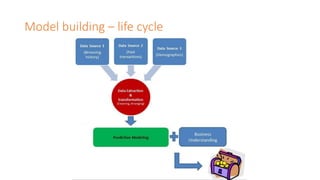
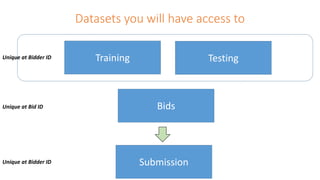
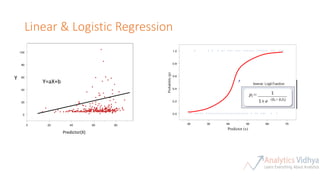
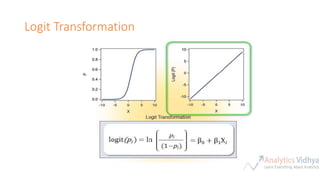
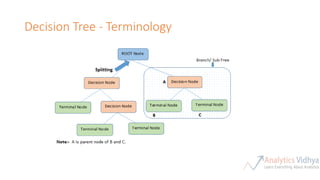
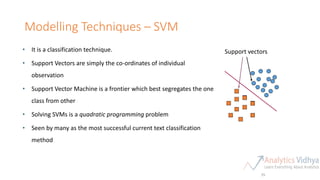
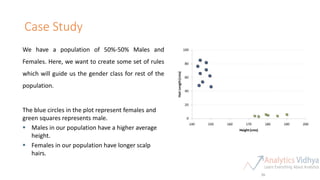
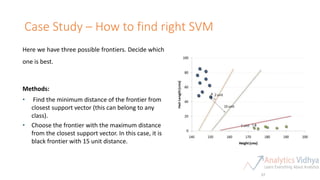
This document provides an agenda for a meetup on data science topics. The meetup will be held once a month, with the next one on June 14th. It aims to provide the best networking and learning platform in Bangalore for areas like data science, big data, machine learning. The agenda includes introductions, an overview of the model building lifecycle, data exploration and feature engineering techniques, and modeling techniques like logistic regression, decision trees, random forests, and SVM. Teams will be formed to predict whether bids are from humans or robots using these techniques. Resources for implementing the techniques in Python and R are also provided.