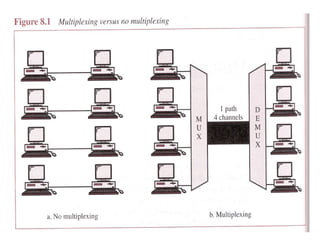
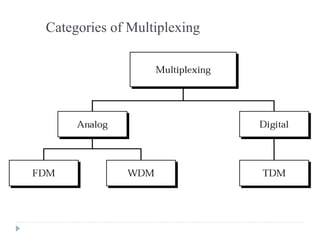
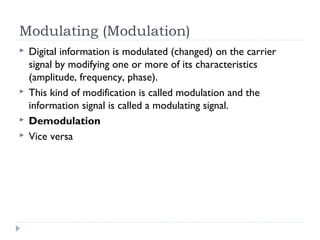
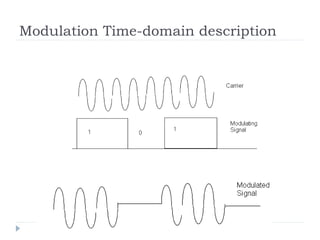
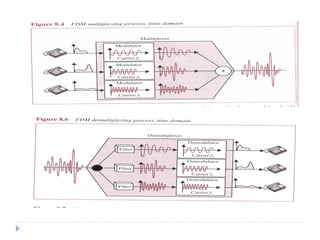
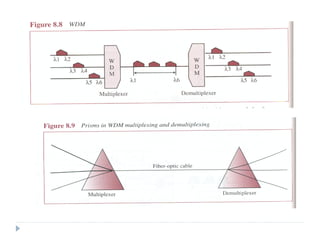
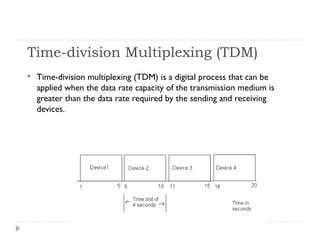
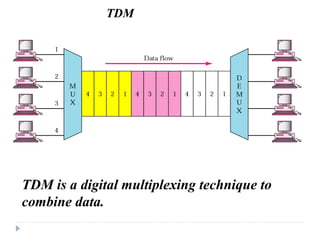
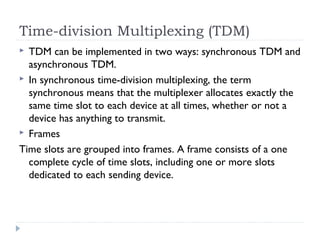
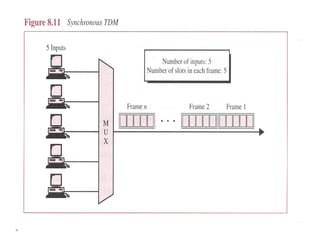
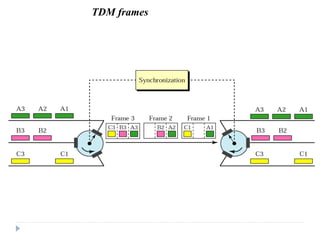
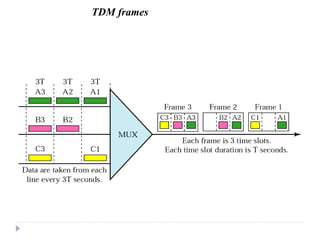
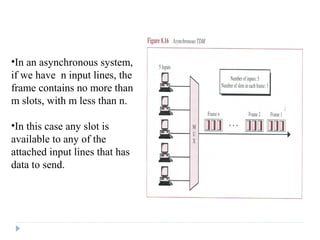
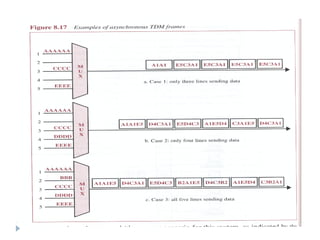
Multiplexing allows the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals across a single data link using techniques like frequency division multiplexing (FDM), wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), and time division multiplexing (TDM). FDM combines signals by allocating each a different frequency band. WDM is similar but uses light signals transmitted through fiber optic channels. TDM is a digital process that combines data by allocating time slots, with synchronous TDM assigning fixed slots and asynchronous TDM allowing flexible slot allocation.