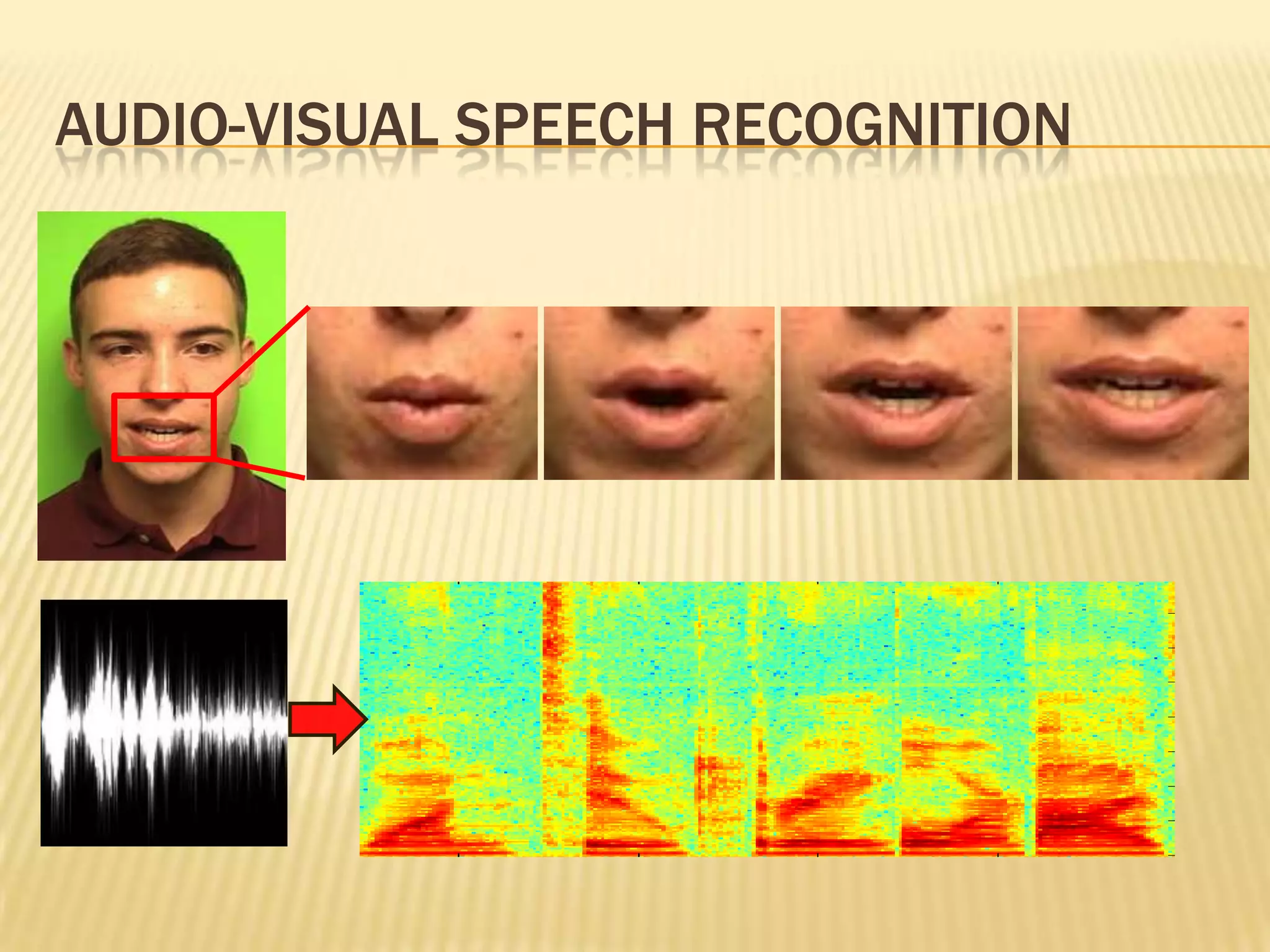
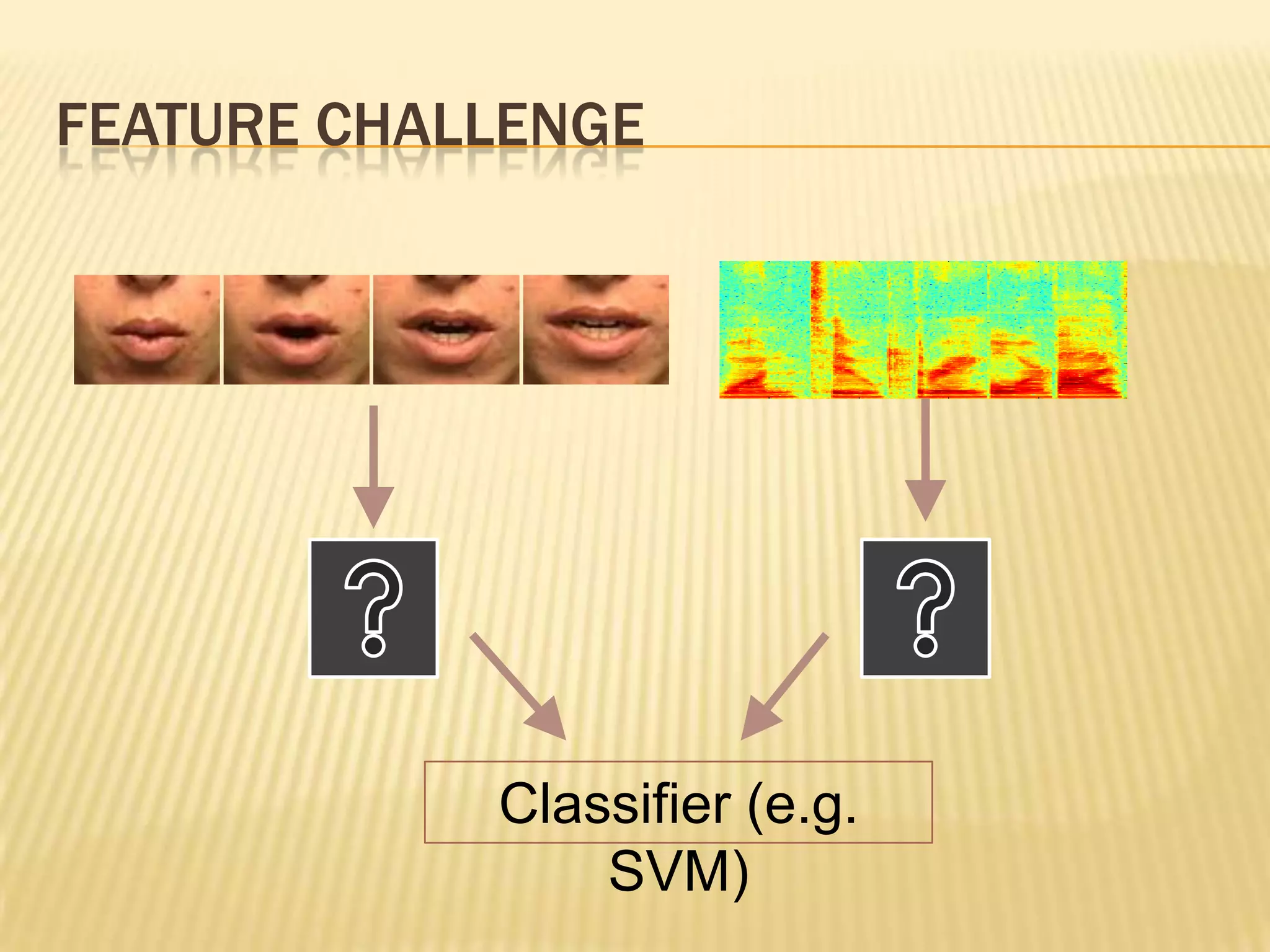
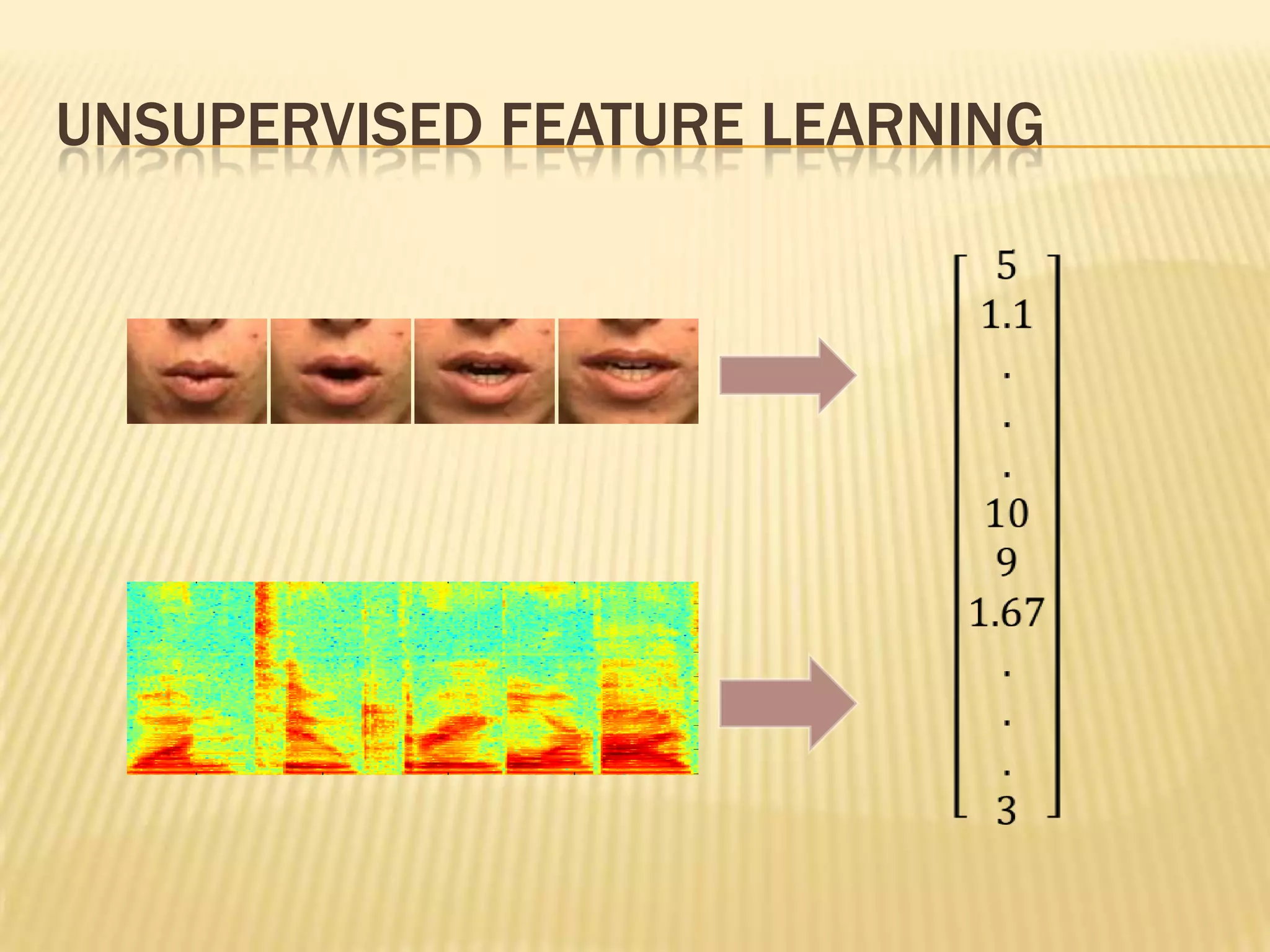
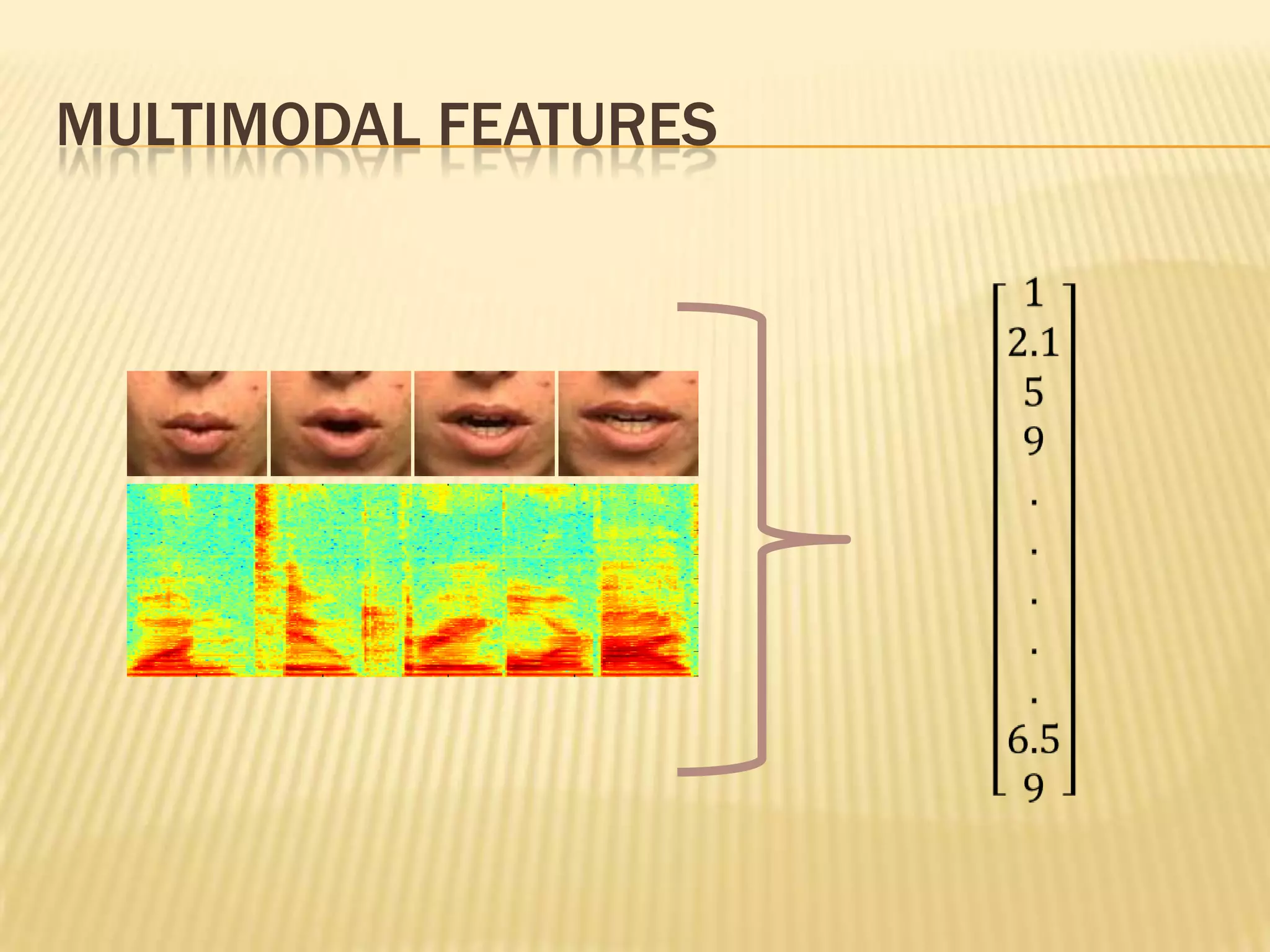
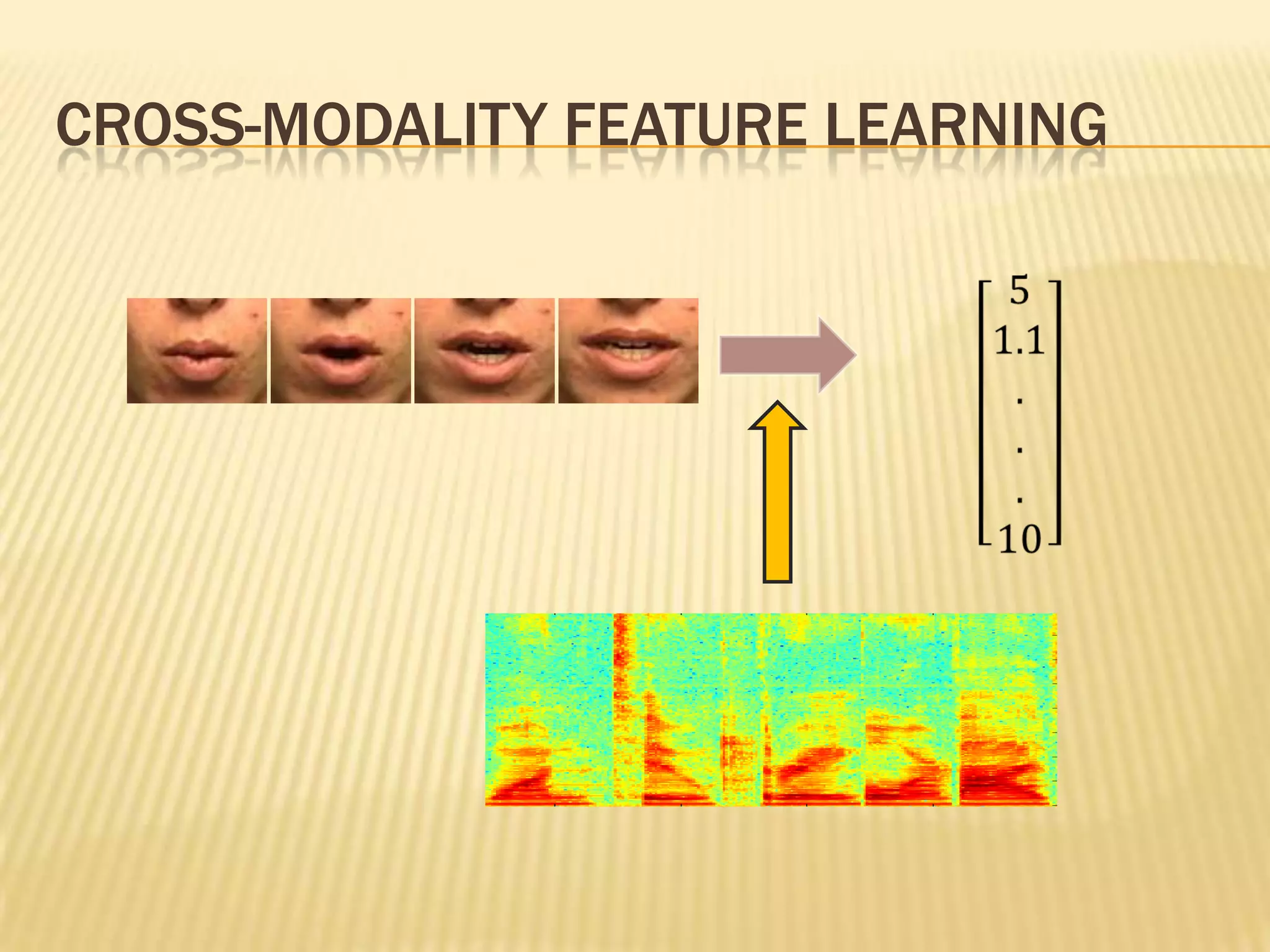
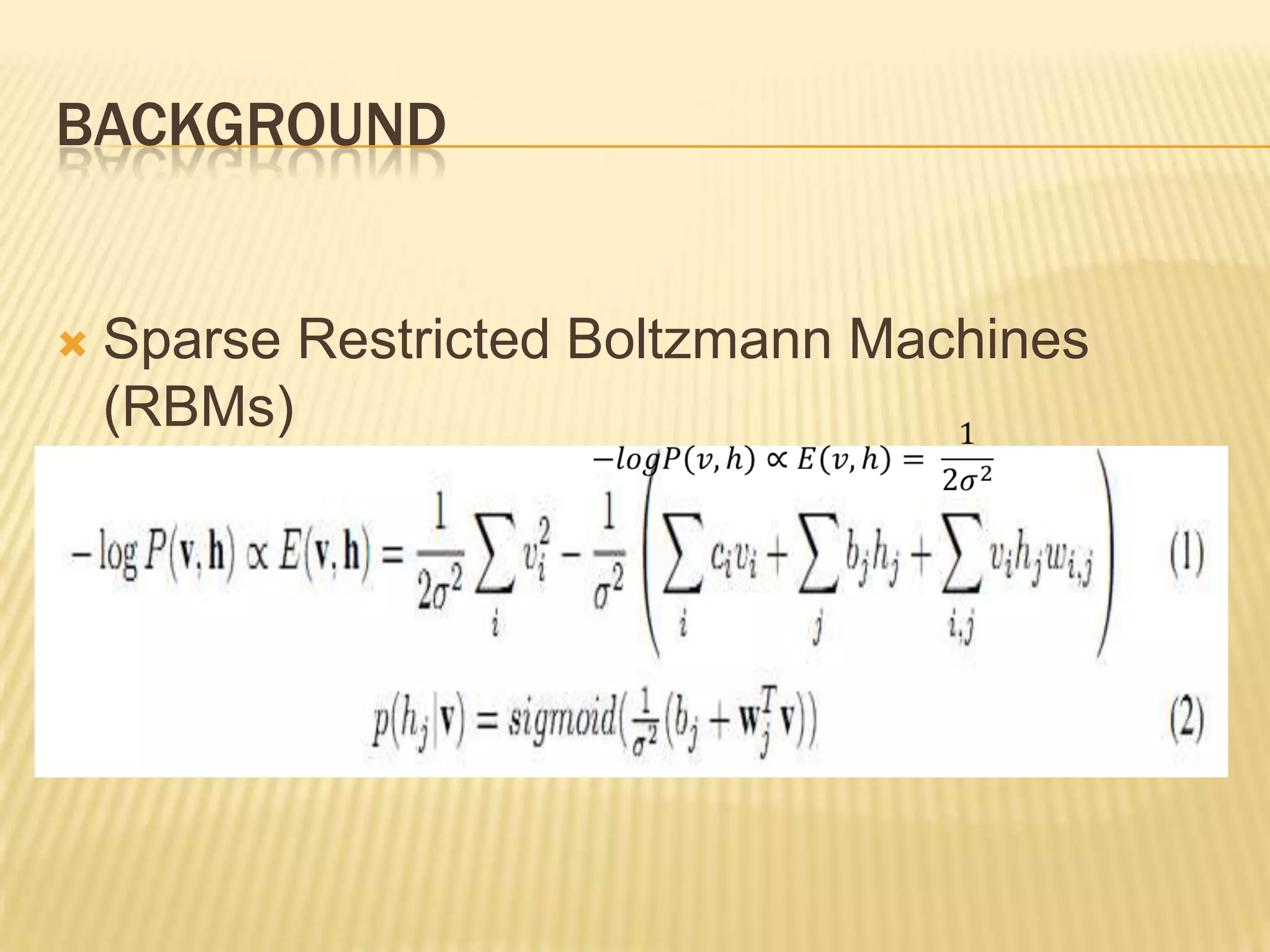
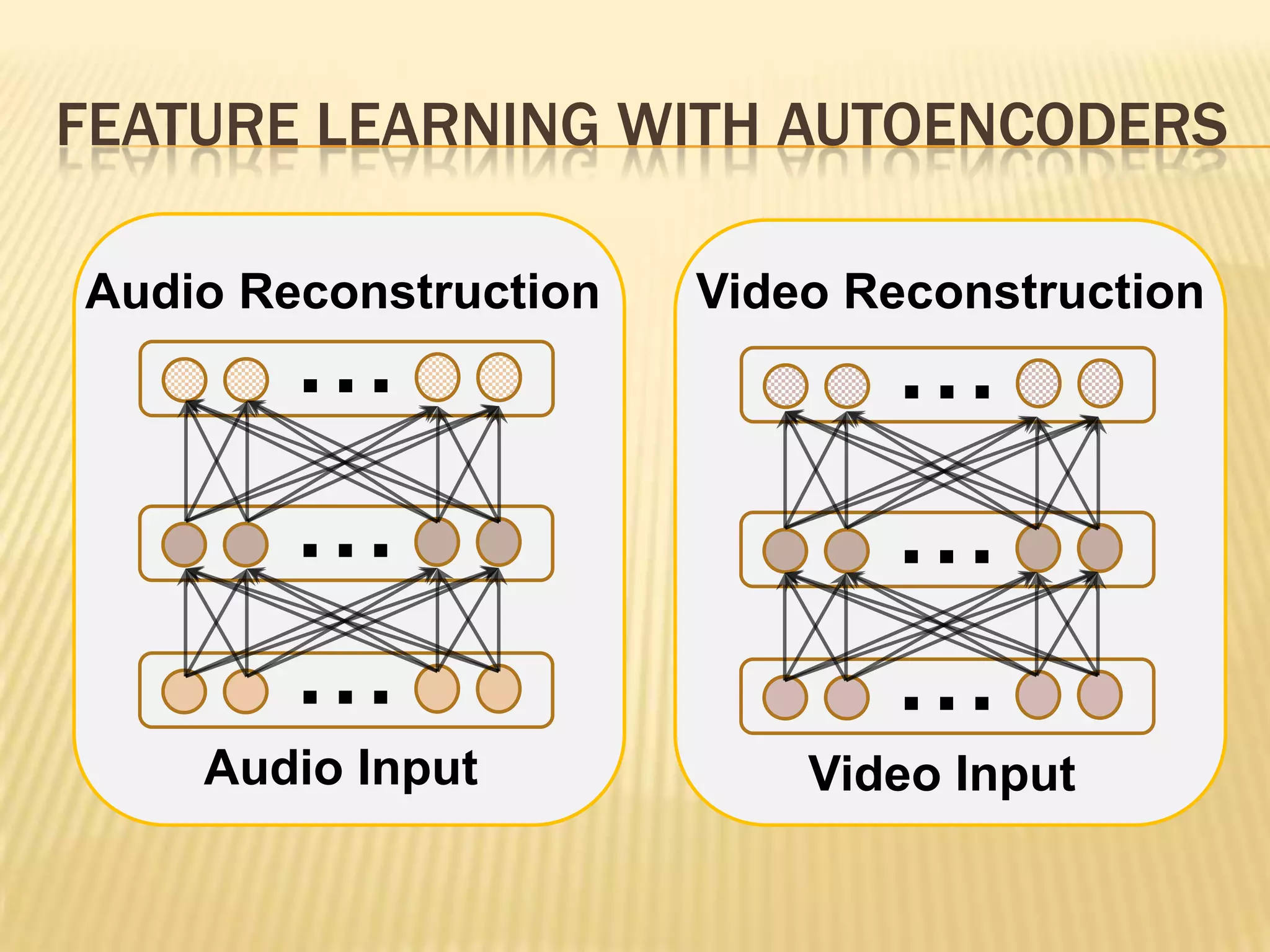
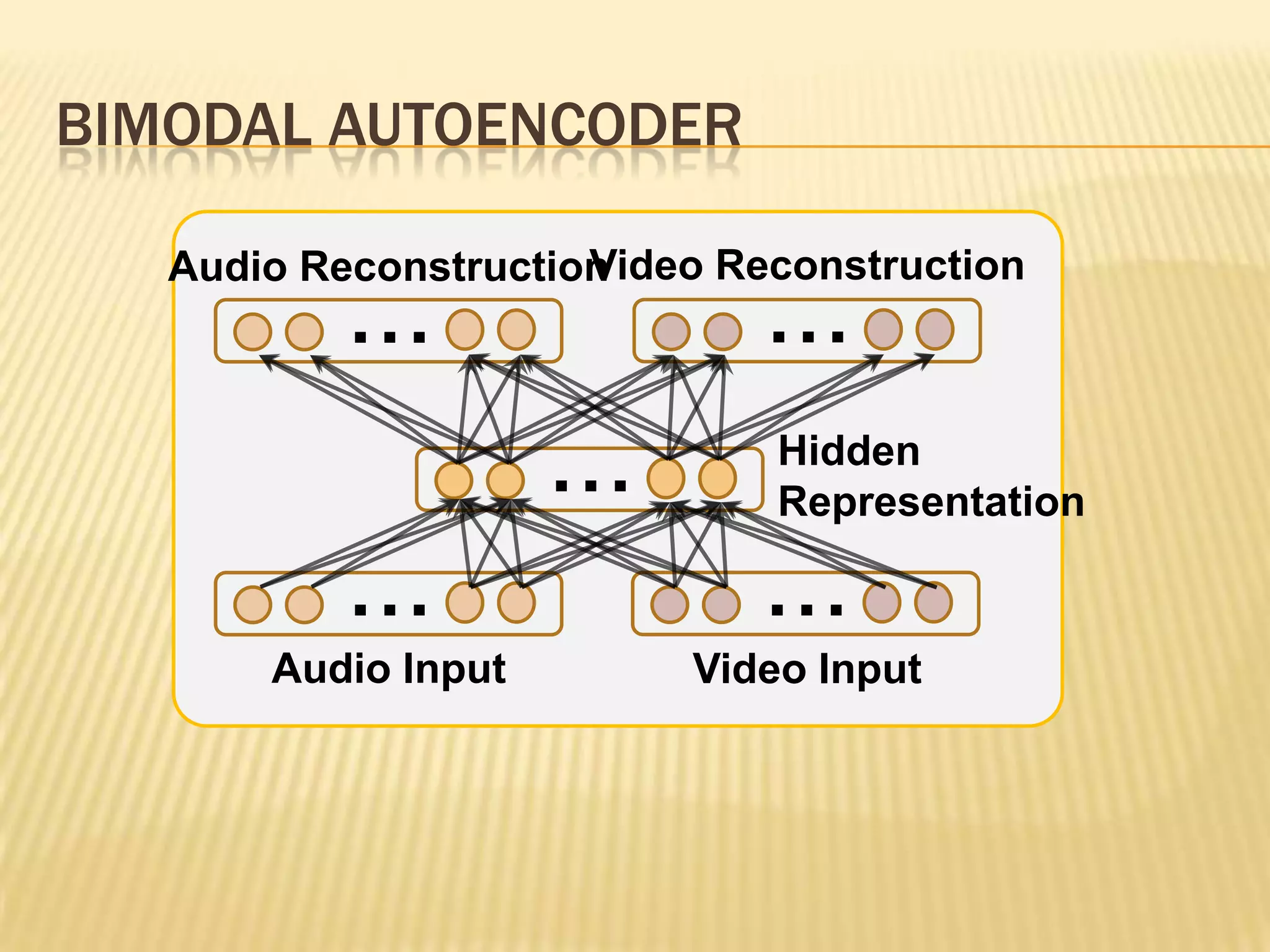
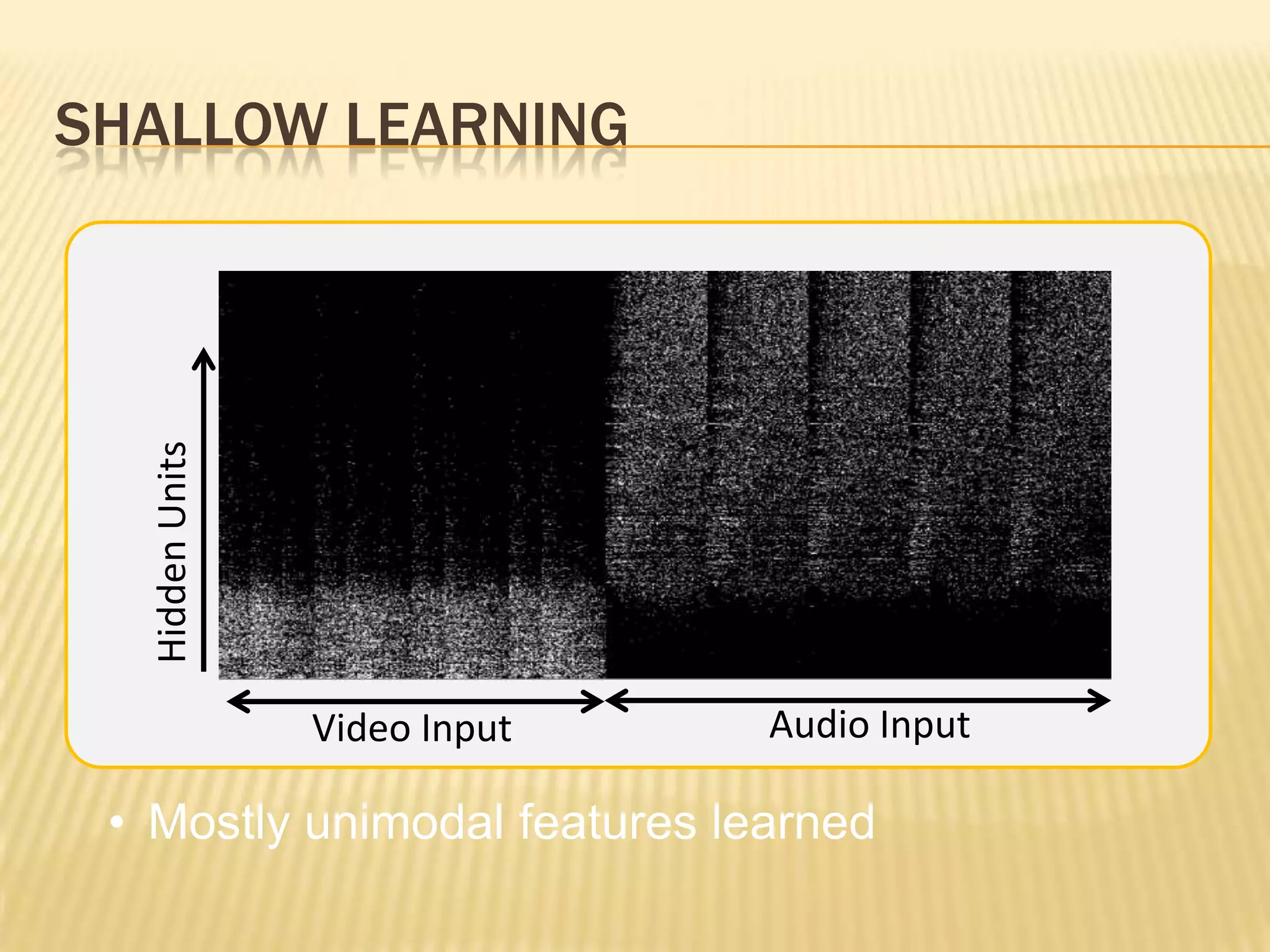
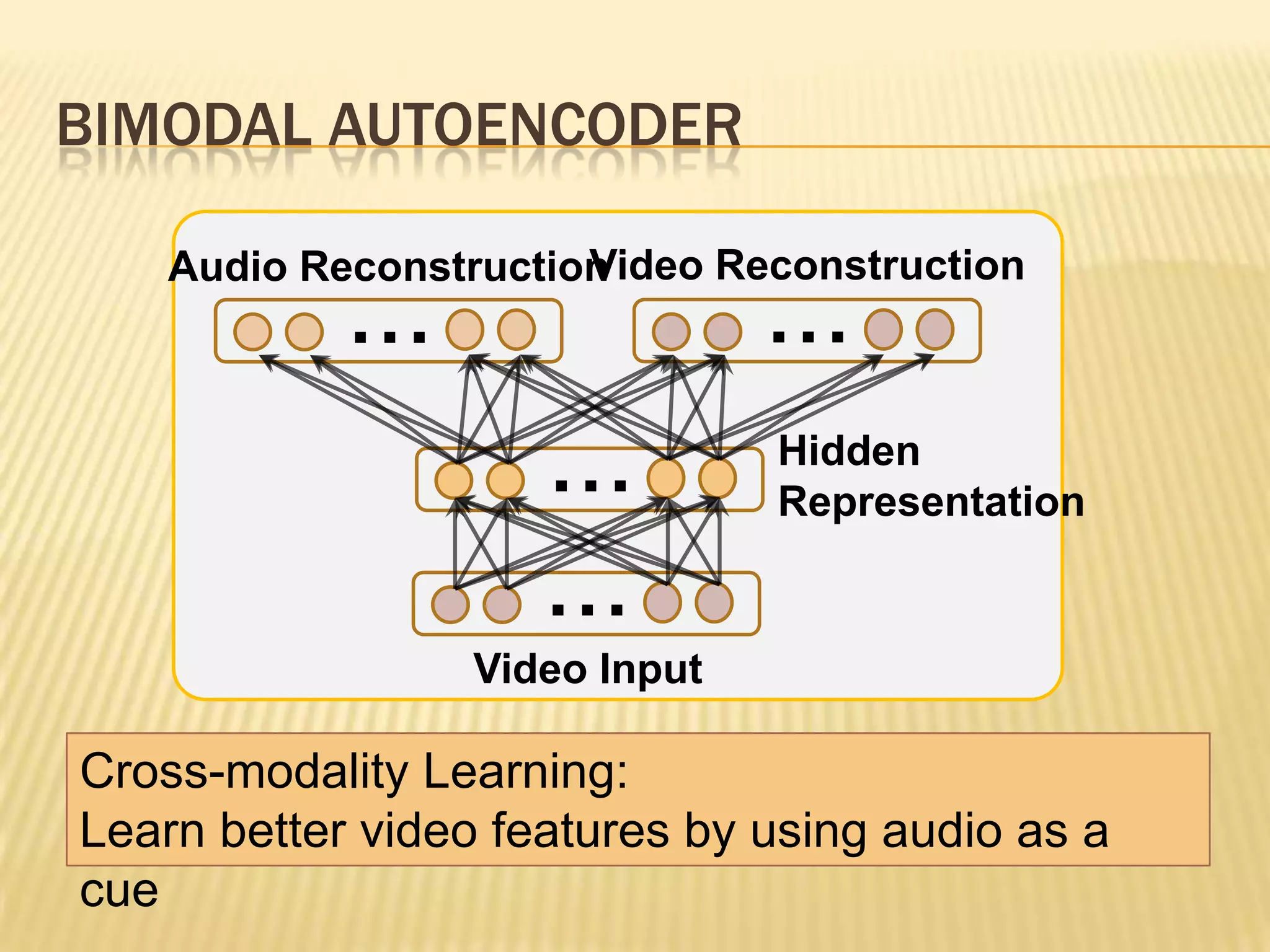
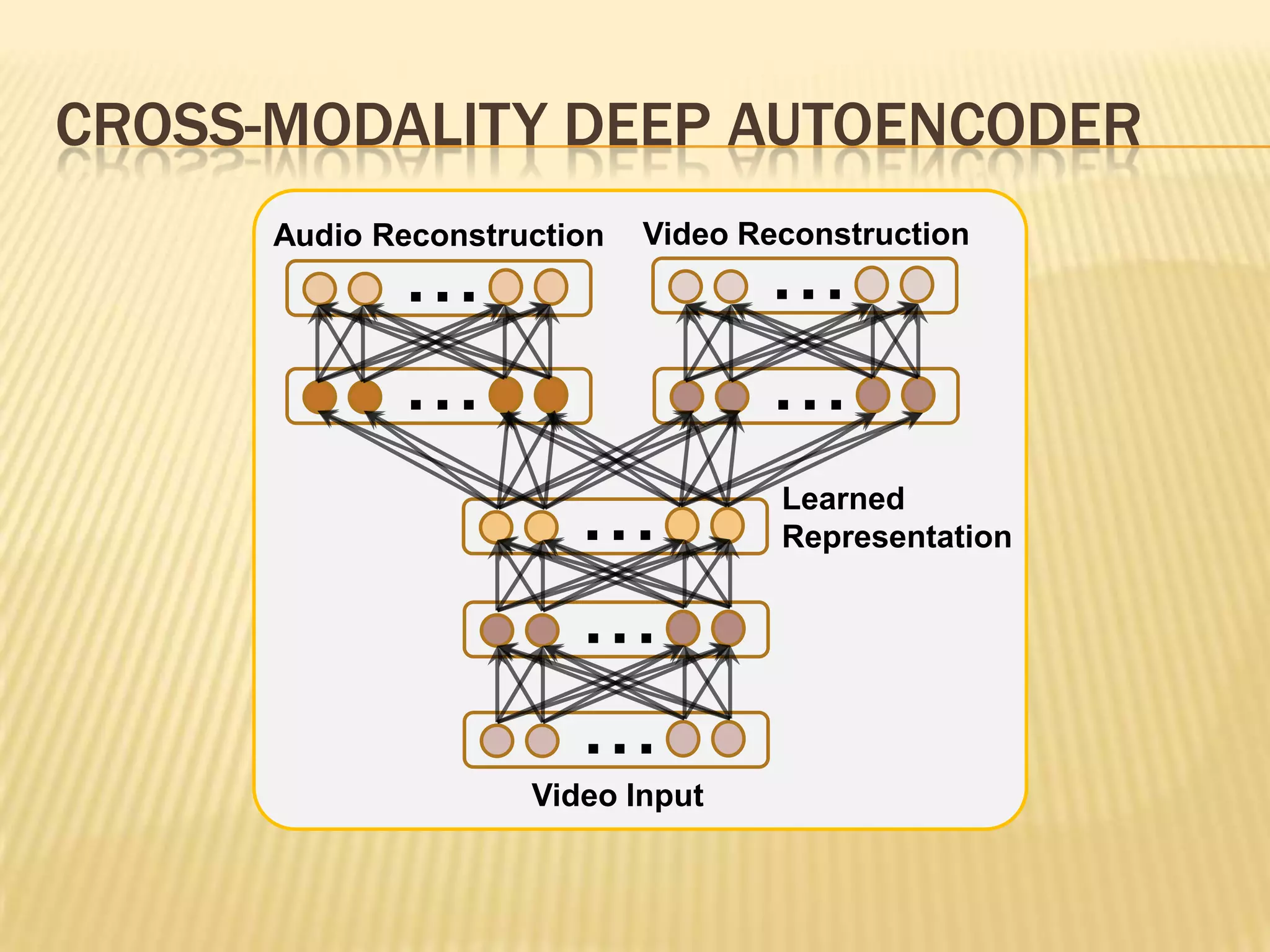
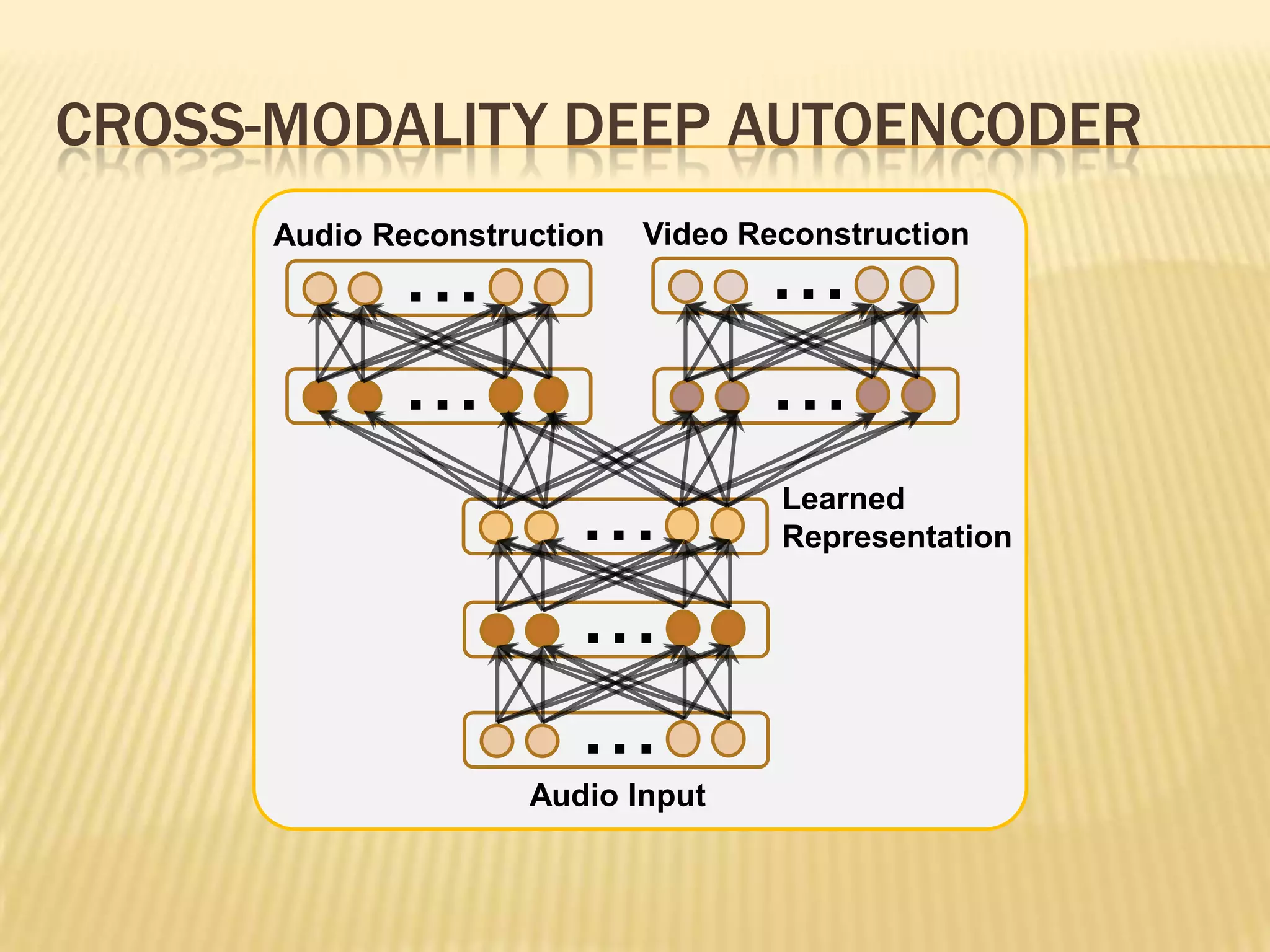
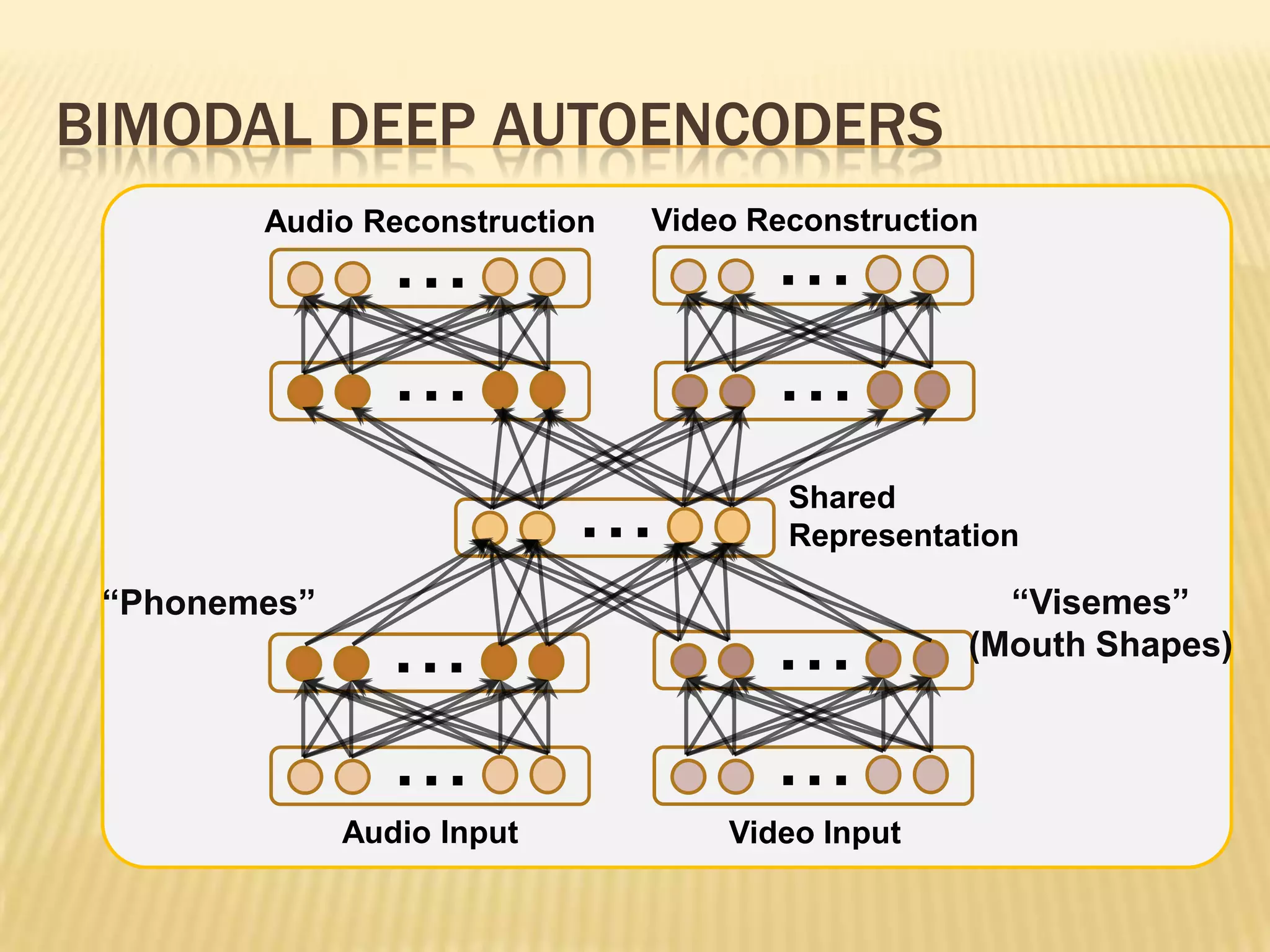
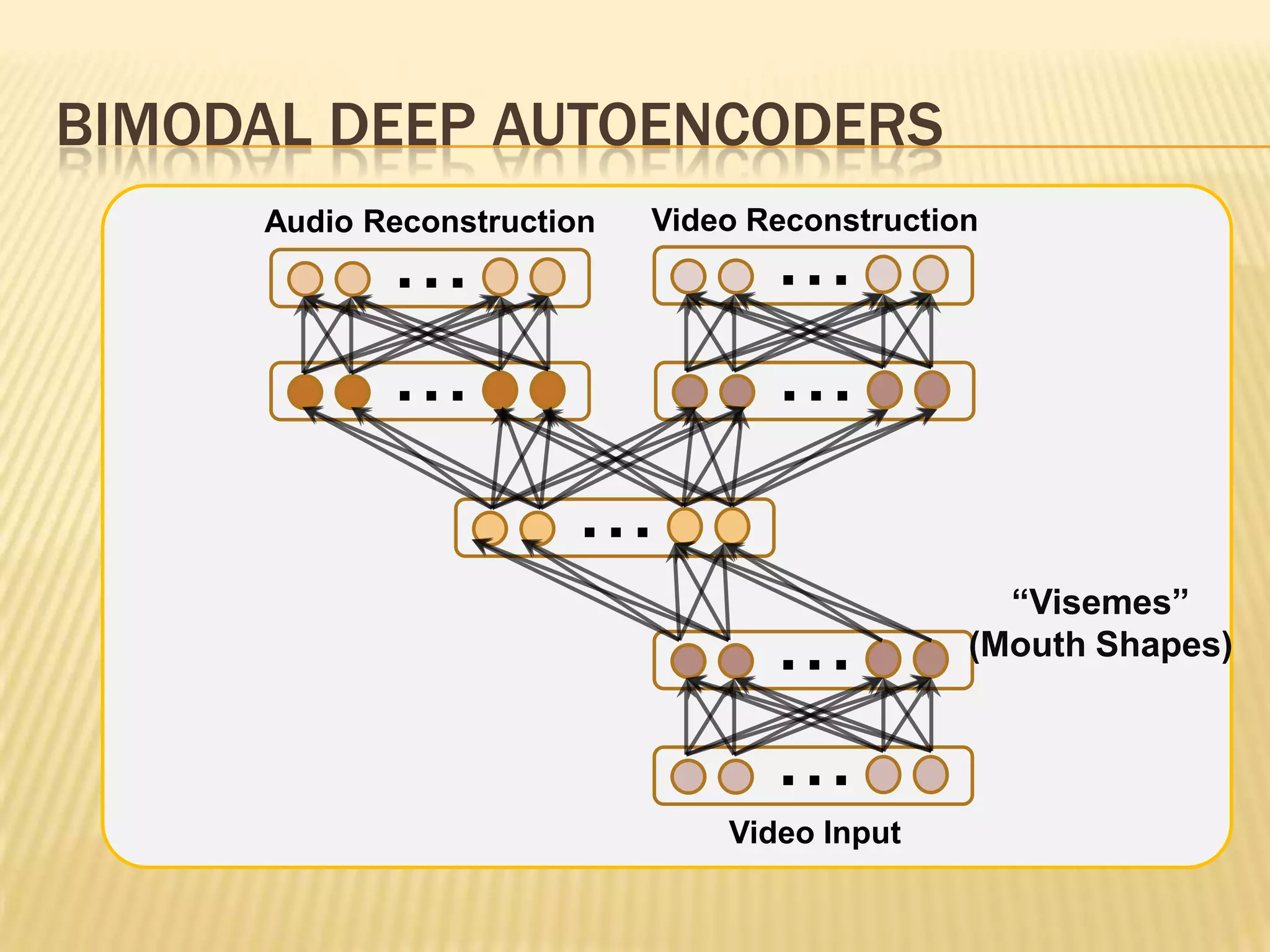
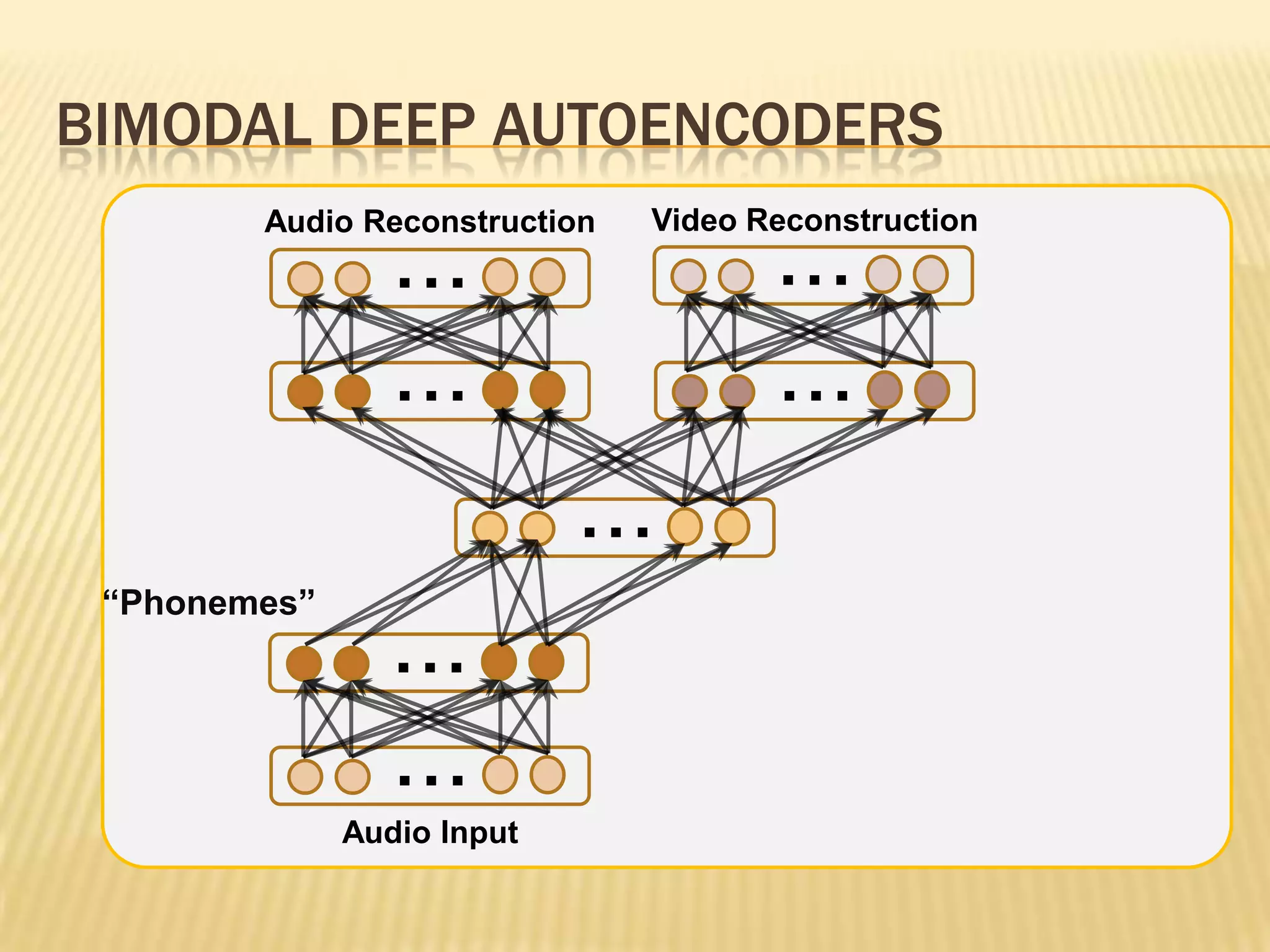
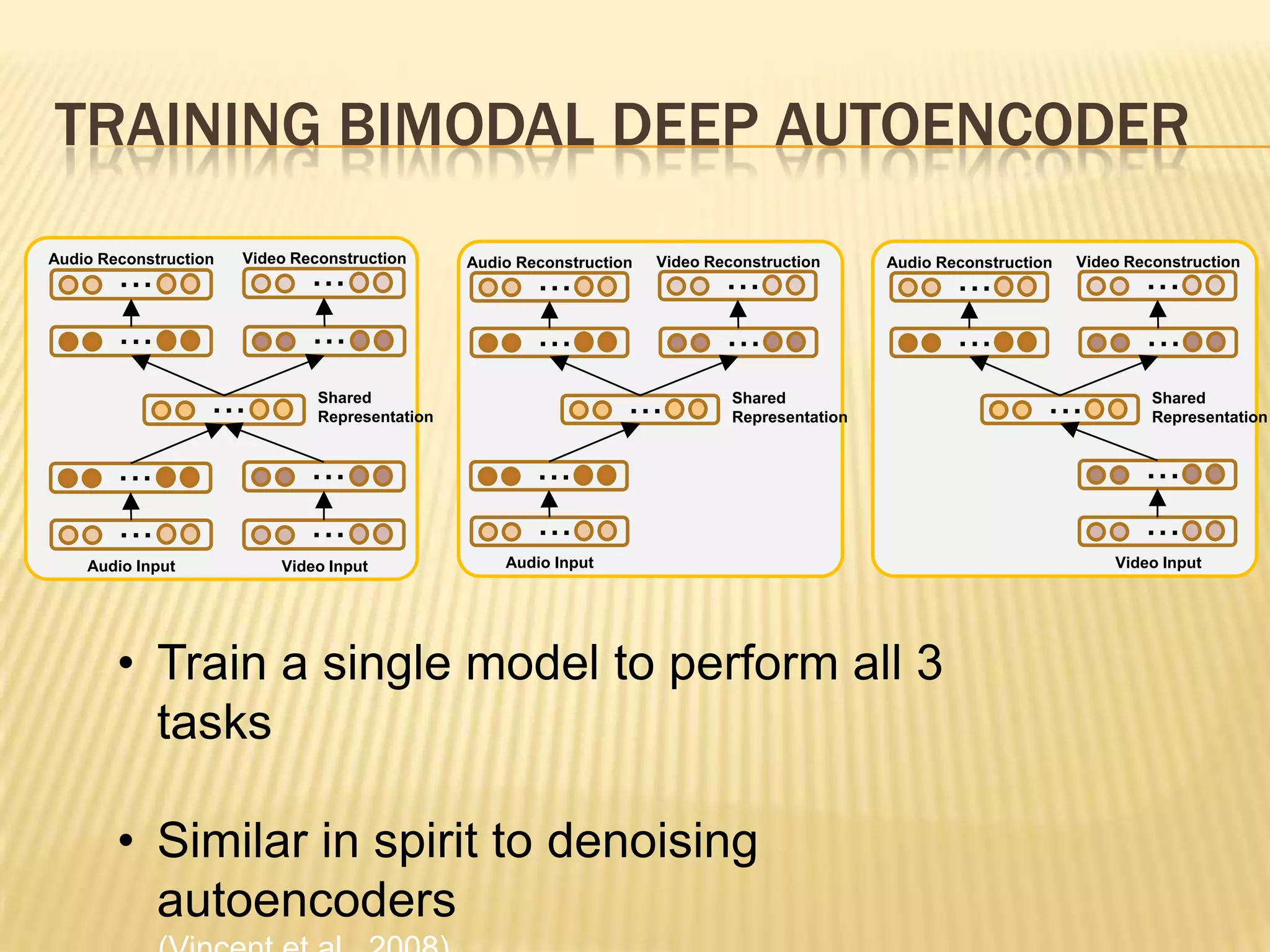
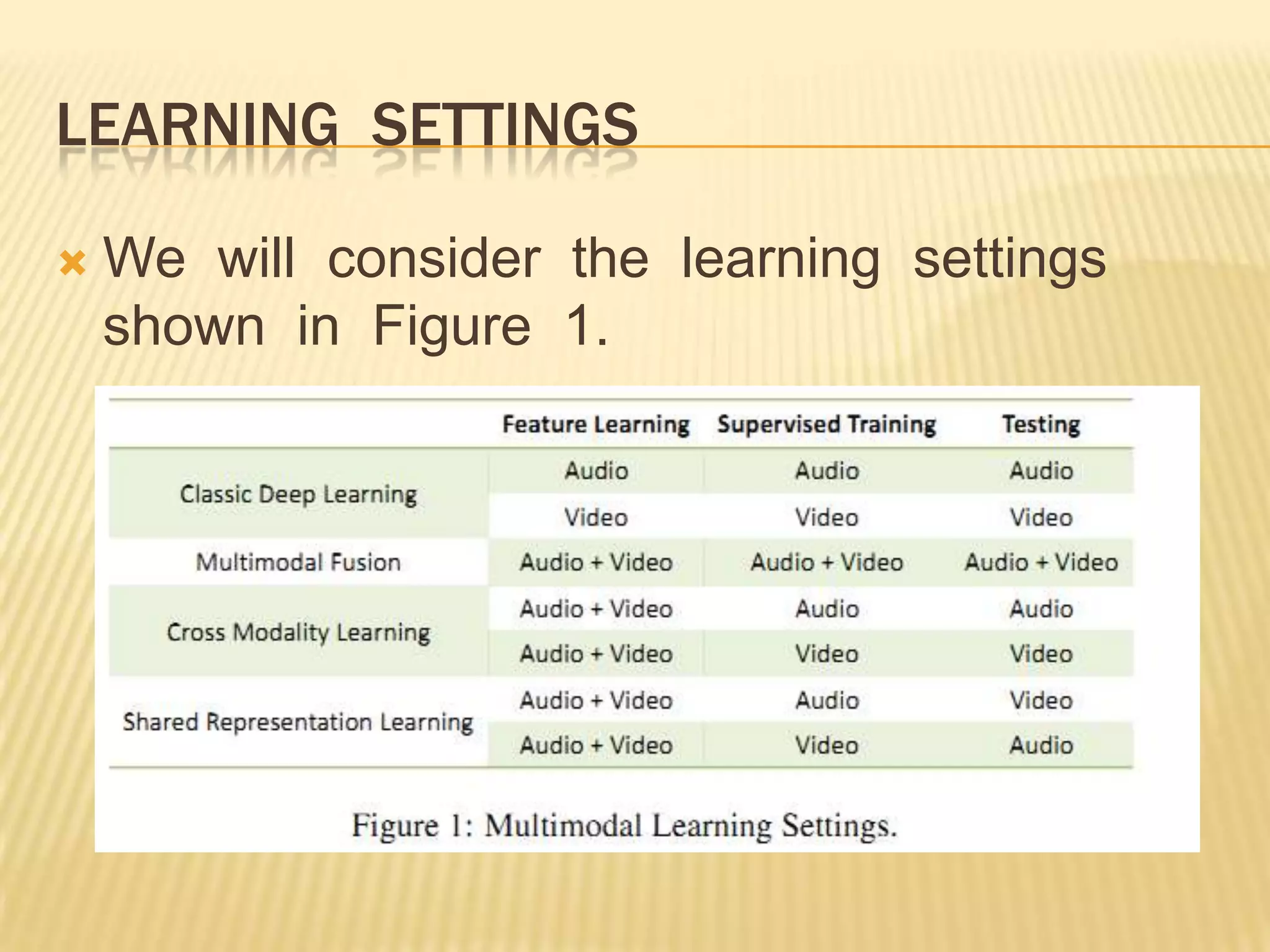
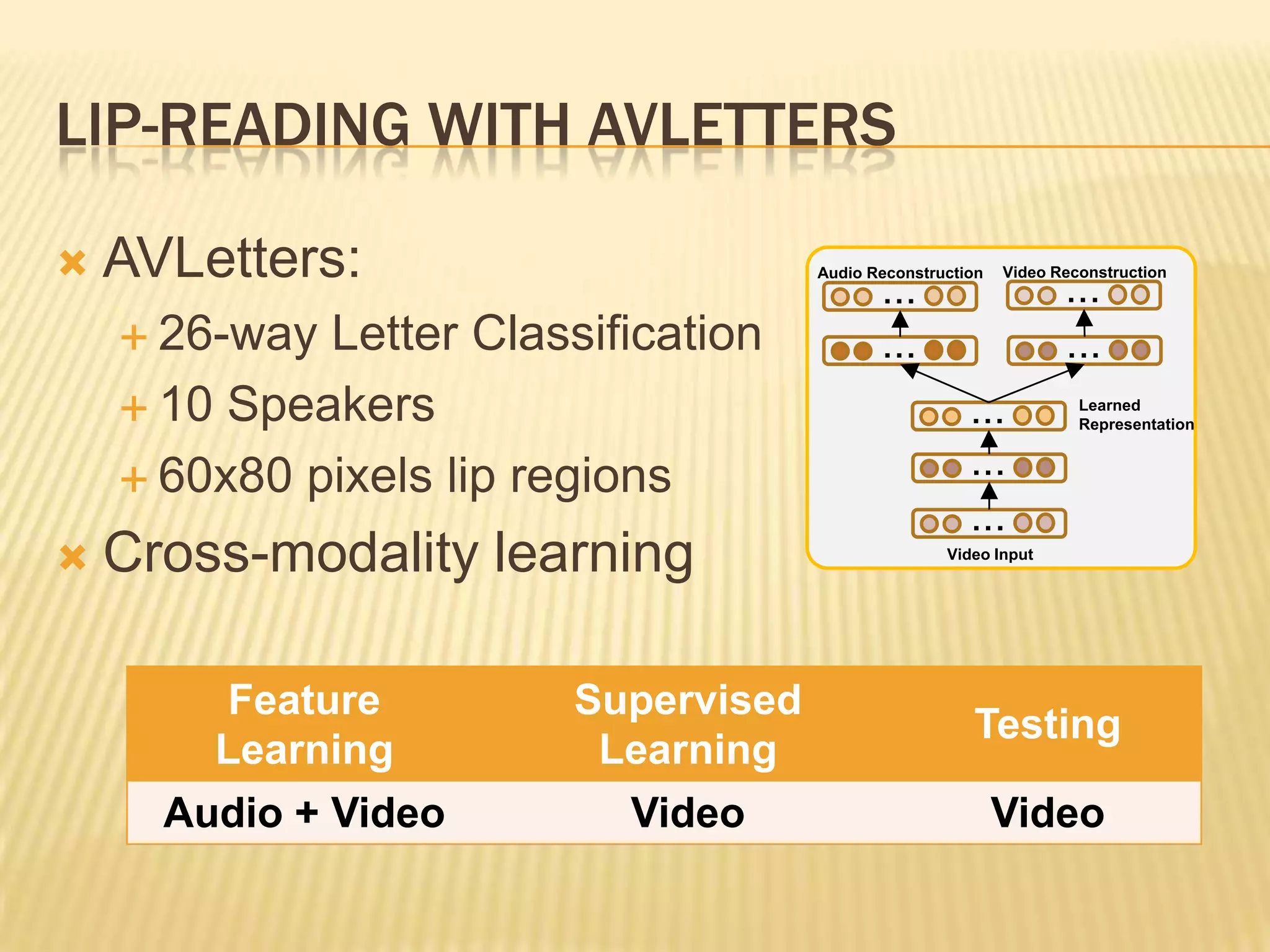
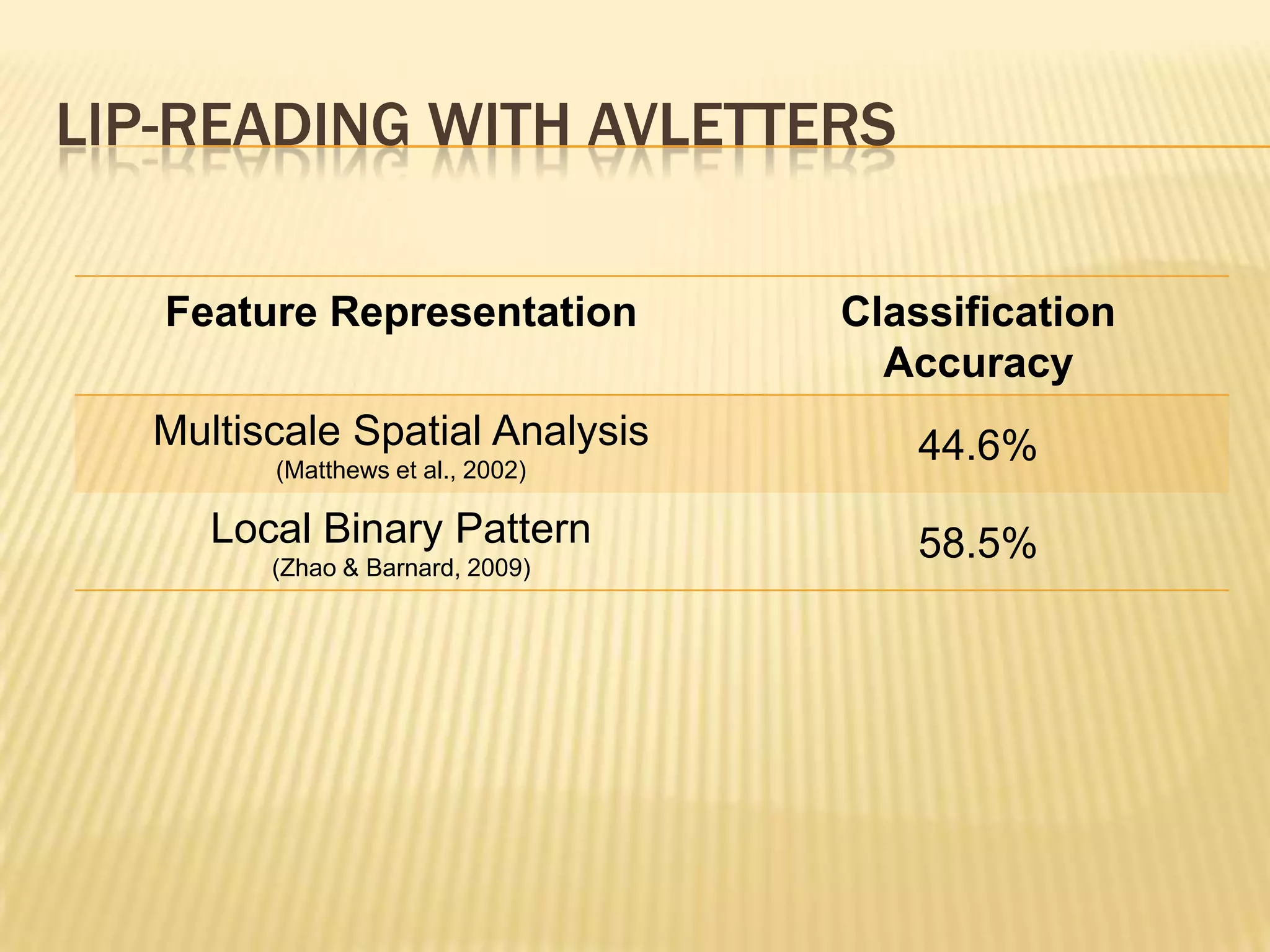
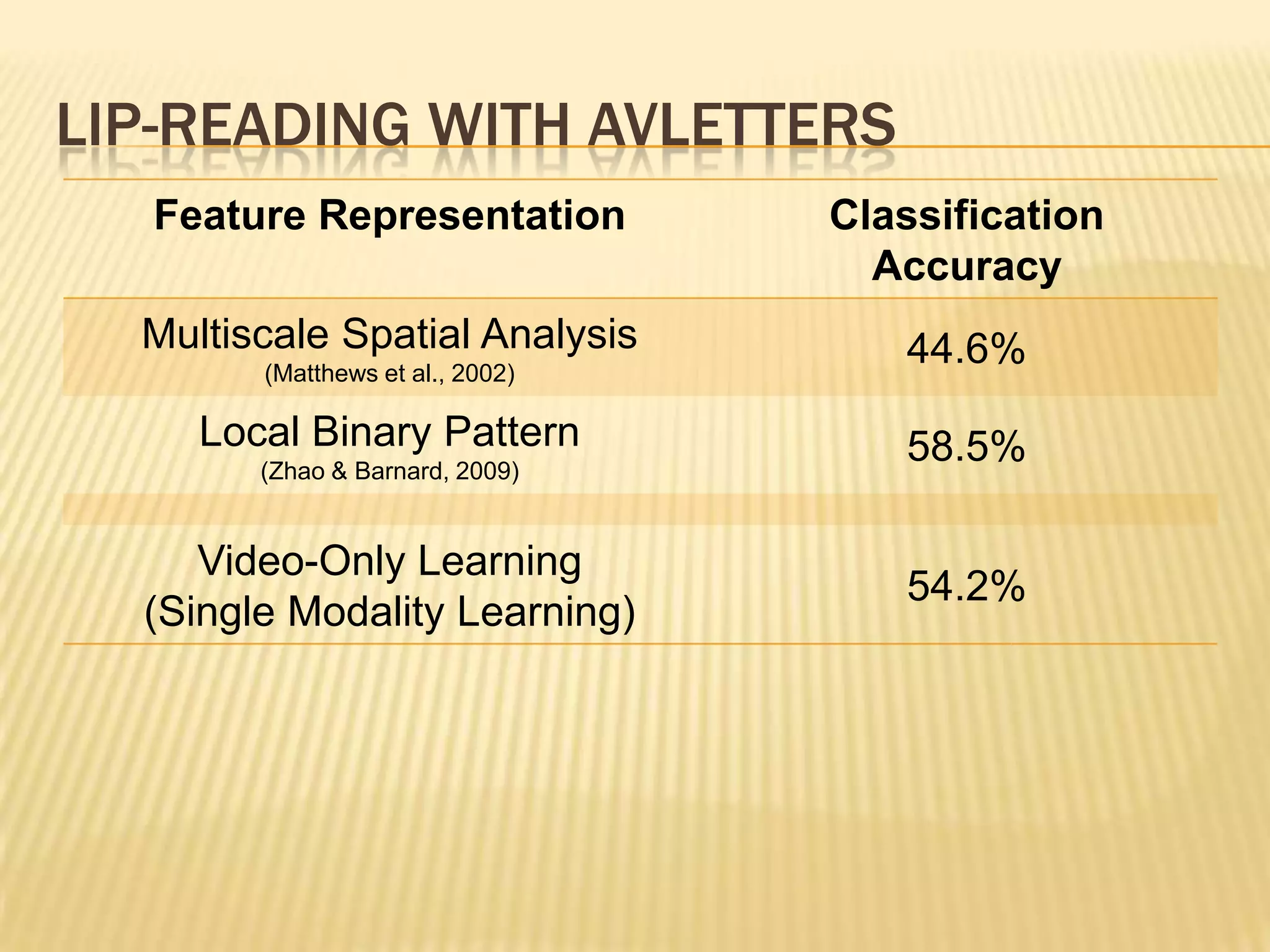
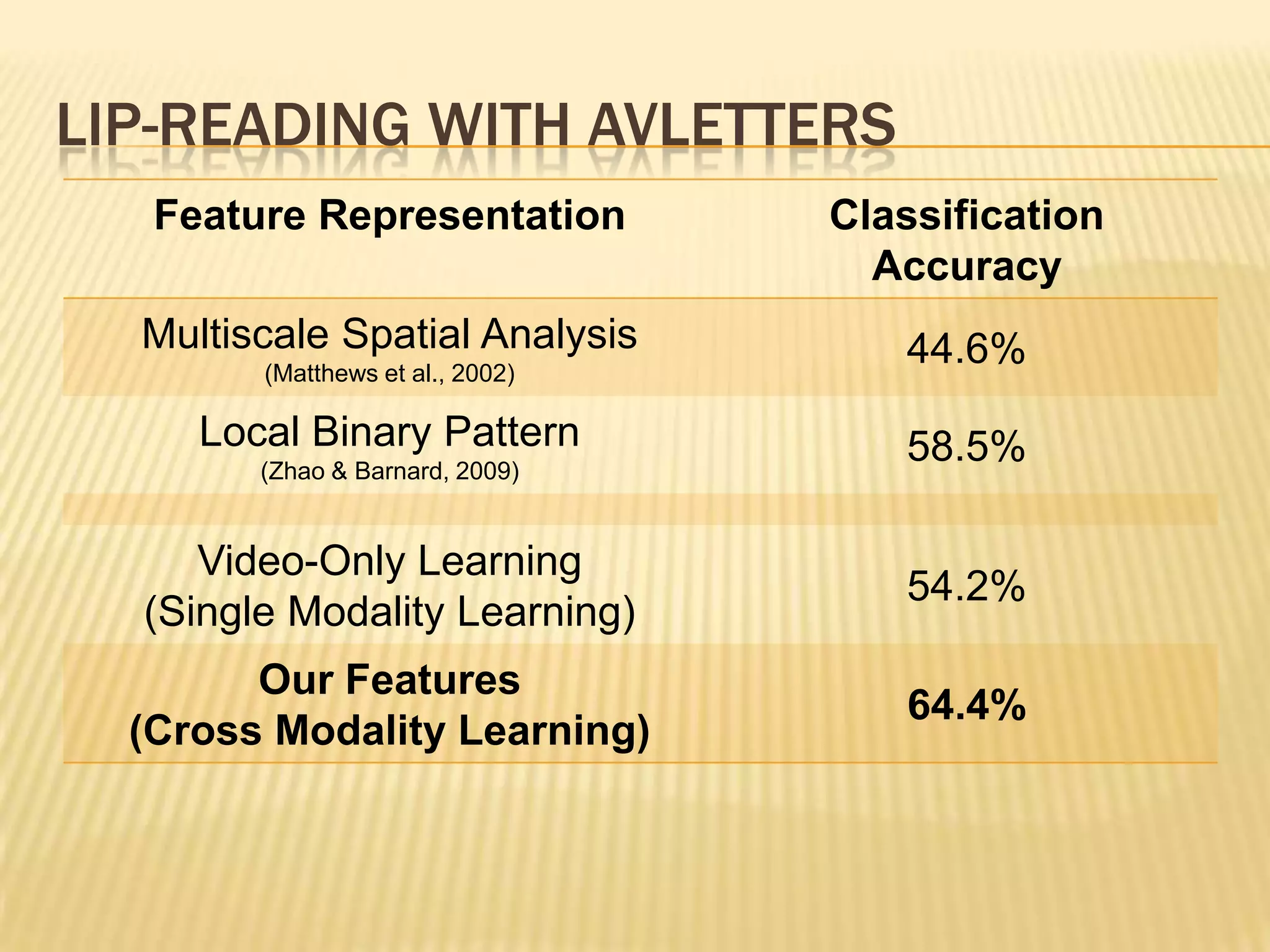
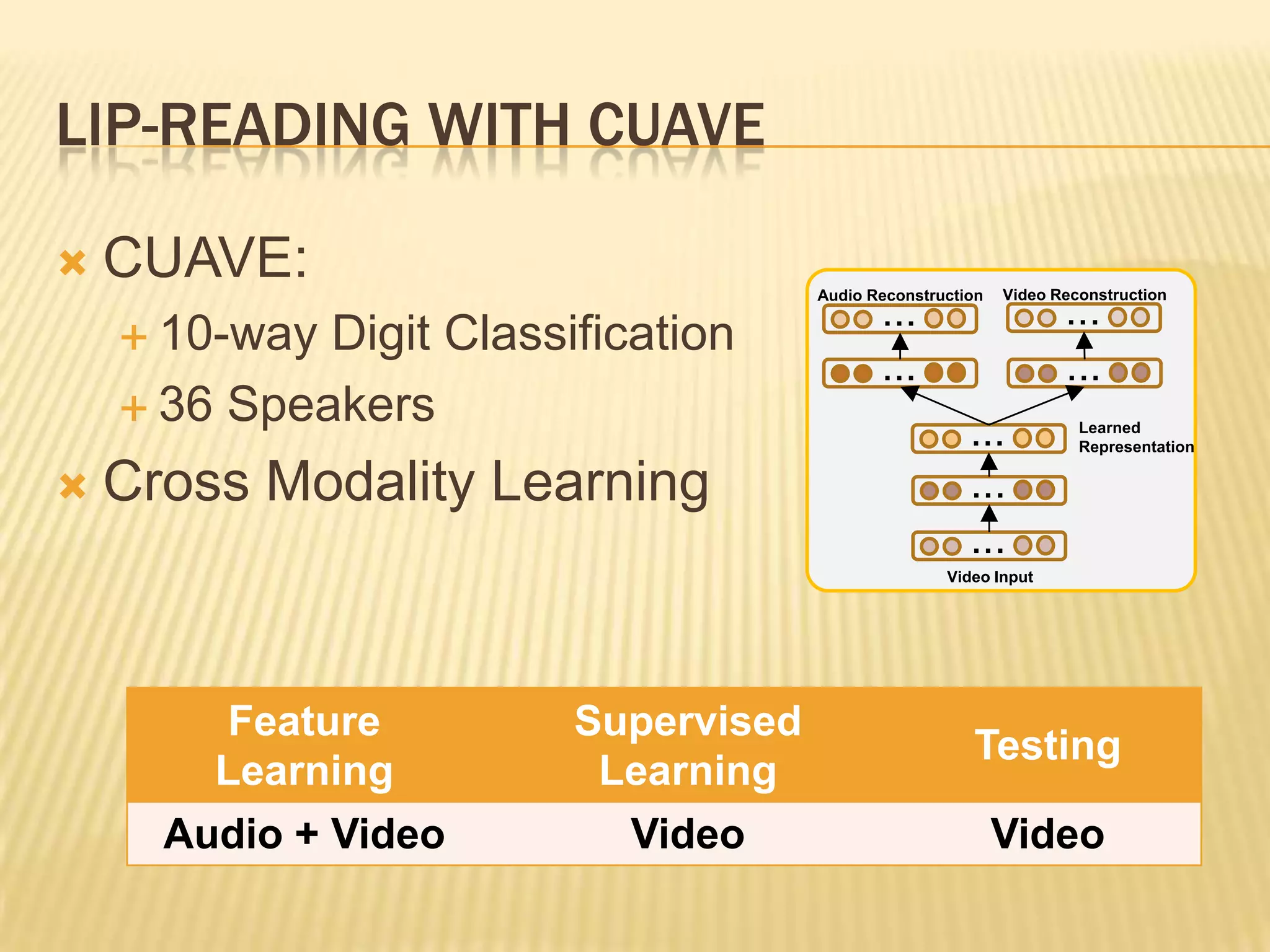
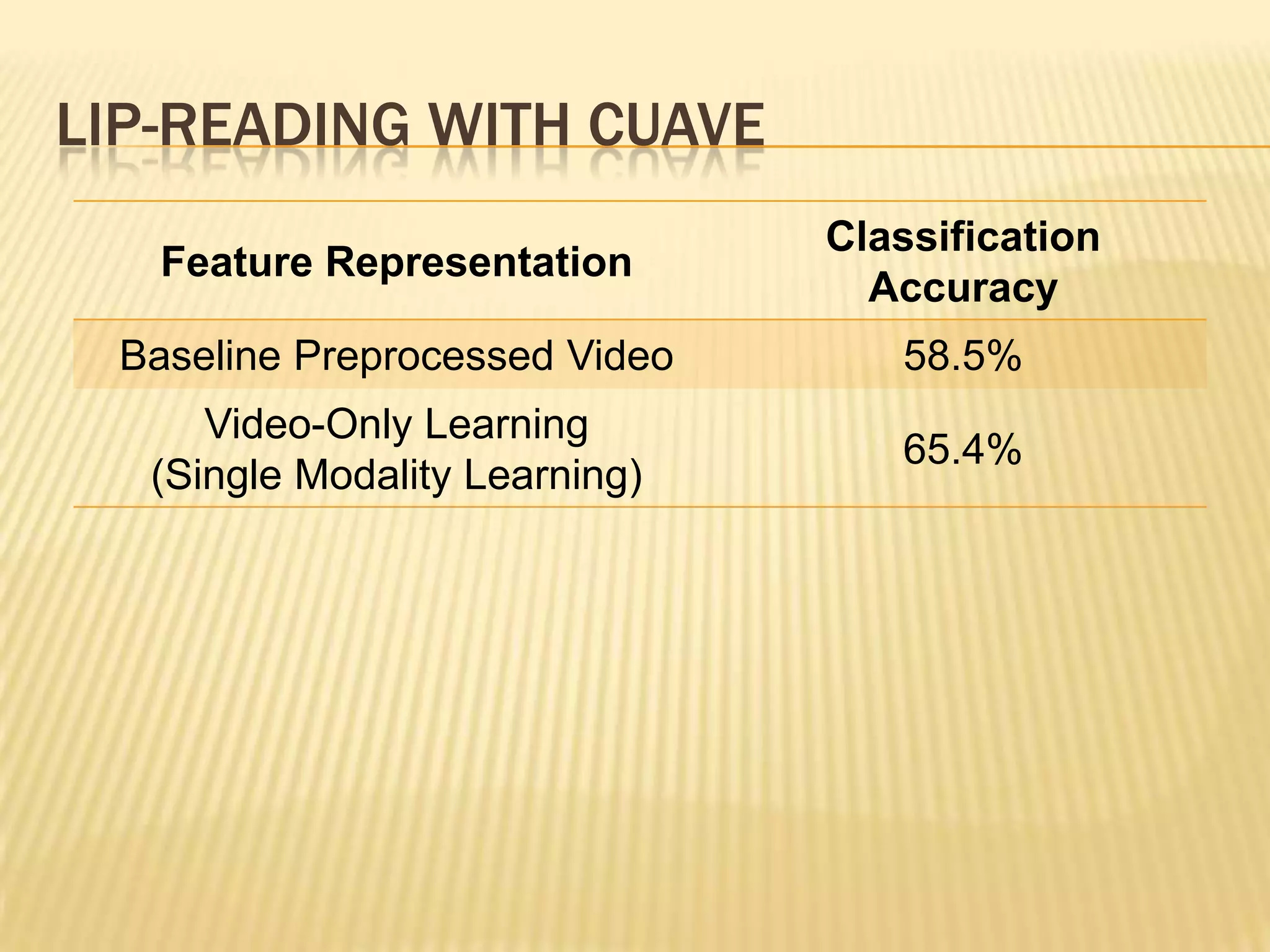
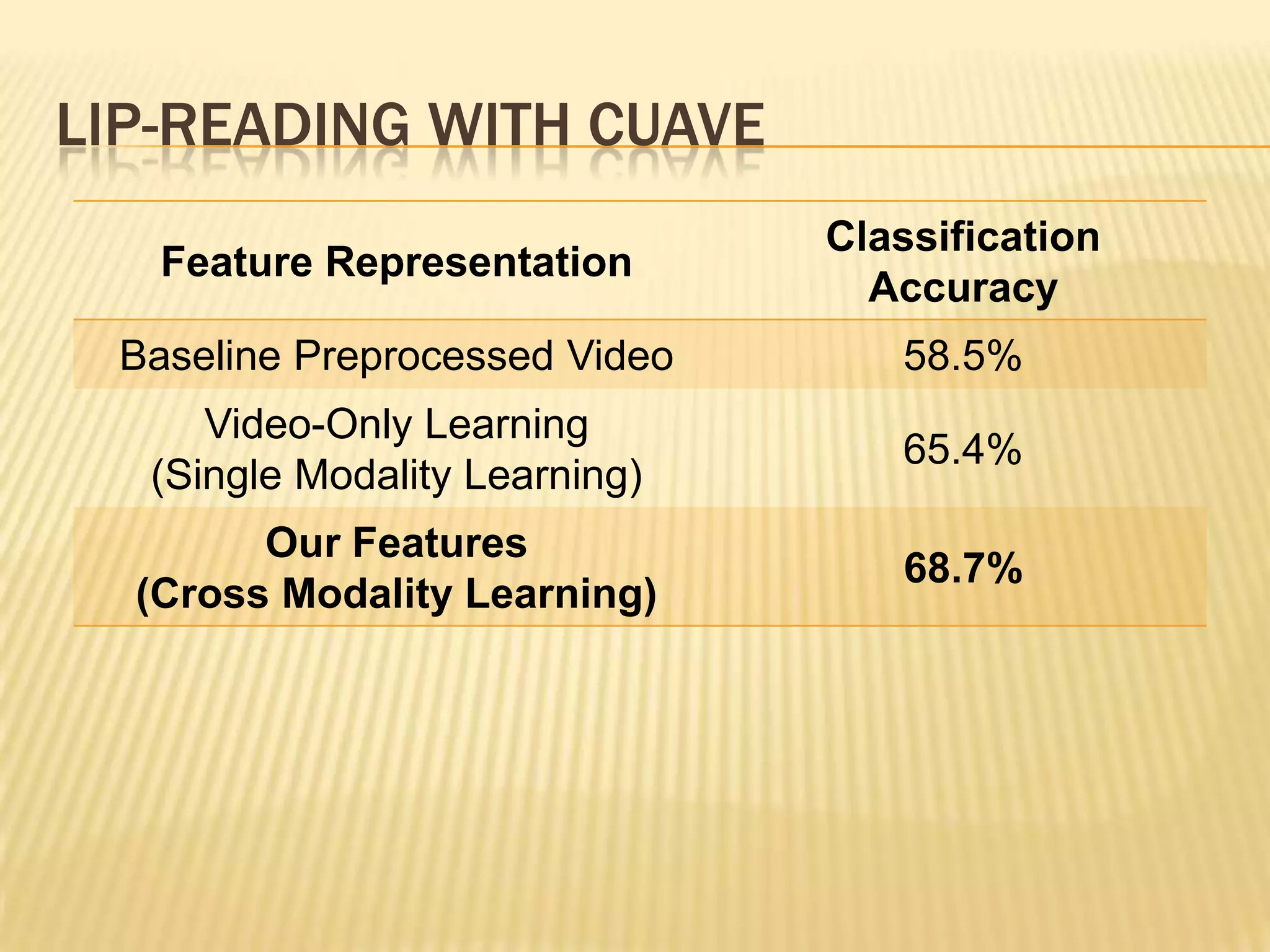
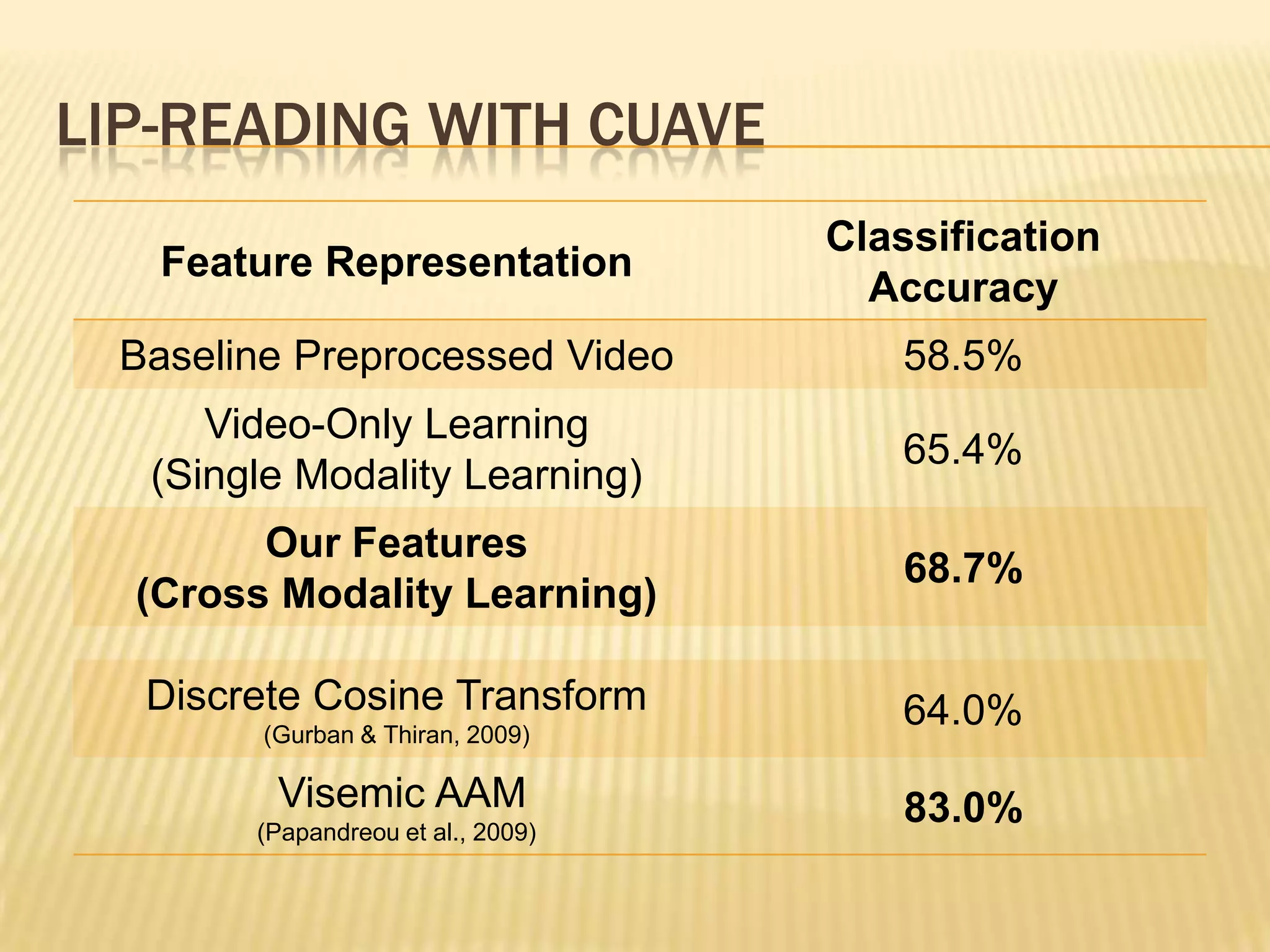
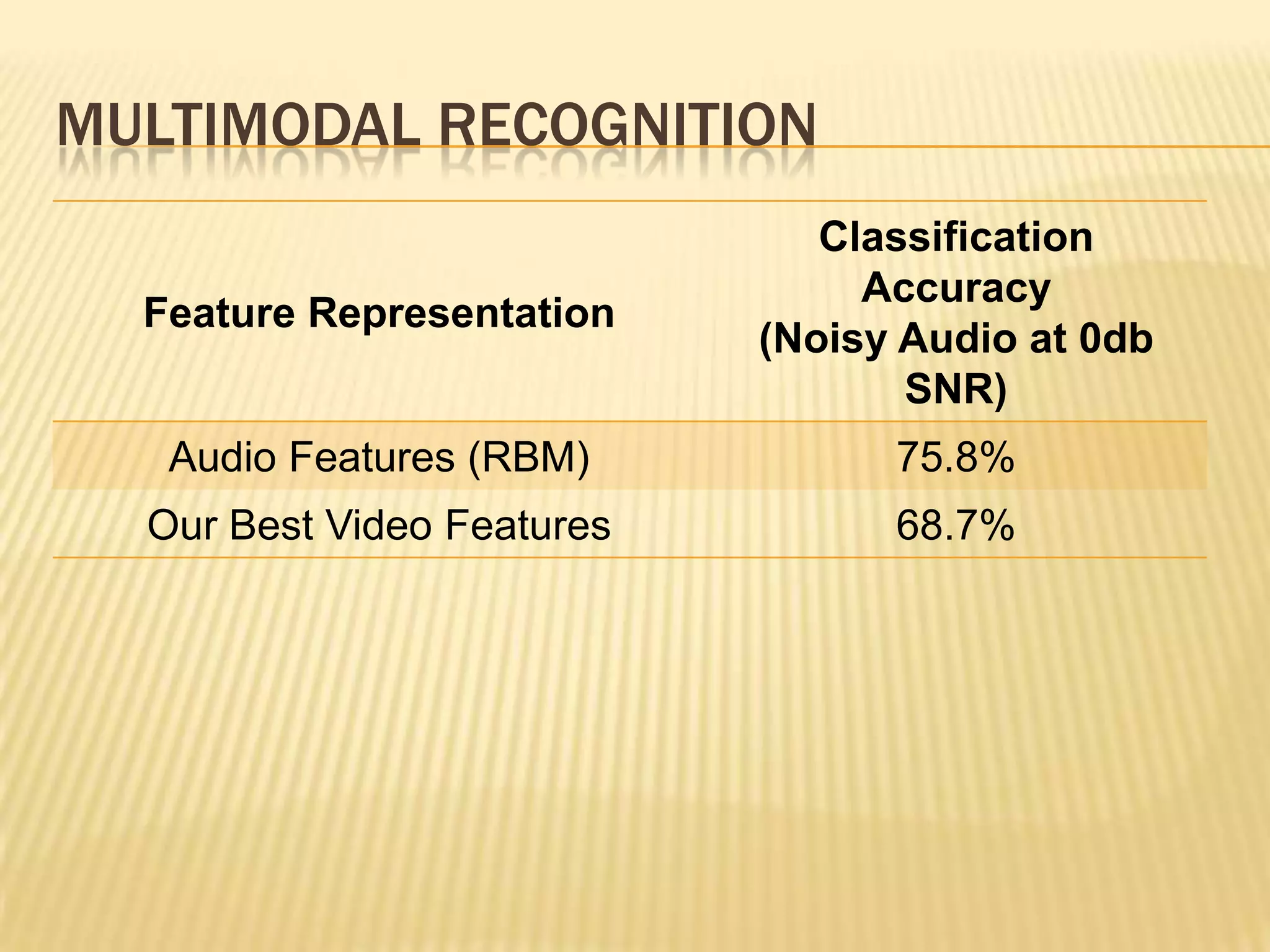
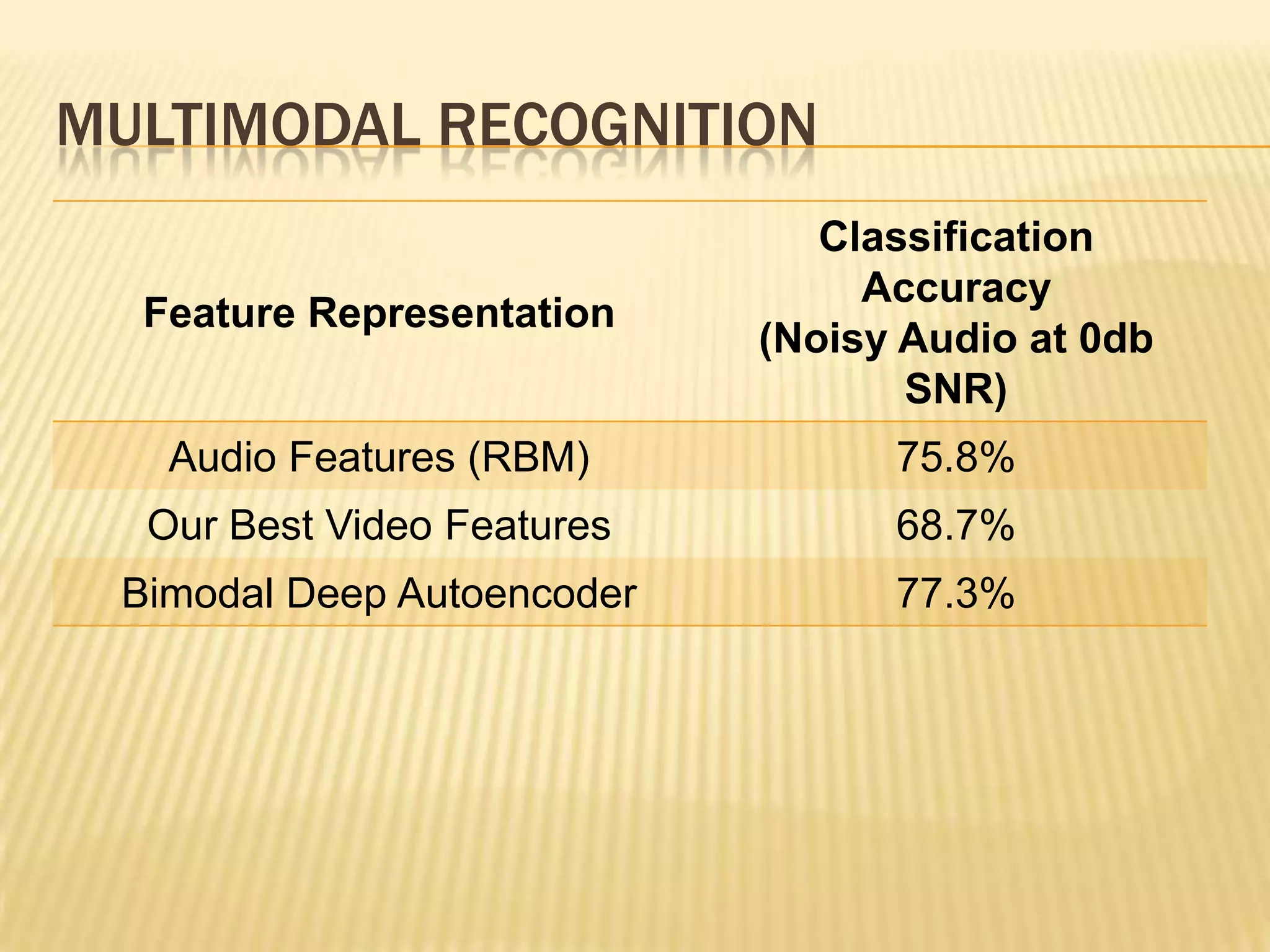
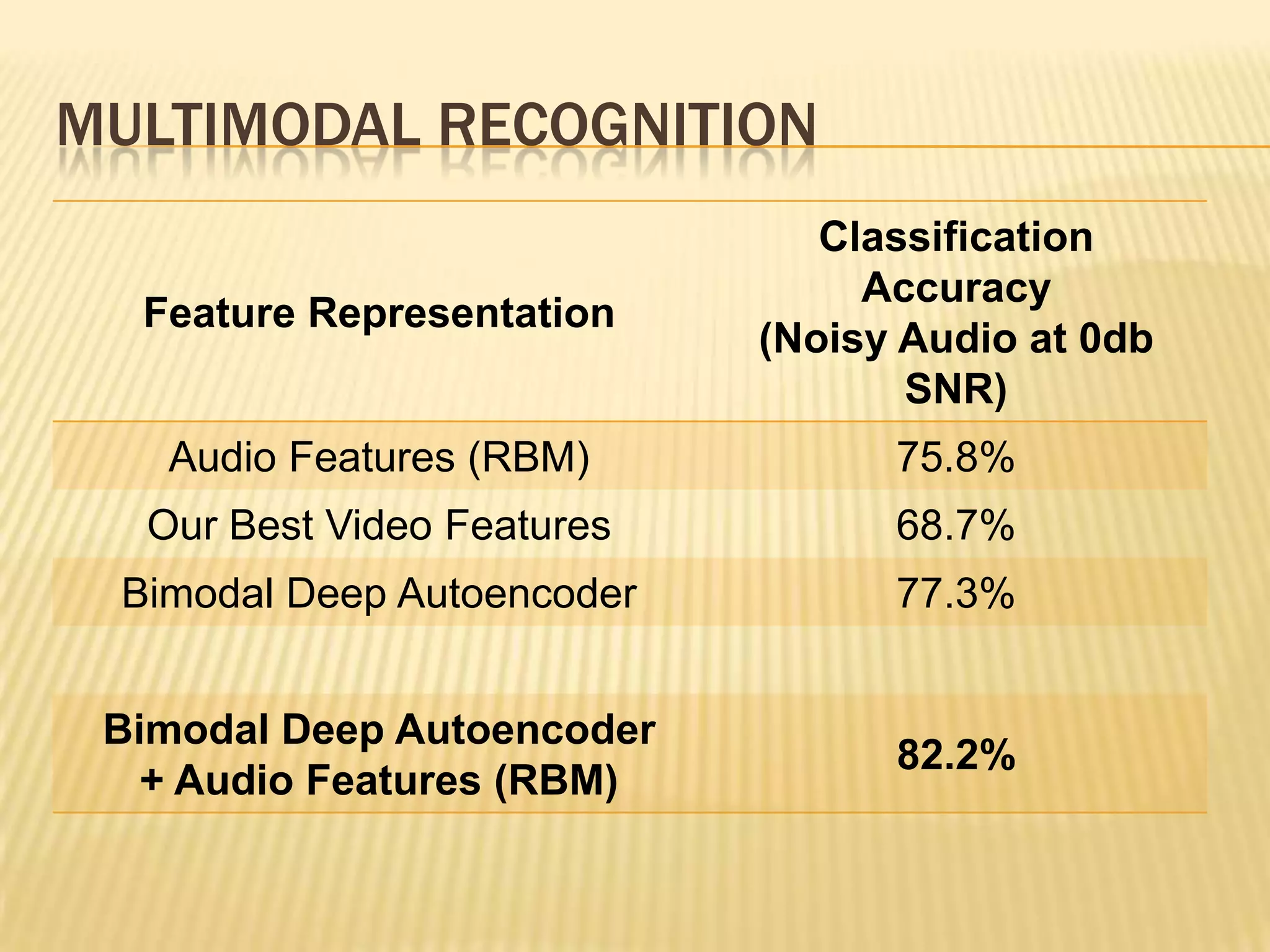
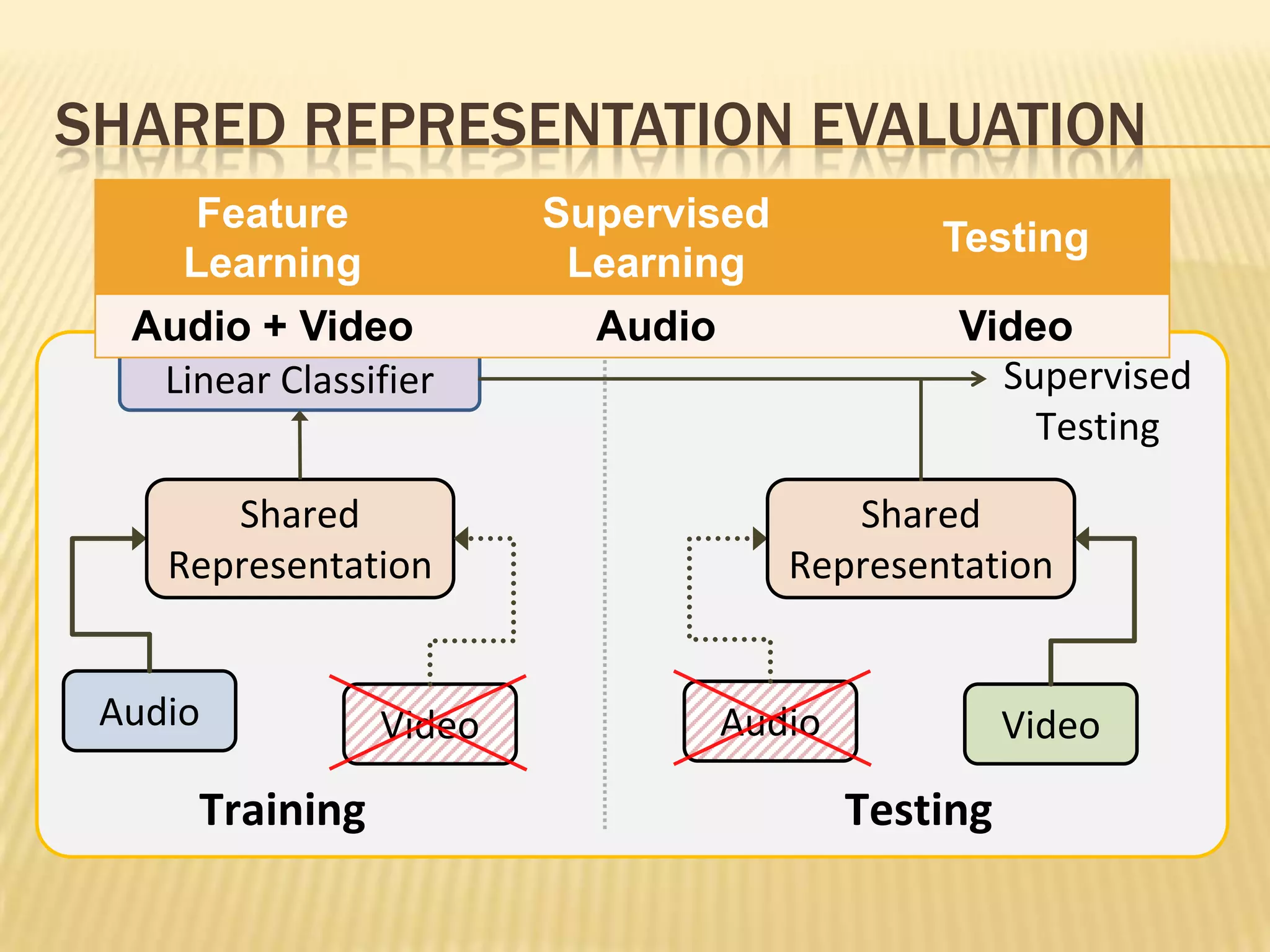
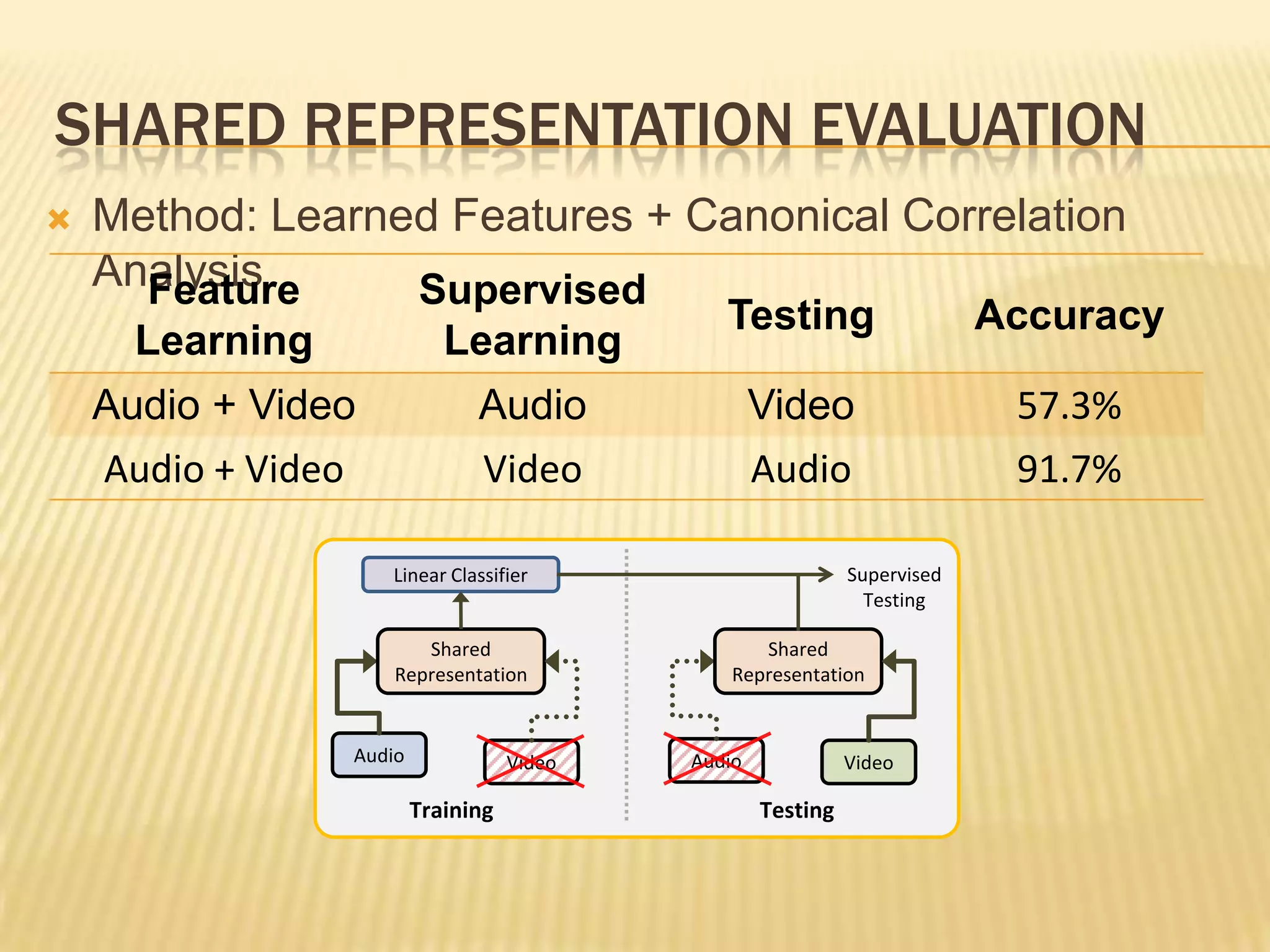
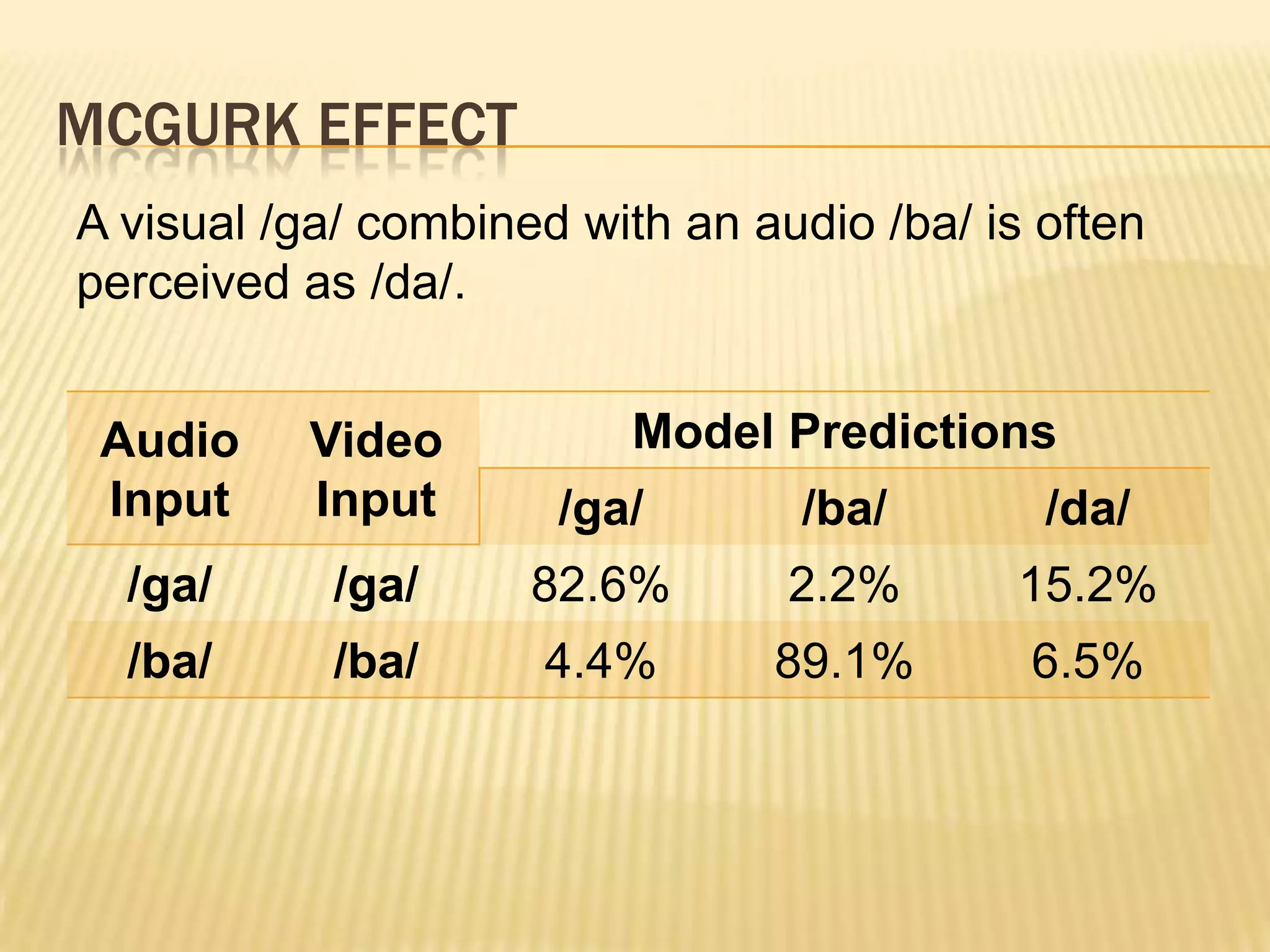
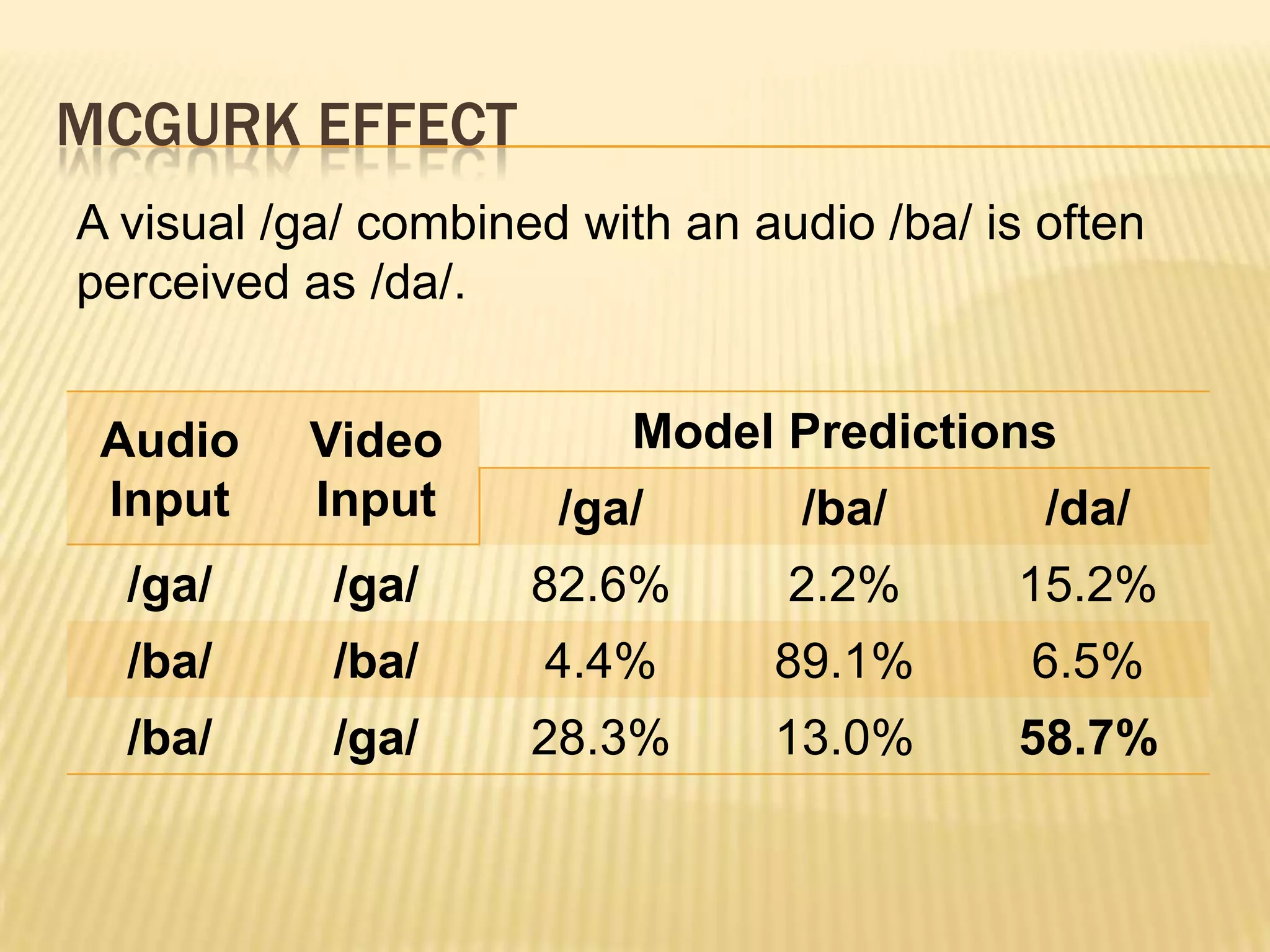
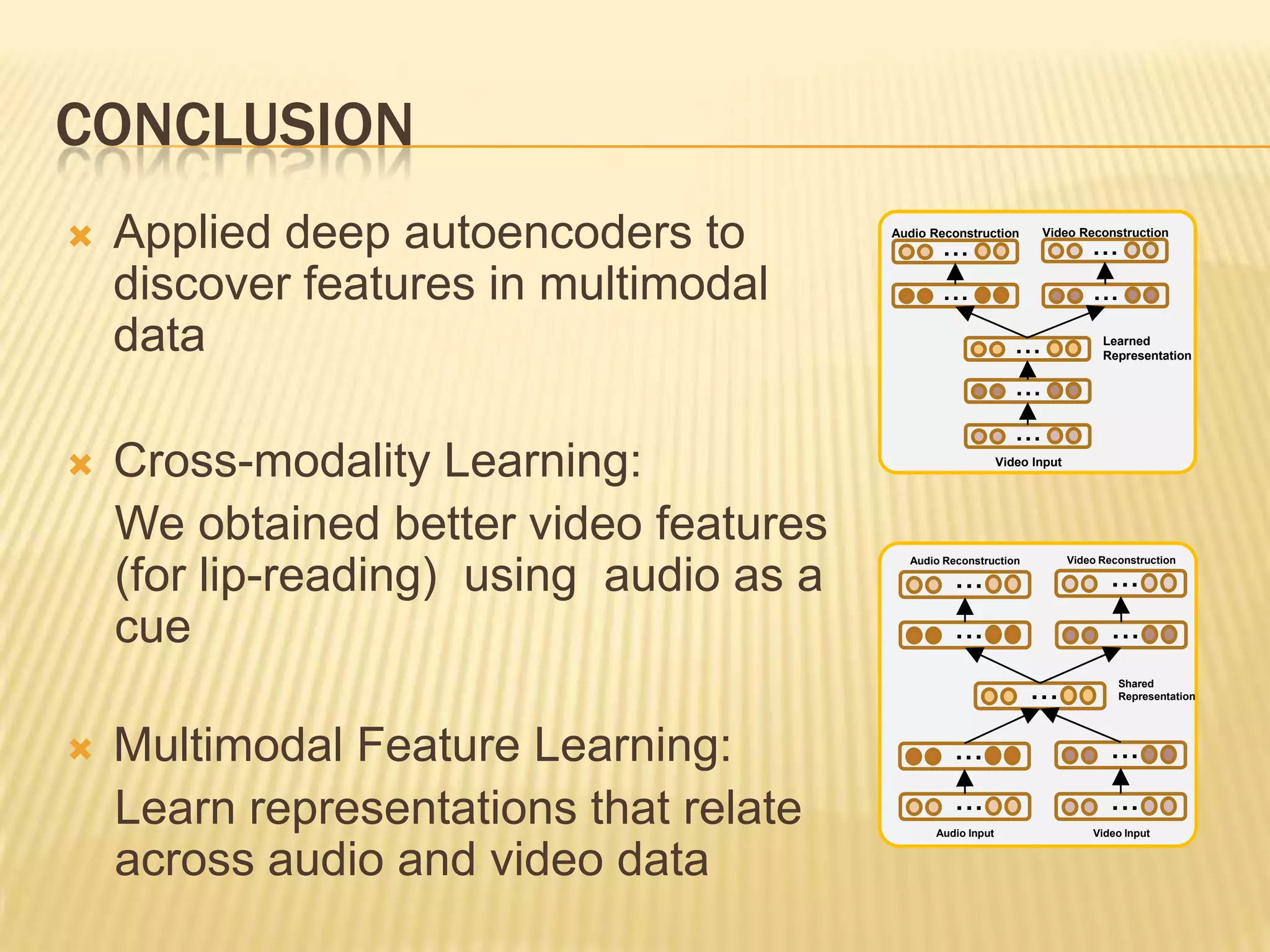
This presentation discusses multimodal deep learning and unsupervised feature learning from audio and video speech data. It introduces the McGurk effect where audio-visual speech is integrated. An autoencoder model is used to learn shared representations from audio and video input that outperform single modality learning on lip-reading tasks. On the AVLetters dataset, the cross-modality features achieved a classification accuracy of 64.4%, and on the CUAVE dataset, an accuracy of 68.7%.