams but lower LET. Neutron beams have high LET properties but poor dose distribution. Heavy charged particle beams like carbon ions have both superior distribution and high LET. BNCT uses boron compounds and neutrons to specifically target tumor cells but is limited by availability and cost. Overall, the document provides an overview of different particle therapies and their advantages over conventional photon radiation.