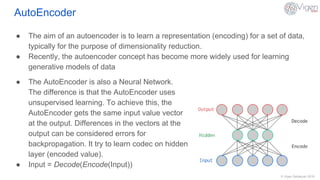
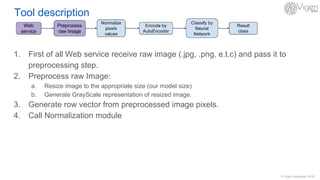
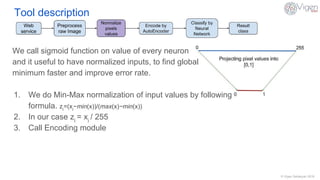
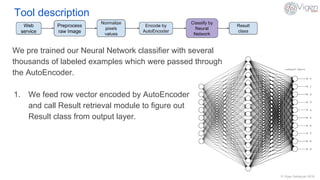
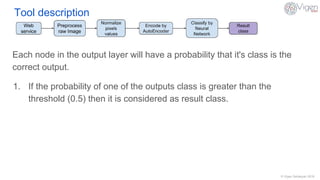
The document outlines a content-based image retrieval (CBIR) system utilizing deep learning, particularly autoencoders, to search for similar images based on their content rather than metadata. It addresses the challenges posed by vast amounts of unlabeled data by employing unsupervised learning to extract high-level features from images. The system has been tested on the MNIST dataset, achieving performance comparable to established algorithms.