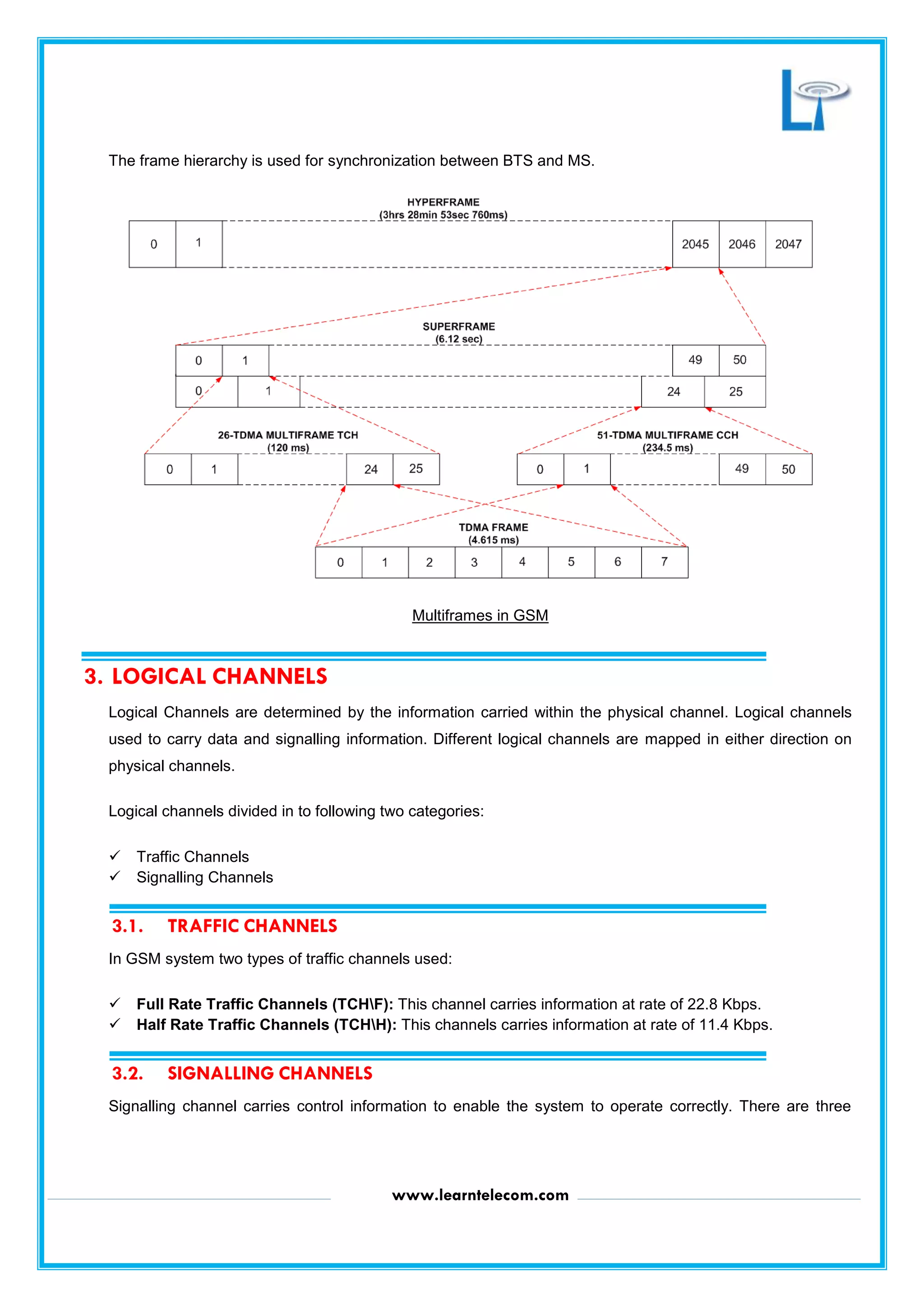
GSM uses a combination of FDMA and TDMA to divide up radio resources on the air interface. It defines physical channels based on frequency and timeslot, and logical channels to carry different types of data and signaling information. Logical channels include traffic channels to carry user data and various signaling channels like broadcast, common, and dedicated control channels which are used to enable network operations like cell broadcasts, paging, call setup, and handovers. Key physical channel structures include TDMA frames, multiframes, superframes, and hyperframes which are used for synchronization between base stations and mobile stations.