Embed presentation
Downloaded 35 times

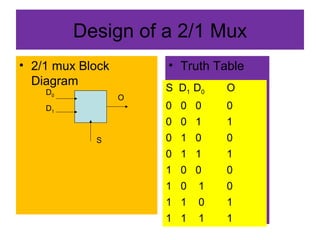
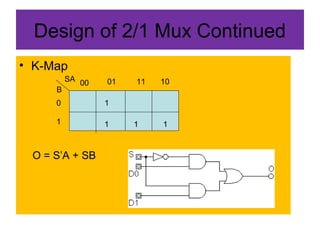
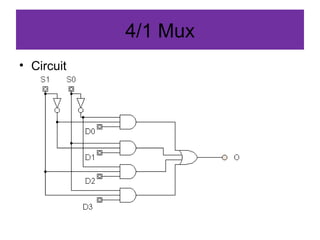
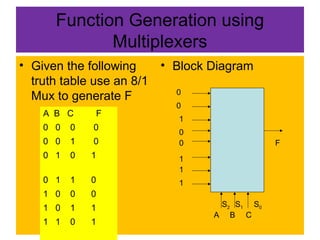
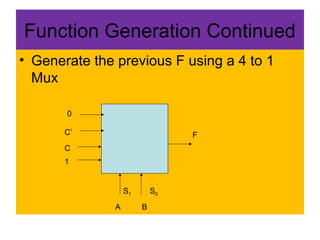
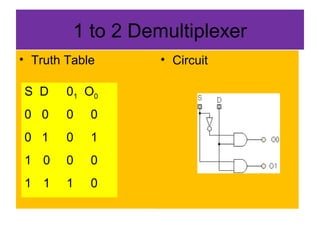
A multiplexer and demultiplexer allow multiple signals to share a single transmission line. A 2/1 multiplexer is described with a block diagram, truth table, and K-map implementation showing it selects one of two inputs based on a select line. A 4/1 multiplexer circuit is also shown. Multiplexers are used in data communications, radio channels, computer routing, and function generation by selecting an output from multiple inputs. An 8/1 multiplexer generates a function from a truth table. A 1 to 2 demultiplexer circuit separates a single input into two outputs based on a select line.







