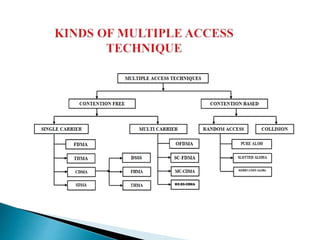
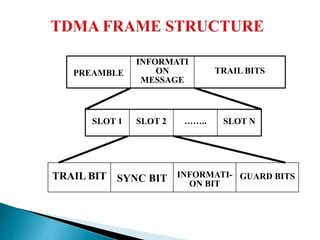
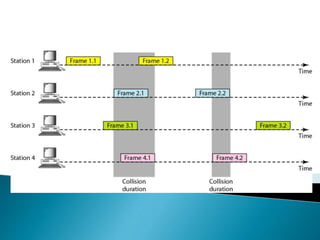
The document discusses multiple access schemes used for efficient sharing of radio spectrum among mobile users, including techniques like FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, and various hybrid approaches. It highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each method in terms of bandwidth efficiency, data rate, and susceptibility to interference. Additionally, it covers contention-based access schemes like ALOHA, emphasizing the need for protocols to manage collisions and improve transmission efficiency.































![B.I.T , MESRA [M.Tech] Assignment : MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multipleaccesstechniquesassignmentfinal-170820115158/85/B-I-T-MESRA-M-Tech-Assignment-MULTIPLE-ACCESS-TECHNIQUES-FOR-WIRELESS-COMMUNICATION-35-320.jpg)