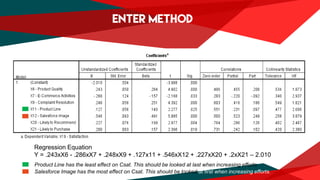
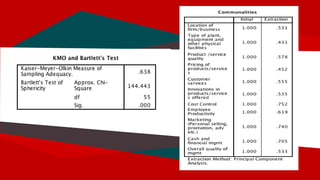
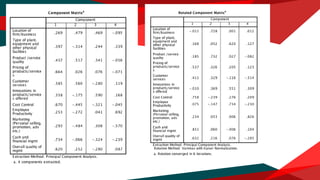
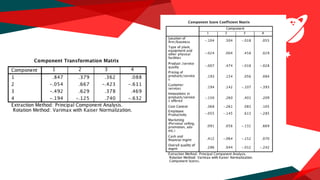
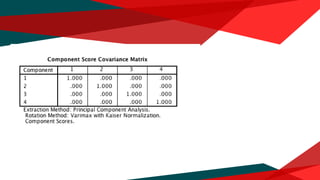
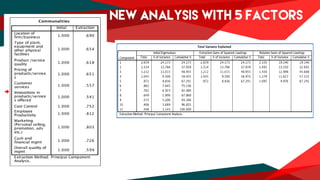
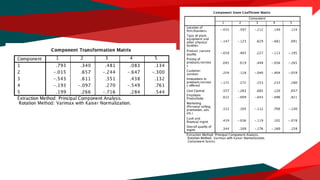
The document presents a regression analysis indicating that salesforce image significantly affects customer satisfaction (csat), whereas product line has the least effect. It also discusses the results of a factor analysis revealing five factors related to various business dimensions like cost management and employee productivity, while addressing issues of multicollinearity through data transformation. Lastly, clustering analysis identifies four clusters without significant gender or usage pattern differences affecting classification.