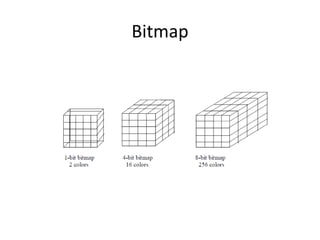
Digital images are represented by a matrix of numeric values where each value corresponds to the intensity of a pixel at a specific location. Images can be binary, representing black and white, or they can have multiple intensity levels represented by integers to capture shades of gray. Standard image file formats specify the spatial resolution in pixels and color encoding using a certain number of bits per pixel. When stored, an image is saved as a two-dimensional array of values, each representing intensity data for a pixel. Bitmap images use a one-dimensional matrix for monochrome and greater bit depth for more colors. Popular graphics software programs allow for image editing, painting and drawing.