The document discusses various topics related to multimodal fluency and learning in the digital age including:
- The need to ground online learning in learning theory and pedagogy to ensure effective design.
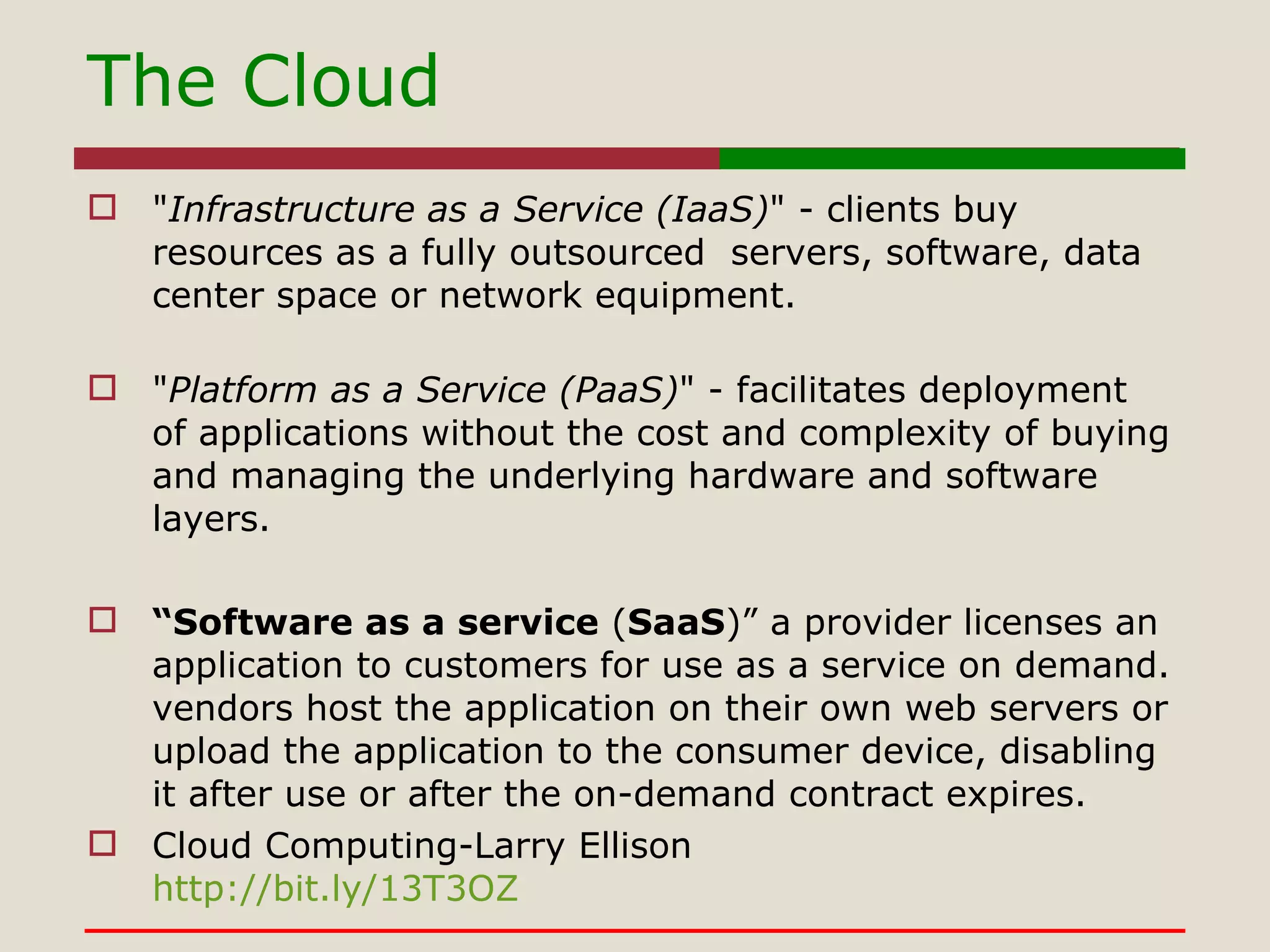
- Different models of cloud computing like Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service.
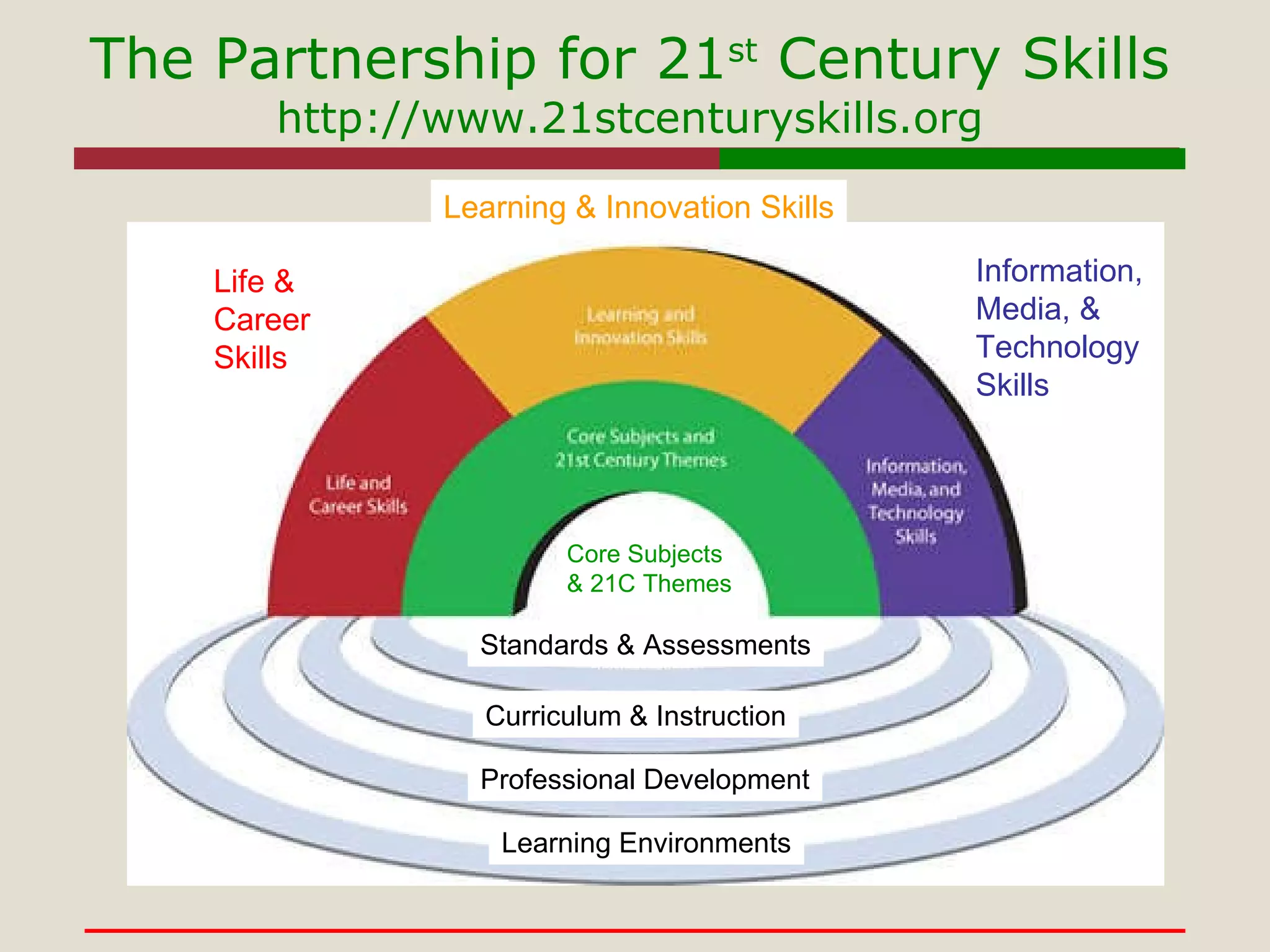
- The importance of developing skills like information literacy, digital literacy, and interpersonal skills for learning and survival in the modern world.
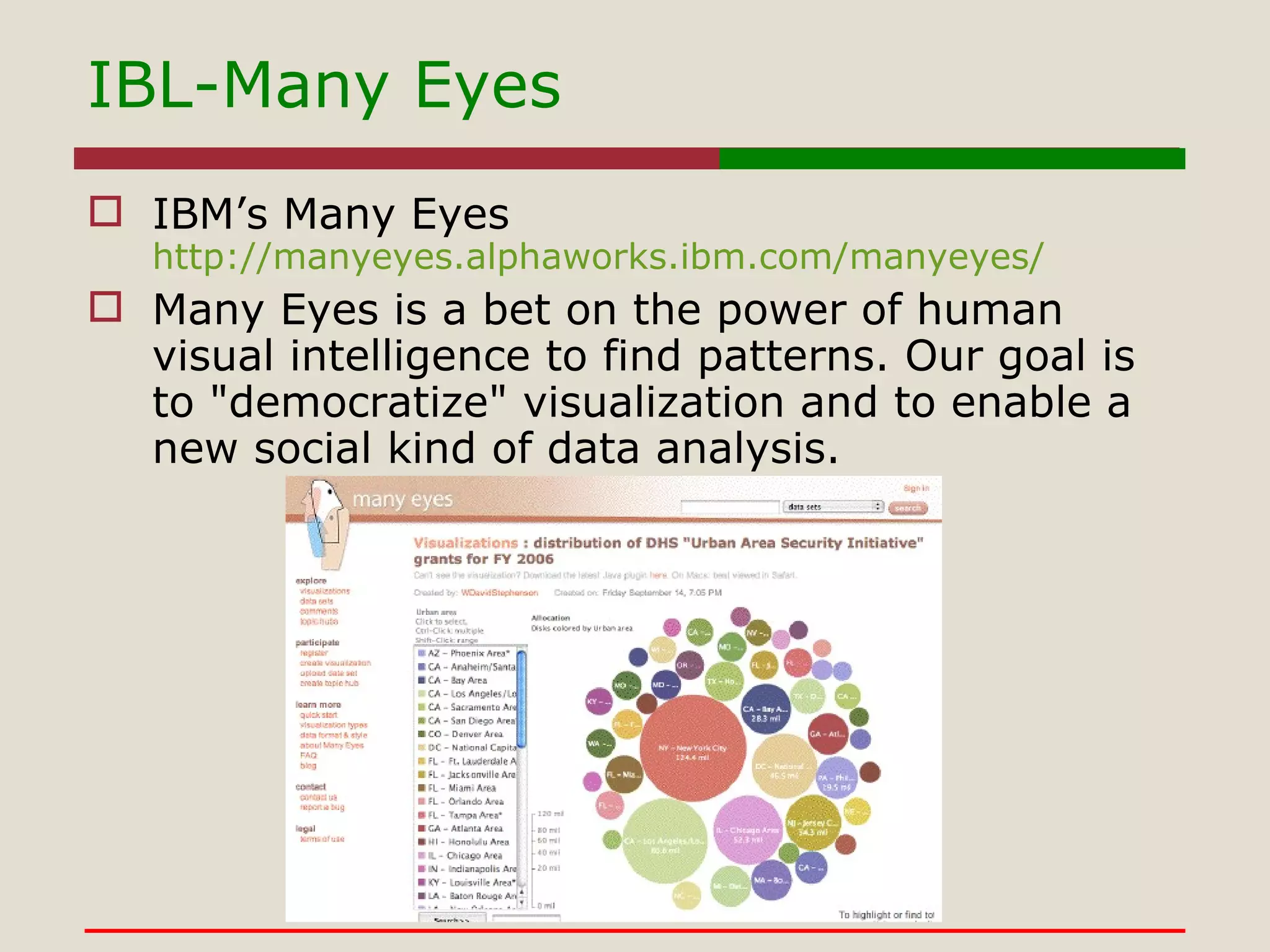
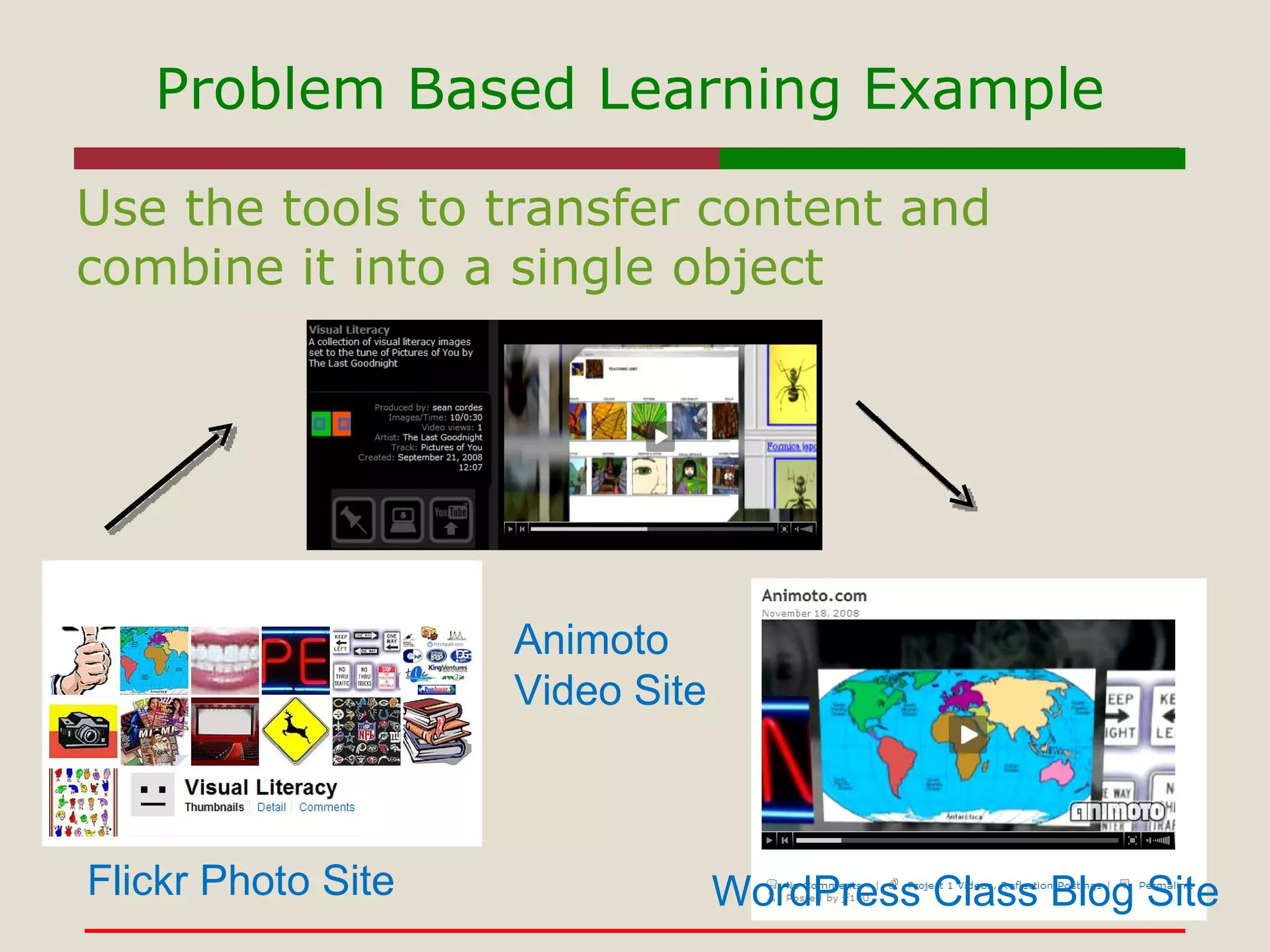
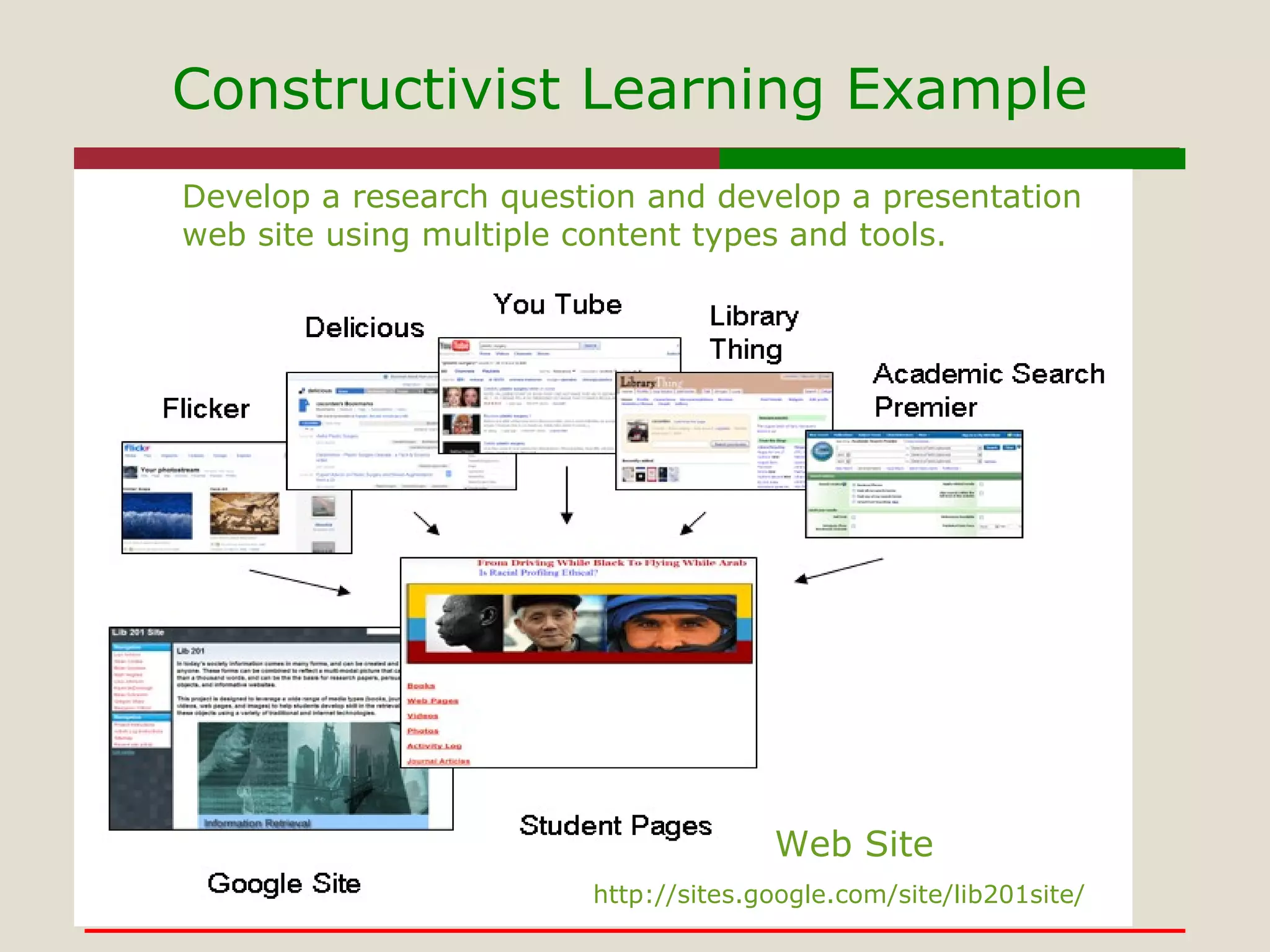
- Various teaching strategies like inquiry-based learning, problem-based learning, and constructivism that can be used with digital tools.
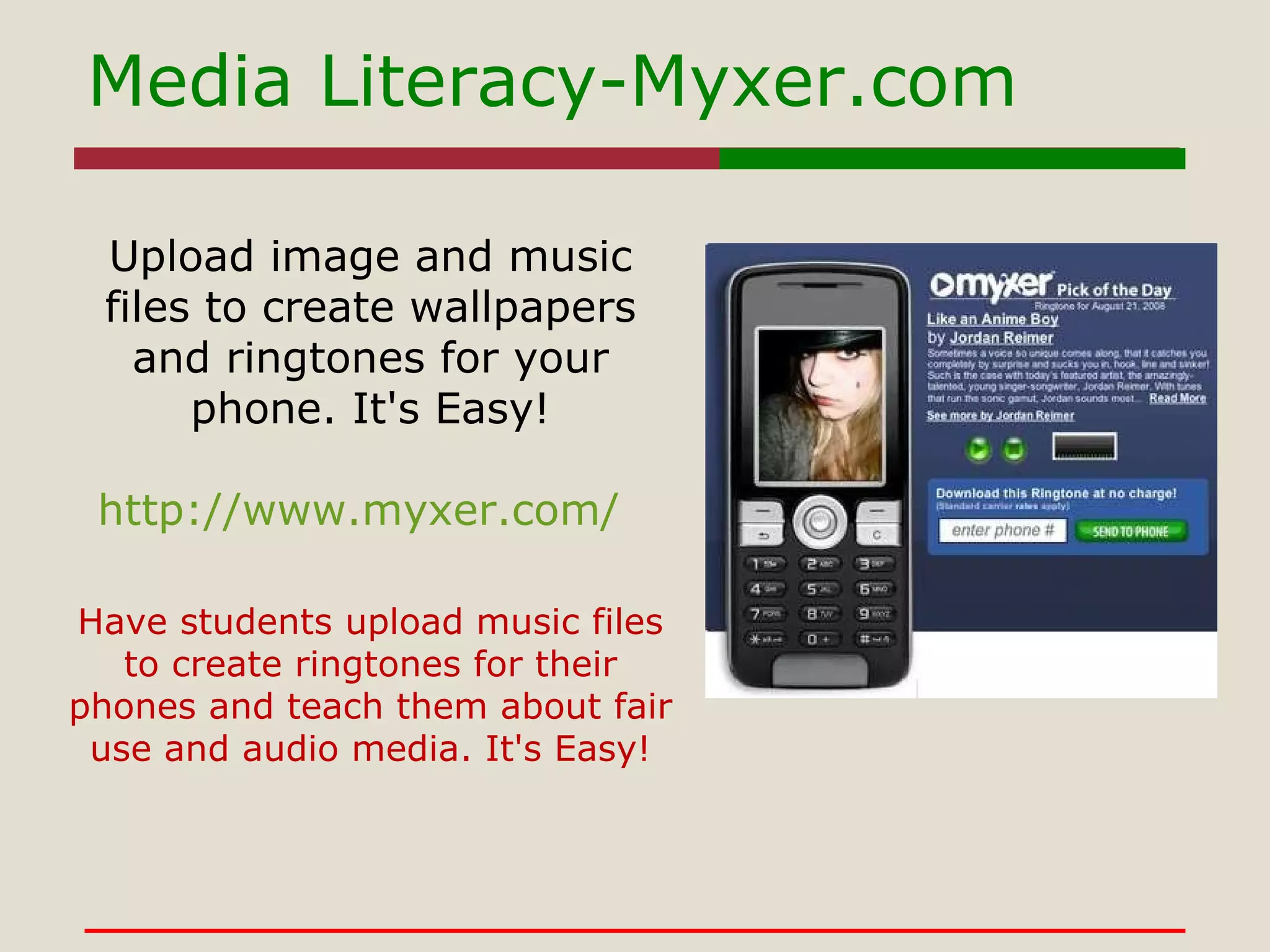
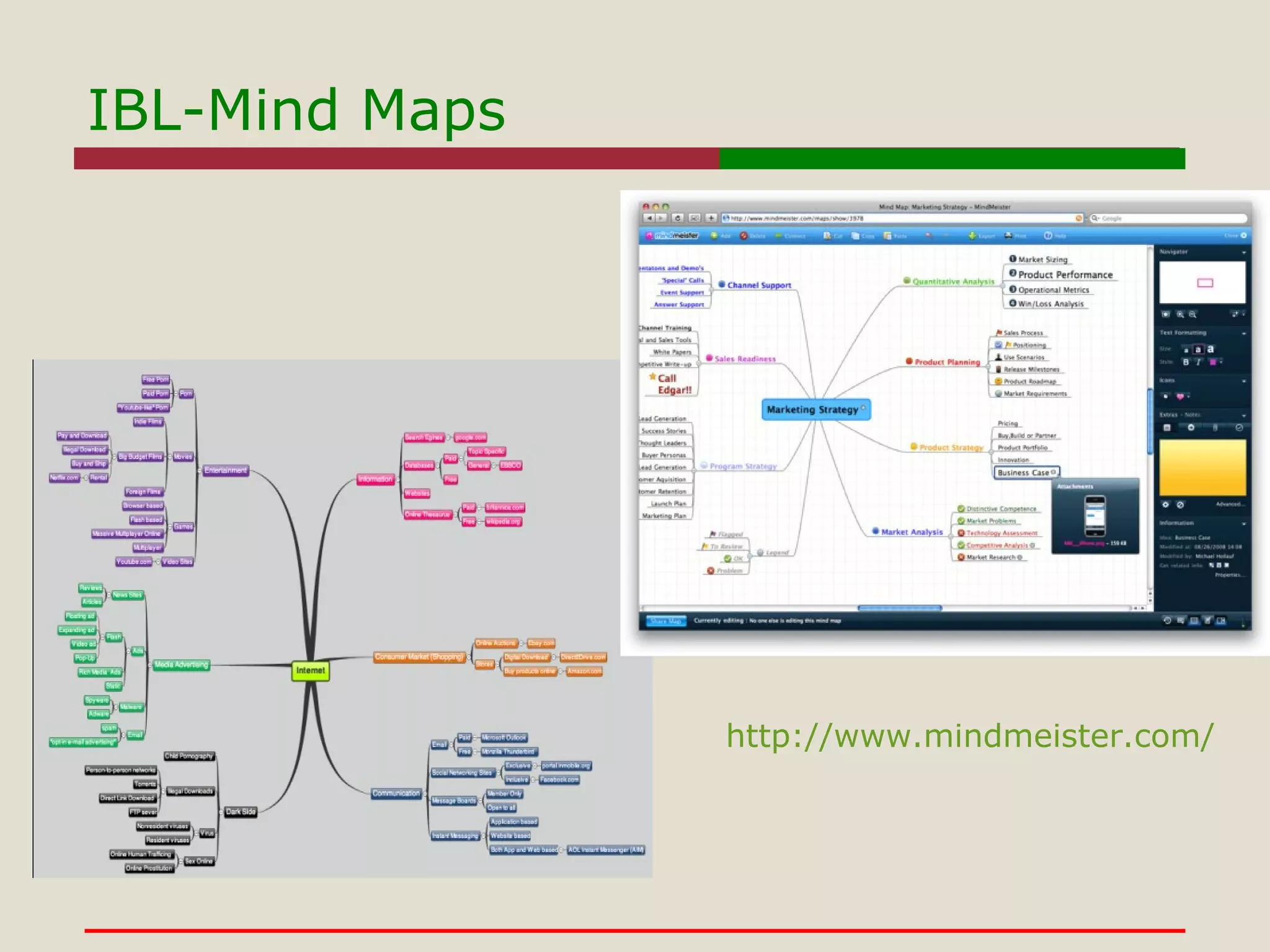
- The use of tools like Google Sites, Flickr, Animoto, and WordPress to support constructivist and problem-based


































![Thank You! [email_address] http://bit.ly/cZZf4J Got Slides?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classroomtothecloud-100315131941-phpapp01/75/Multimodal-Fluency-Classroom-to-the-Cloud-43-2048.jpg)