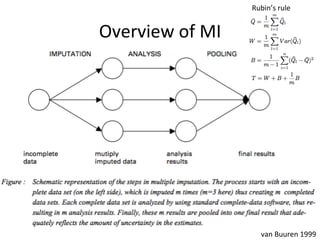
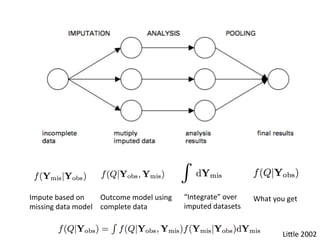
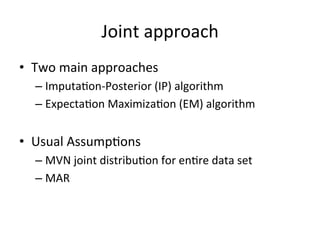
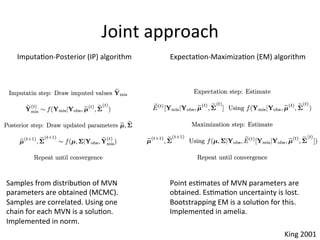
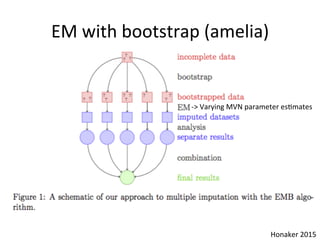
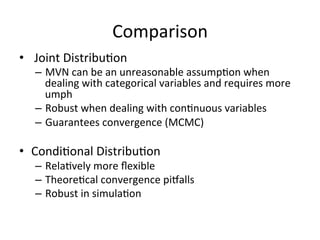
The document discusses multiple imputation (MI) as a method for addressing missing data in datasets, reviewing its algorithms, strengths, and weaknesses. It contrasts joint distribution MI and conditional distribution MI approaches, noting implications for high-dimensional data and the challenges faced with covariance matrices. The conclusion emphasizes that while the joint approach is theoretically sound, both methods struggle with high-dimensional cases where covariates exceed observations.











![High-dimensional data
• The joint MI has an issue with a huge
covariance matrix many parameters, whereas
the condi$onal MI has an overfinng issue for
each regression model.
• Introducing structures for the covariance
matrix (joint MI)[1] and using regulariza$on
(condi$onal MI)[2] have been examined.
• Widely available soqware implementa$ons
are lacking.
[1] He 2014; [2] Zhao 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20151215apresentation-151216031138/85/Multiple-Imputation-Joint-and-Conditional-Modeling-of-Missing-Data-21-320.jpg)

