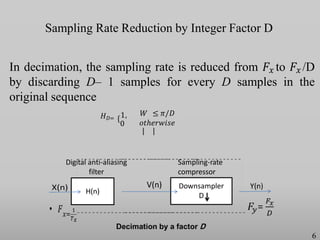
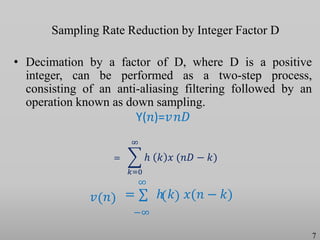
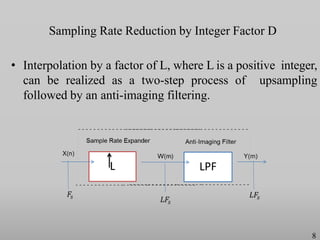
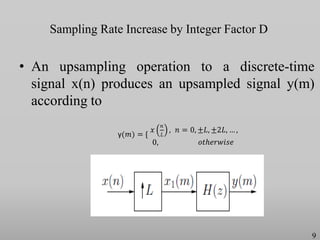
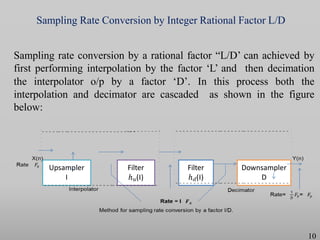
The presentation discusses multirate digital signal processing systems, which utilize multiple sampling rates to enhance performance or computational efficiency. It covers key concepts such as up-sampling and down-sampling along with their mathematical characterizations and applications including sampling-rate conversion. Additionally, it highlights the benefits of oversampling, such as improved filtering and reduced noise power spectral density.



![Up-Sampler
Time-Domain Characterization:
An up-sampler with an up-sampling factor L, where L is a positive
integer, develops an output sequence with a sampling rate that
is L times larger than that of the input sequence x[n]
Block-diagram representation
L
x[n] ]
[n
xu
]
[n
xu
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multiratesignalprocessing-210617114513/85/Multirate-signal-processing-4-320.jpg)
![Down-Sampler
Time-Domain Characterization:
An down-sampler with a down-sampling factor M, where M is a
positive integer, develops an output sequence y[n] with a sampling rate
that is (1/M)-th of that of the input sequence x[n]
Block-diagram representation
M
x[n] y[n]
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multiratesignalprocessing-210617114513/85/Multirate-signal-processing-5-320.jpg)