The document presents a seminar on deep convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks (DCGANs) by Hansol Kang, highlighting advancements in GAN architecture and training techniques. It discusses various aspects such as model architecture modifications, adversarial training details, empirical validations on datasets, and visualizing network internals through latent space exploration. The concludes with a comparison of GANs to Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) and addressing future work in generative modeling.













![Summary
2018-10-05
34
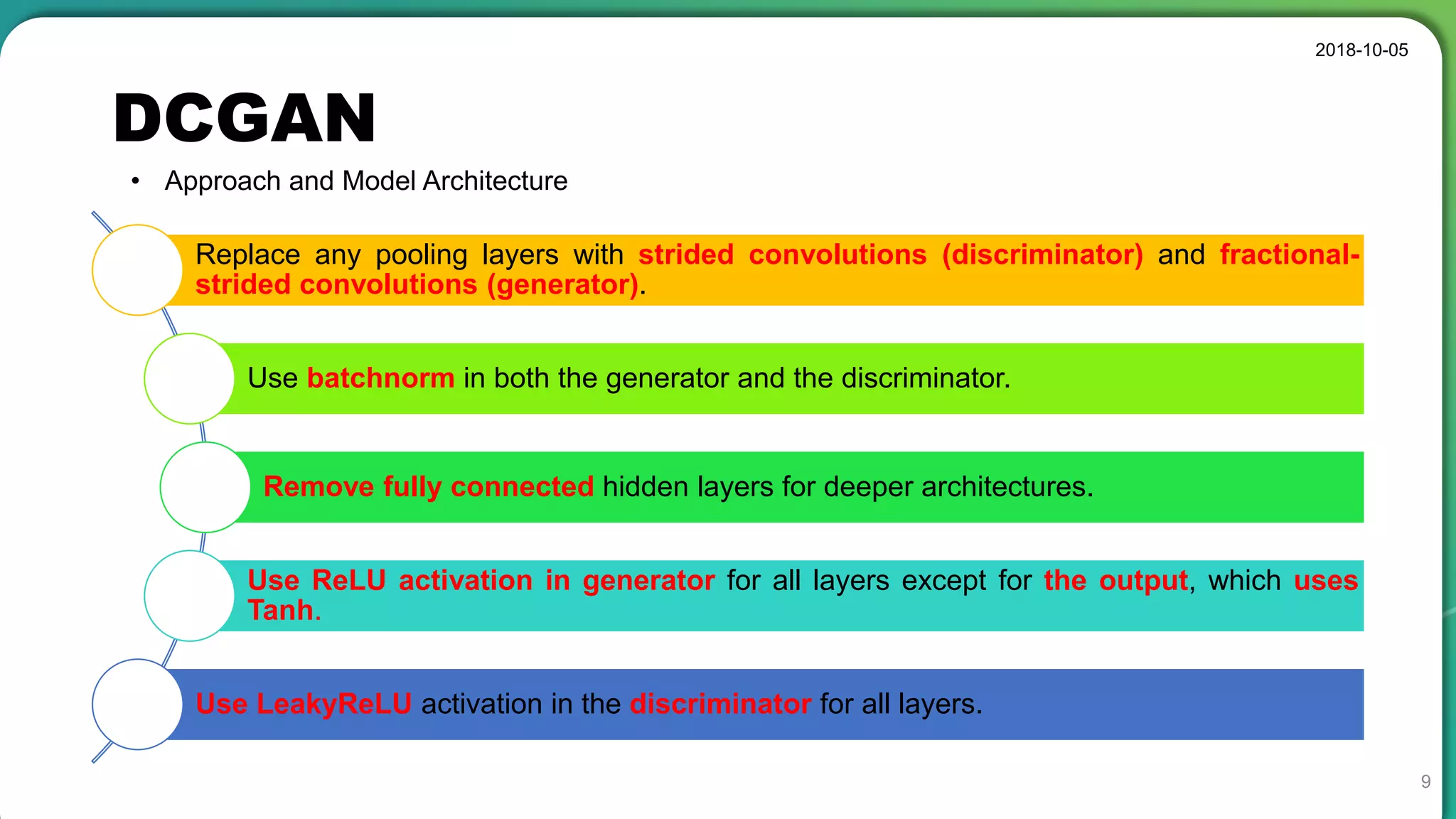
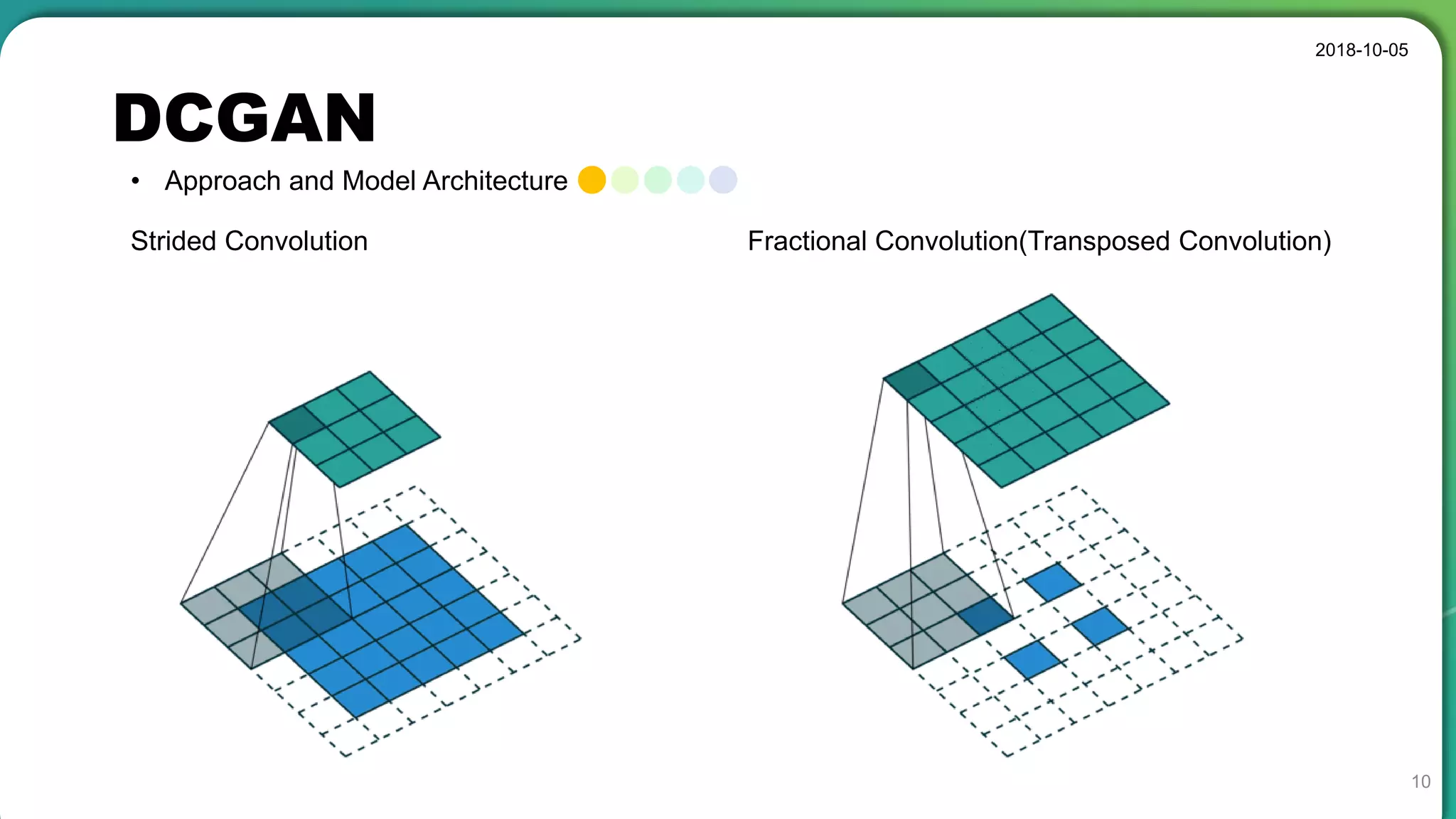
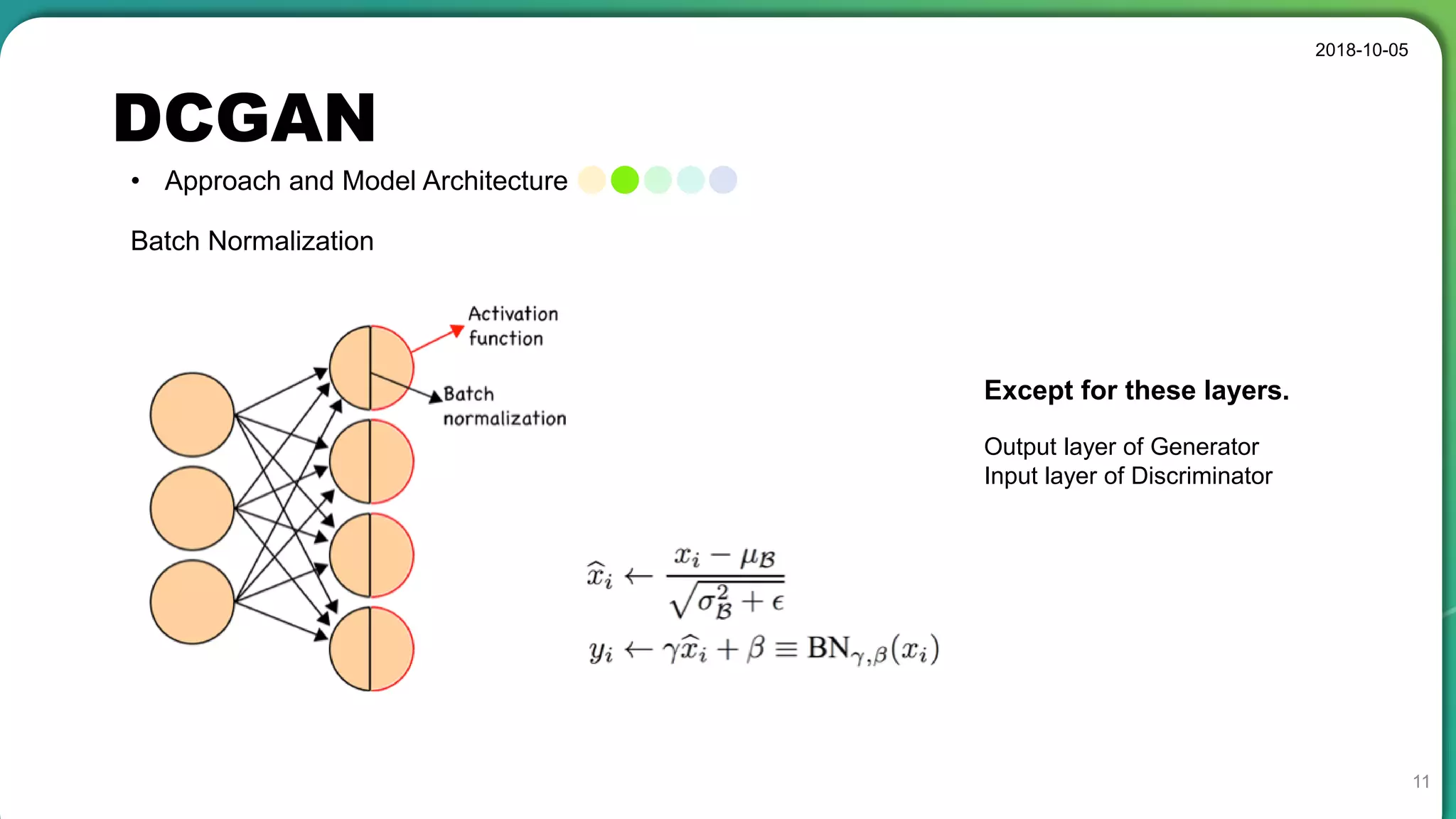
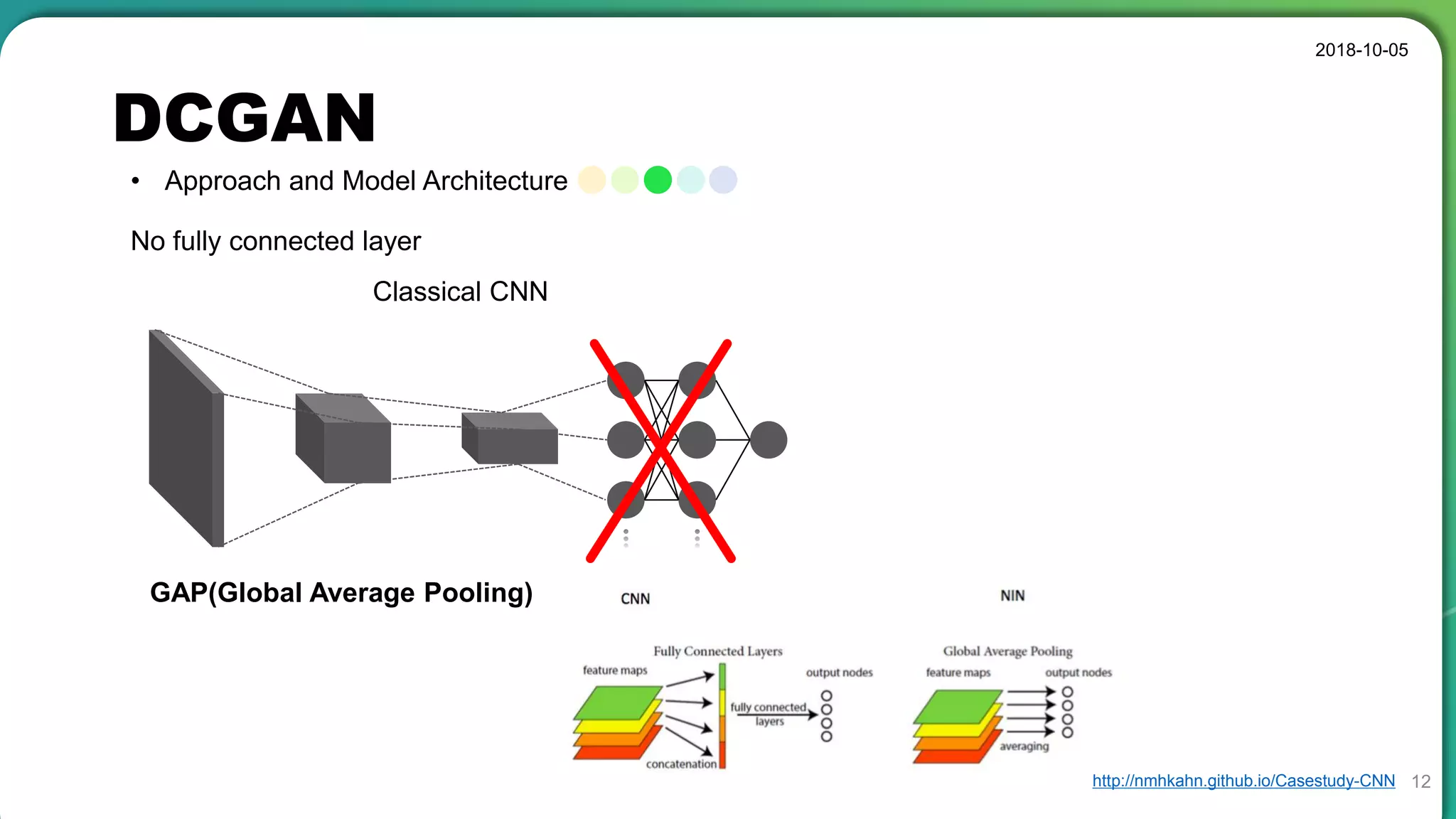
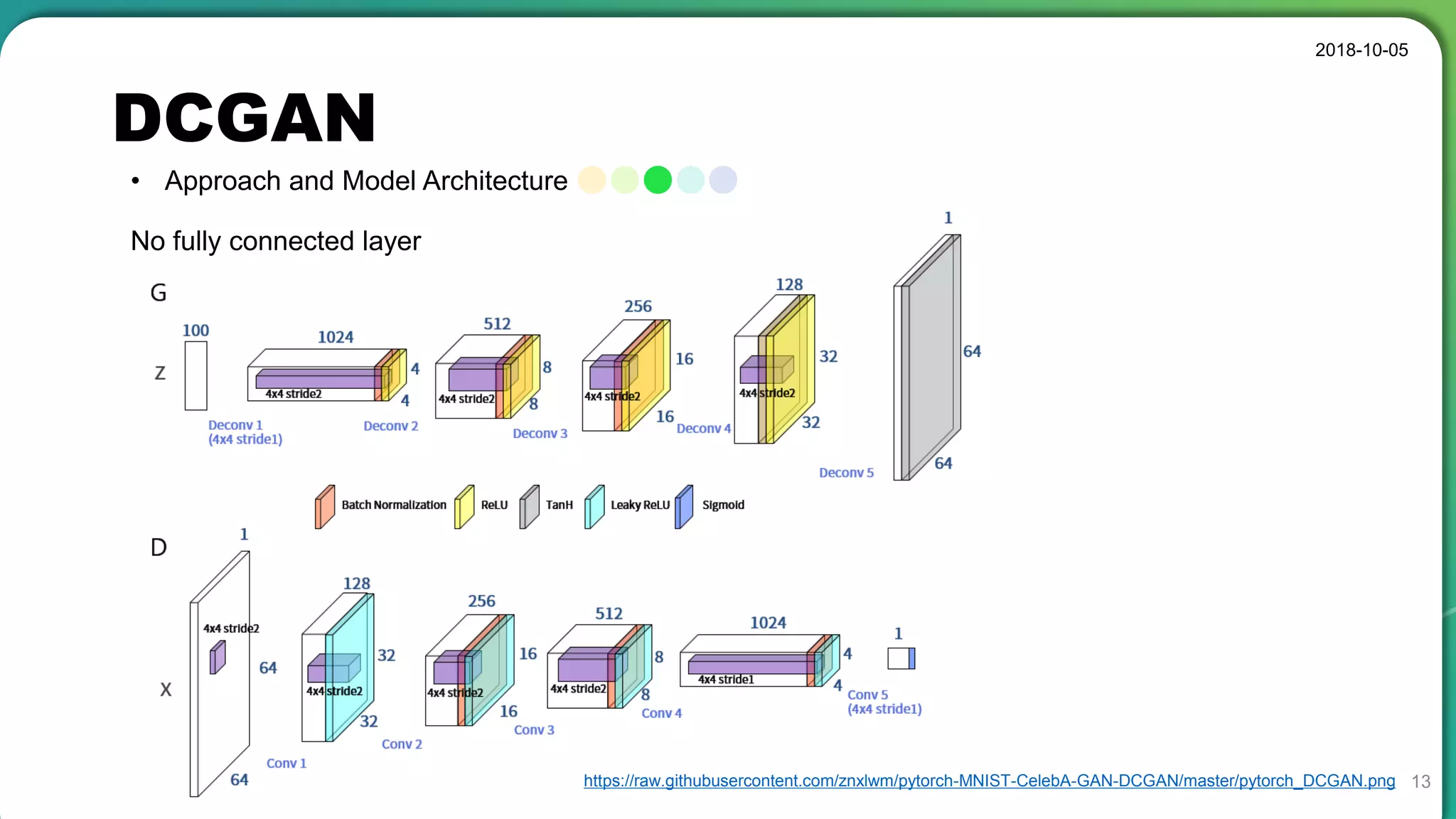
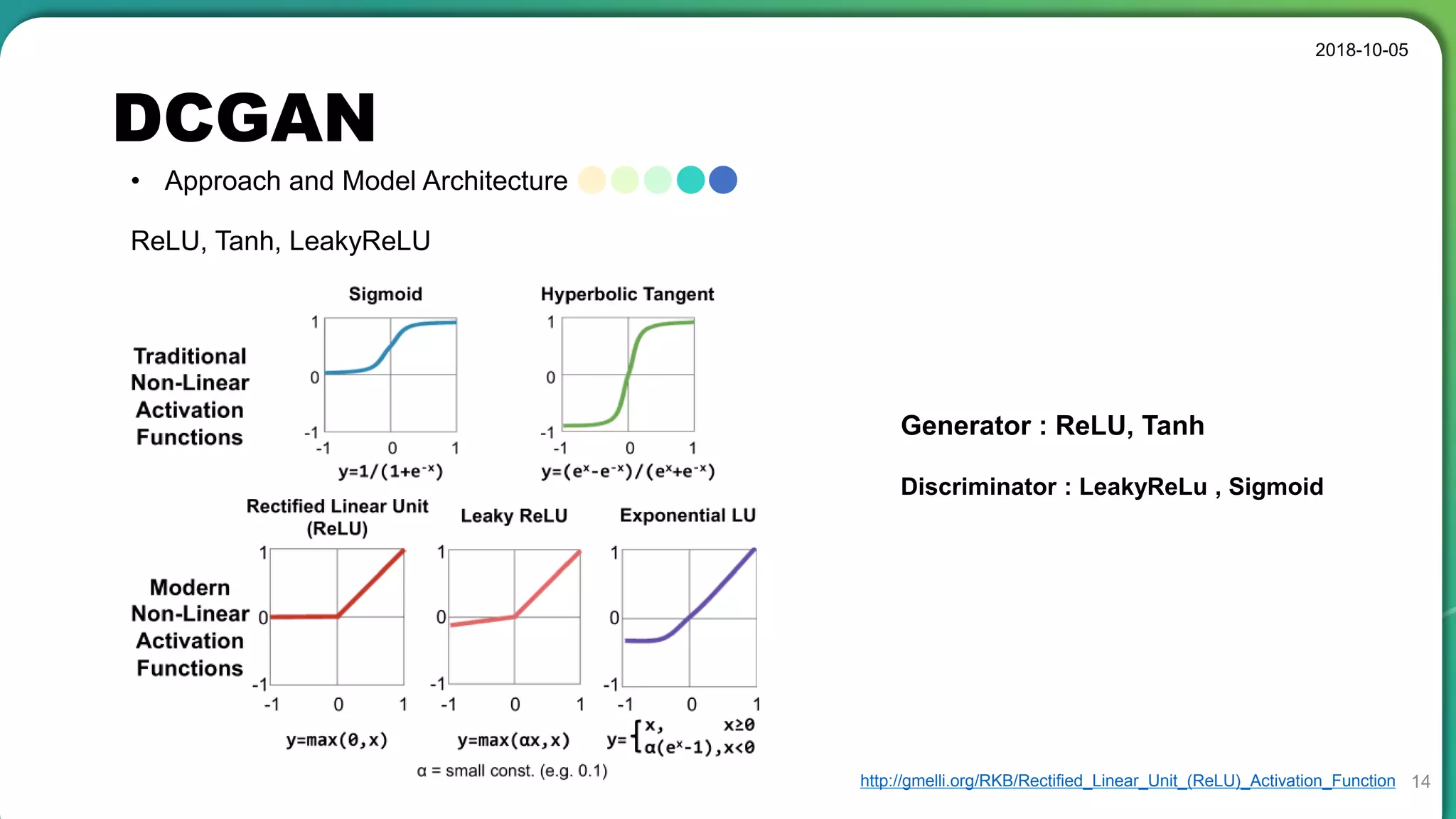
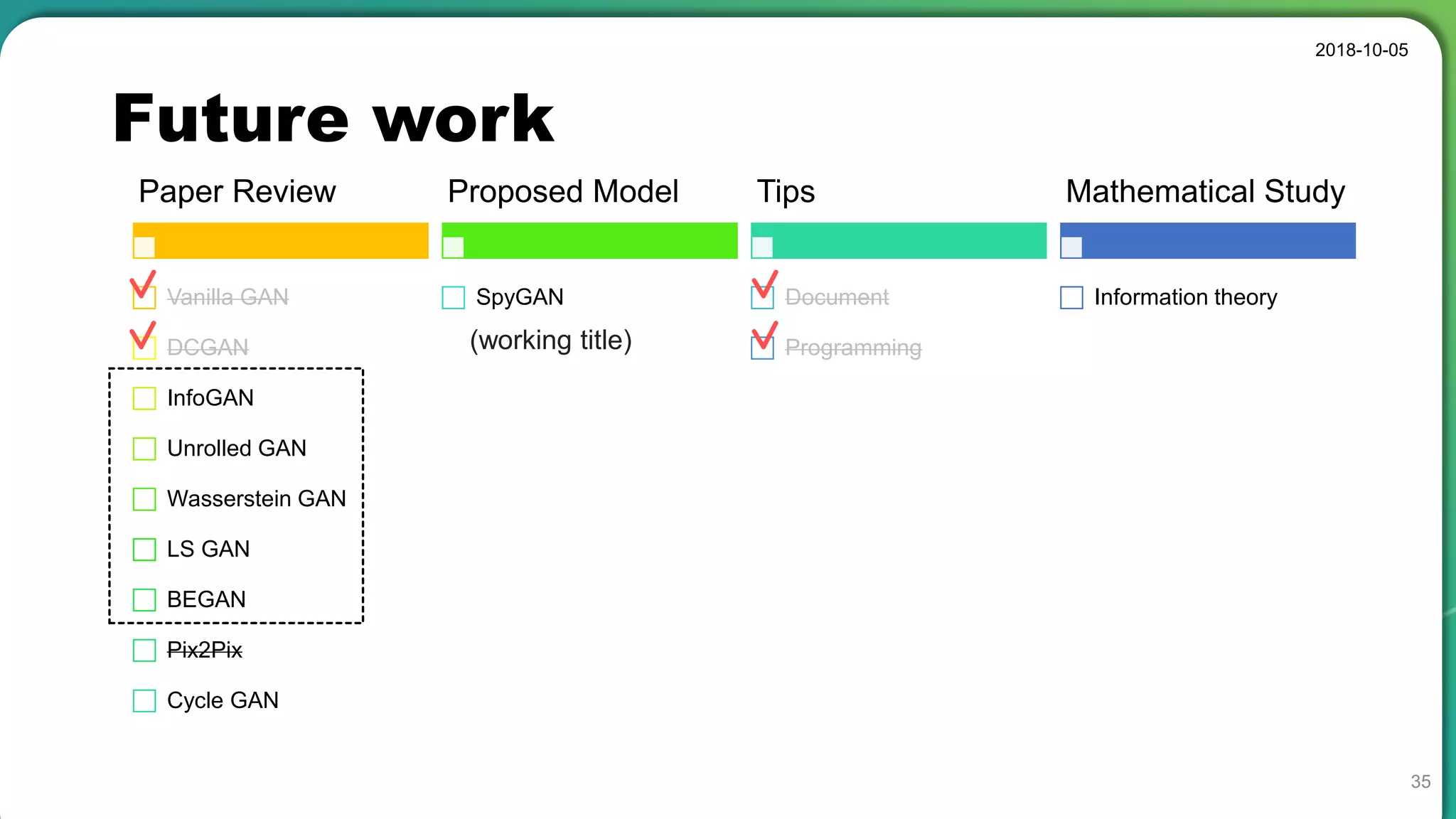
• Stable set of architectures for training generative adversarial networks
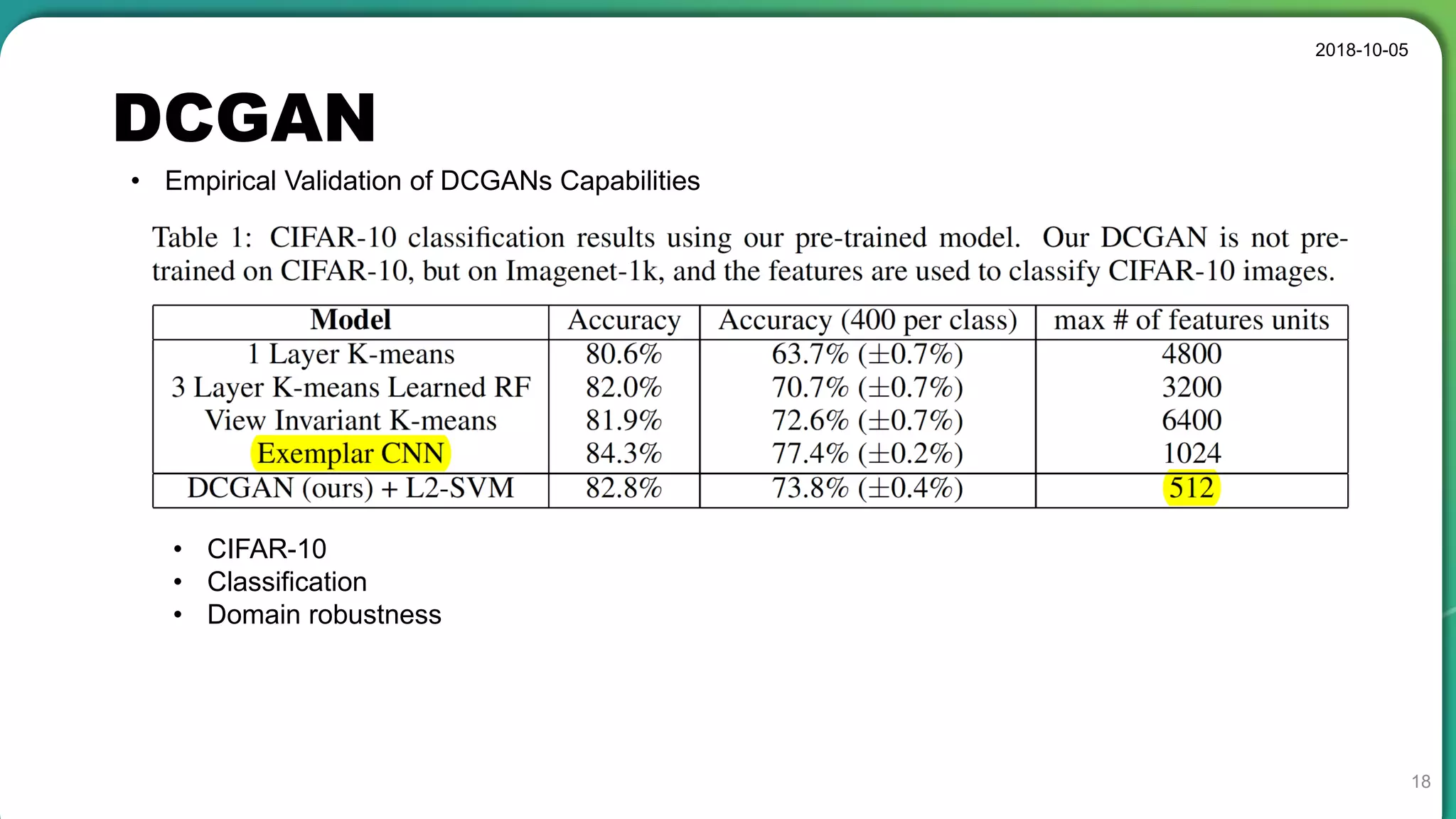
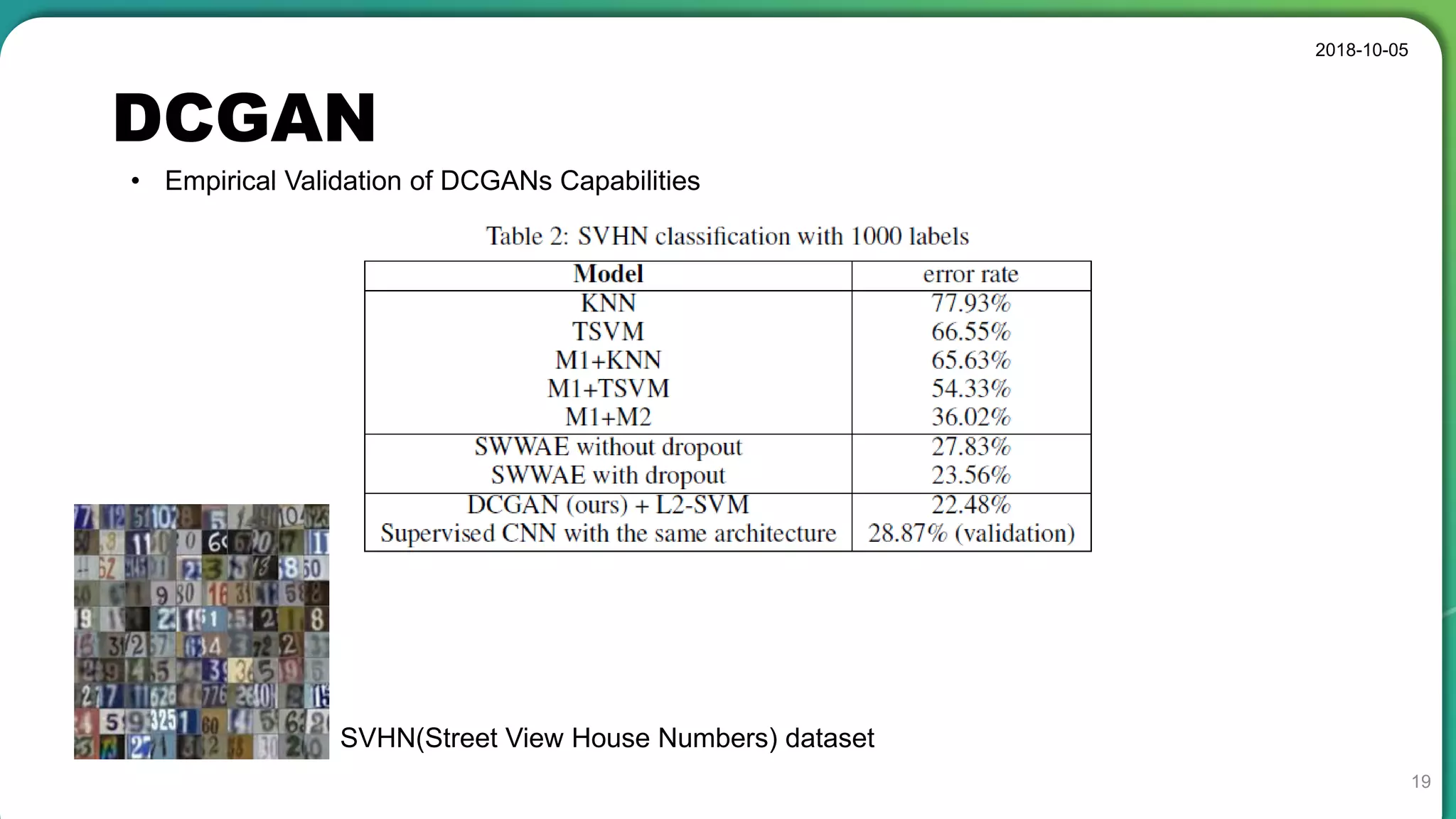
• Good representations of images for supervised learning and generative modeling
• Sometimes collapse a subset of filters to a single oscillating mode
• Latent code has a special meaning, not a simple noise component.
[Instability of GAN]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcgan-181005083557/75/Deep-Convolutional-GANs-meaning-of-latent-space-34-2048.jpg)



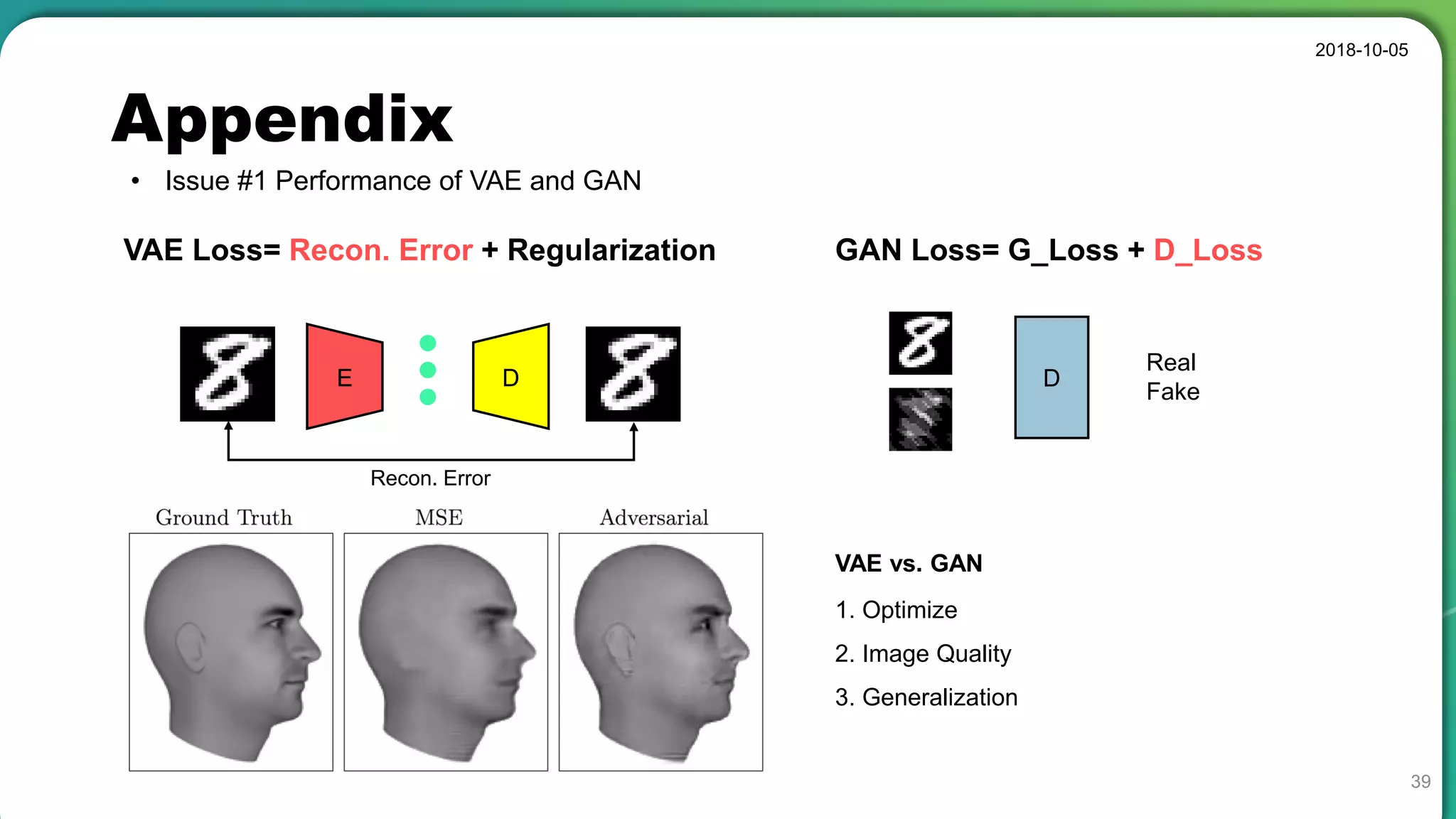
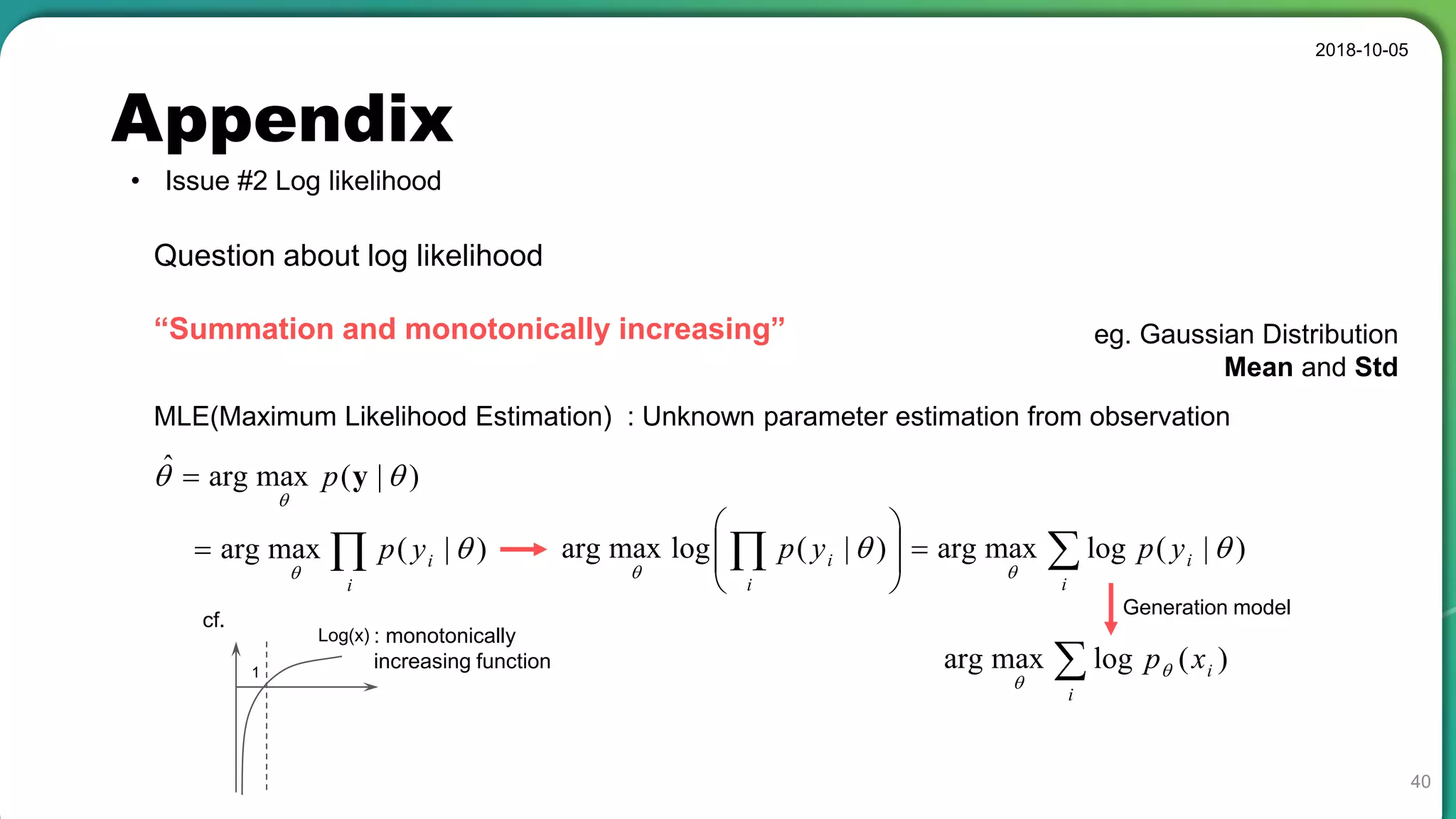
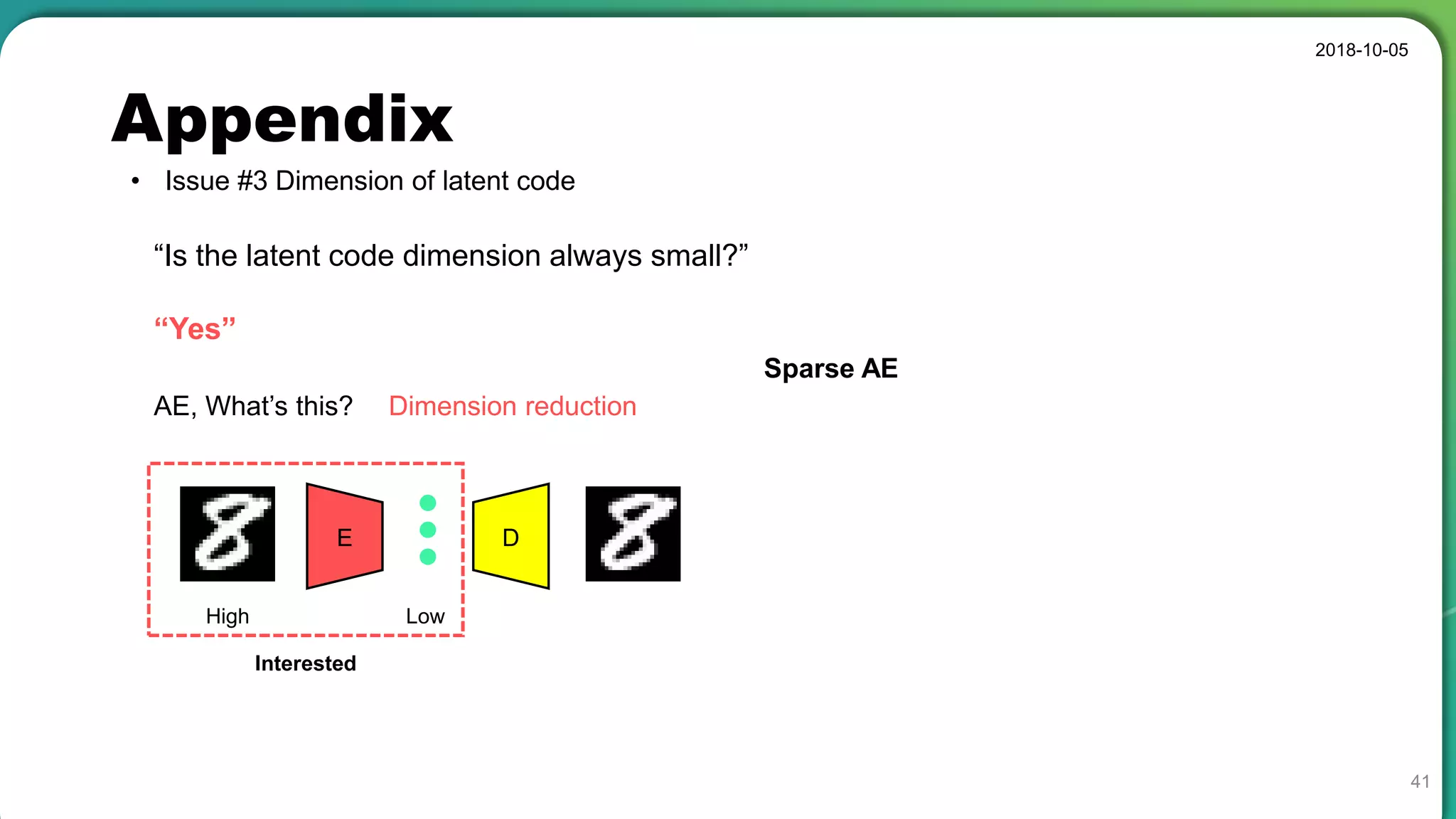
![Appendix
• PyTorch (Variable length inputs)
2018-10-05
43
Shape = {Size} torch.Size([128, 3, 32, 32])
Shape = {Size} torch.Size([128, 64, 16, 16])
Shape = {Size} torch.Size([128, 16384])3x32x32
CIFAR-10
Shape = {Size} torch.Size([128, 64, 109, 89])
Shape = {Size} torch.Size([128, 3, 218, 178])
Shape = {Size} torch.Size([128, 620864])
3x178x218
CelebA
Conv
Input
Pool
FC
Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, k_size, s, p)
Reshape(bat_sz,-1)
Input size is not fixed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcgan-181005083557/75/Deep-Convolutional-GANs-meaning-of-latent-space-43-2048.jpg)