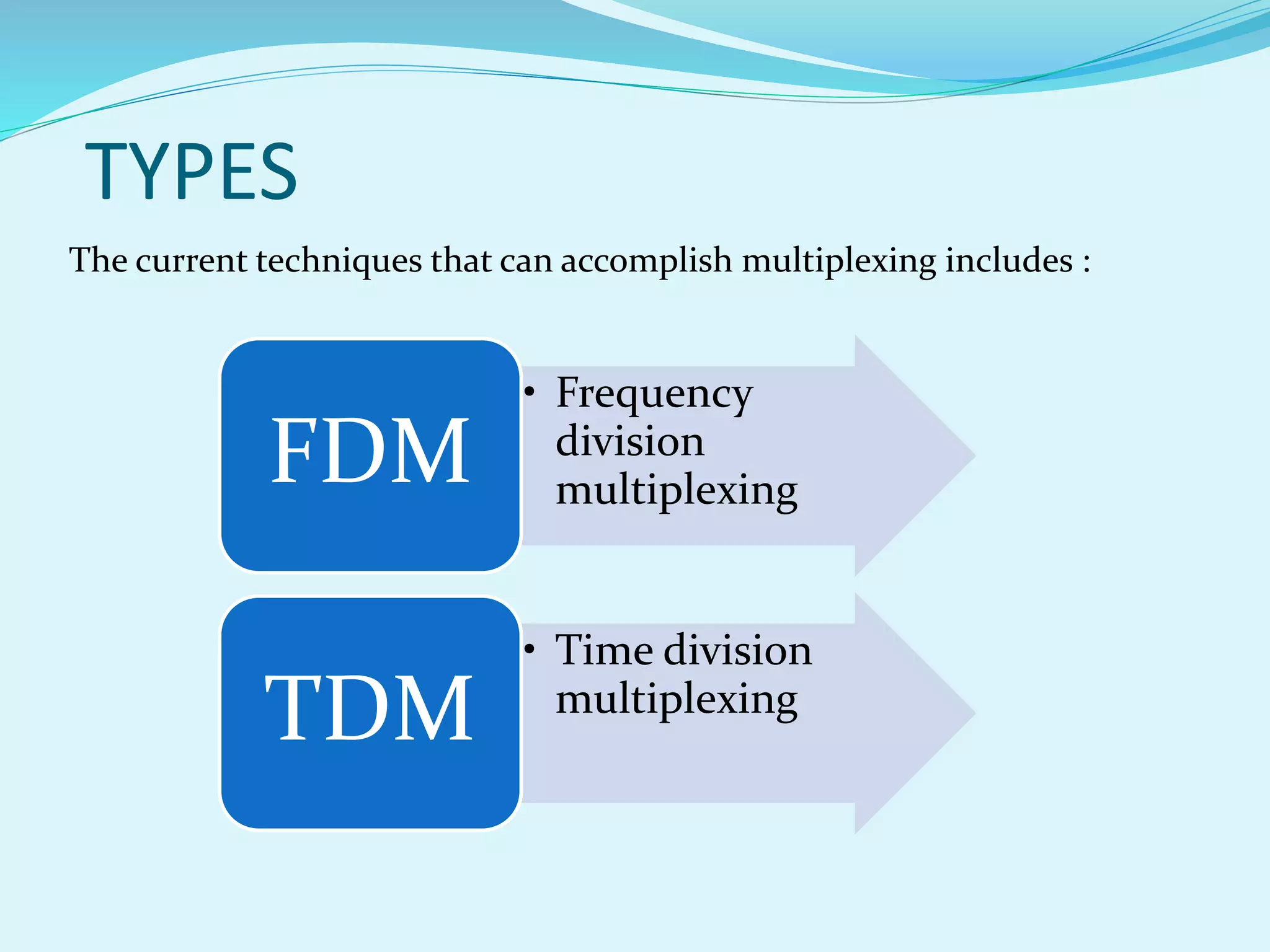
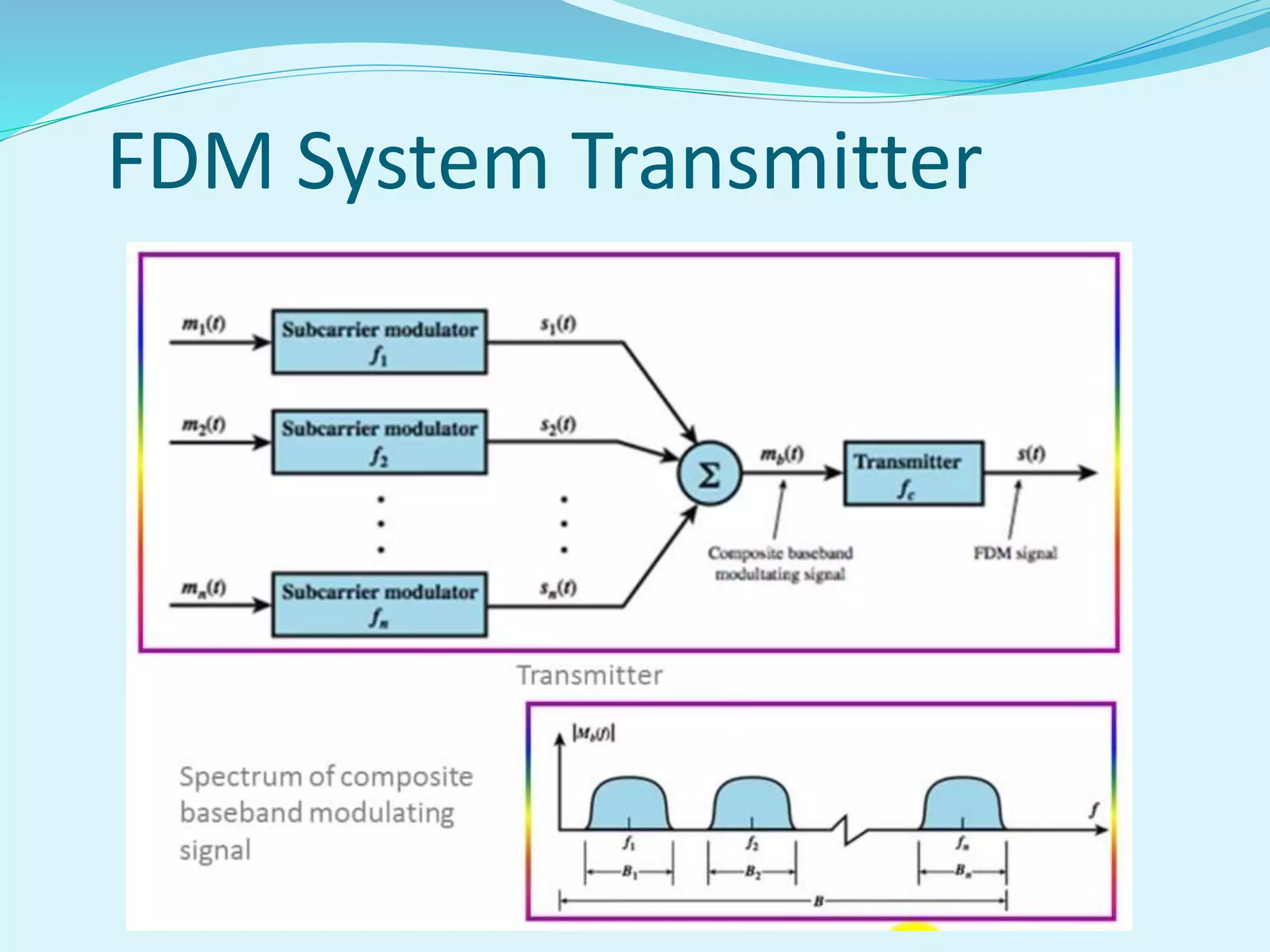
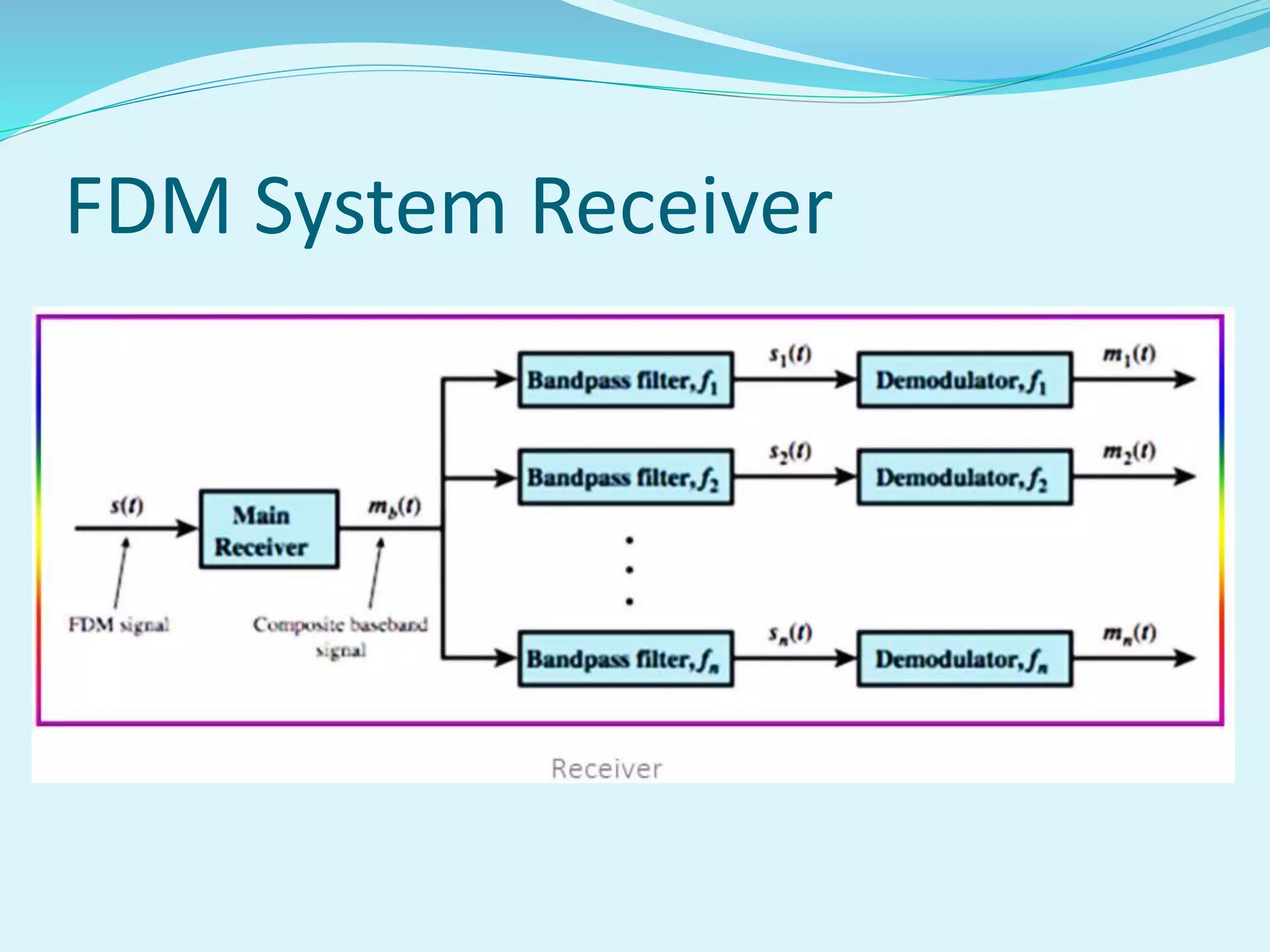
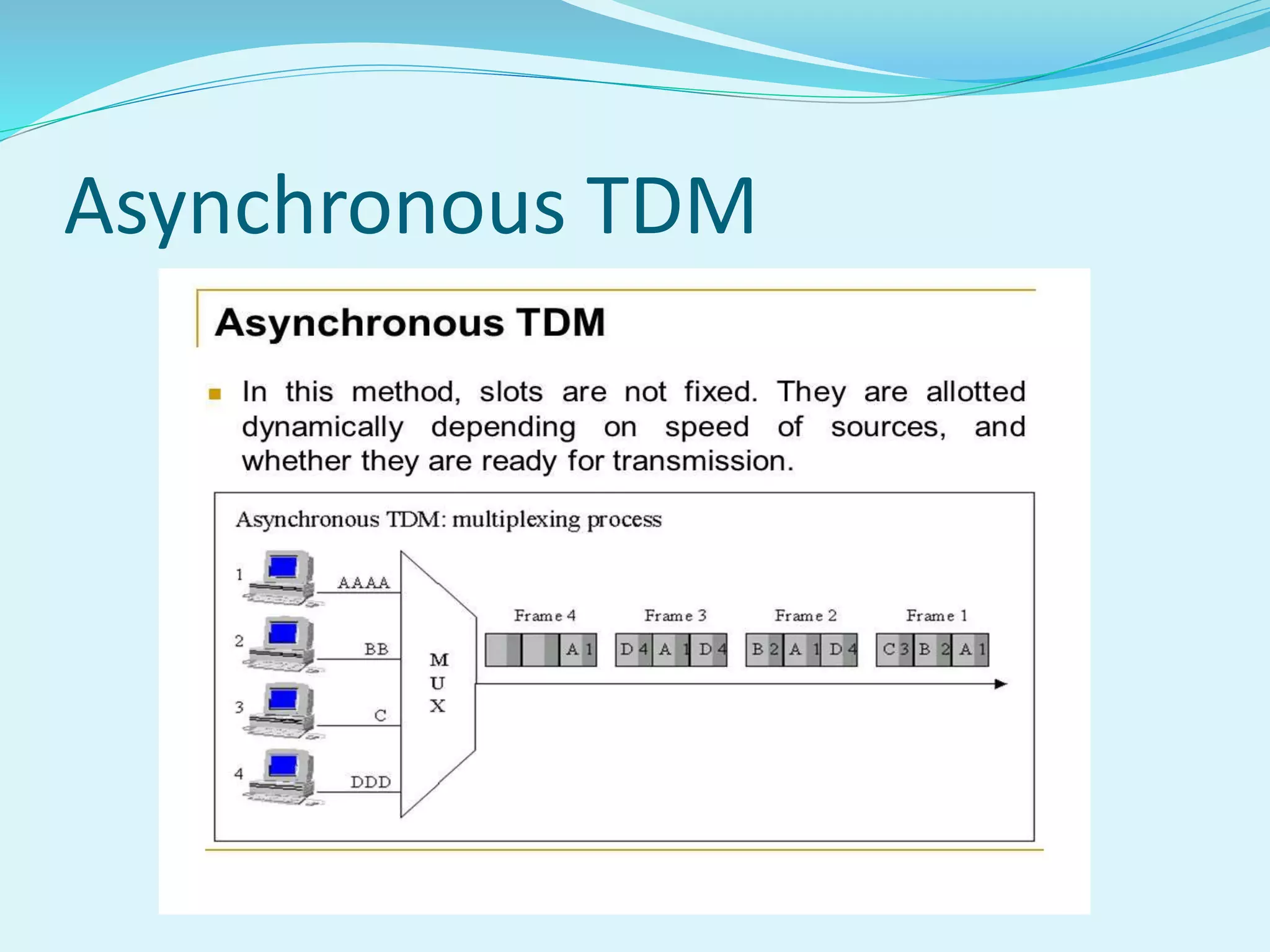
The document discusses multiplexing techniques necessary for transmitting multiple signals through a single medium without interference. It covers frequency division multiplexing (FDM) and time division multiplexing (TDM), explaining how they enable efficient use of bandwidth and reduce costs for businesses. The document also highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each technique, including issues like signal overlap in FDM and the importance of clock synchronization in TDM.