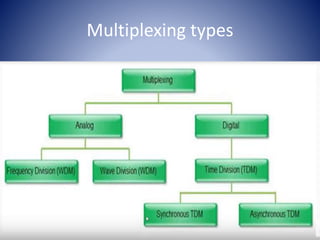
Multiplexing is a technique that allows multiple signals to be transmitted over a single data link by combining or dividing the signals. There are different types of multiplexing including frequency division multiplexing (FDM), wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), and time division multiplexing (TDM). FDM and WDM are analog techniques that modulate signals onto different carrier frequencies or wavelengths. TDM is a digital technique that assigns fixed or dynamic time slots to different signals to allow transmission over the same link.