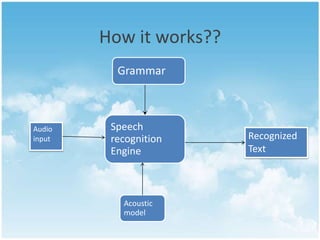
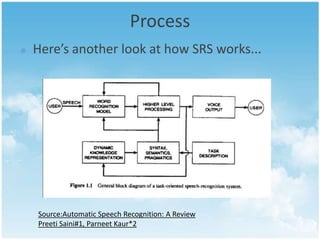
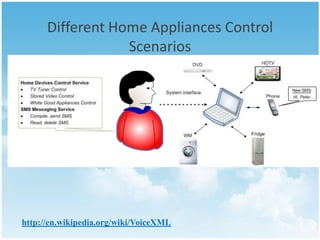
This document provides an overview of speech recognition technology. It defines speech recognition as the ability to translate spoken words to text. The key components of a speech recognition system include an audio input, grammar, speech recognition engine, acoustic model, and recognized text output. The speech recognition engine uses the acoustic model and grammar to analyze the audio input and return recognized text. Applications of speech recognition include dictation, data entry, and assisting individuals with disabilities. While speech recognition technology has advanced, challenges remain around digitization of speech, signal processing, and accurately recognizing different speakers. The future of assistive technology using speech recognition in education looks promising.