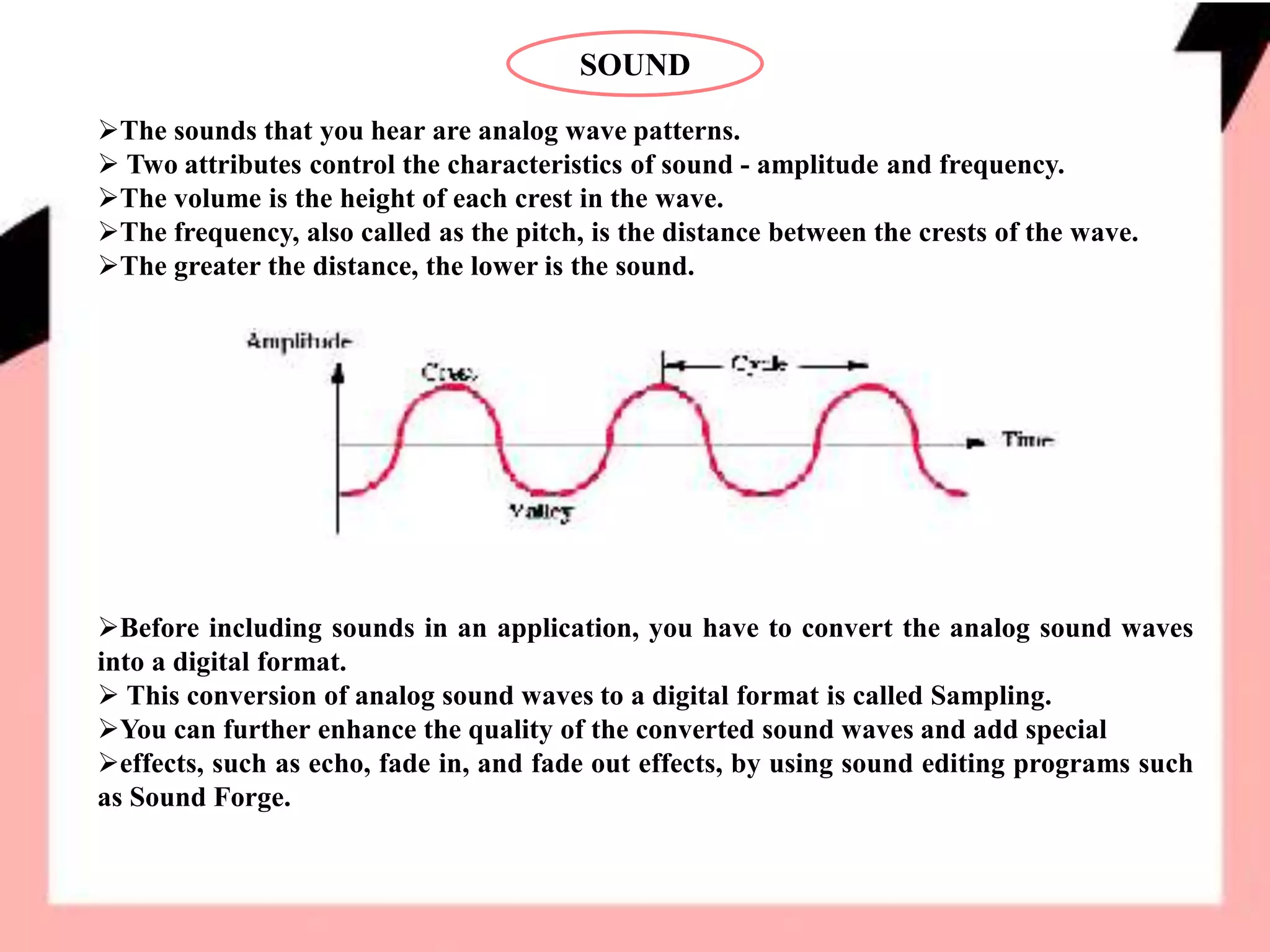
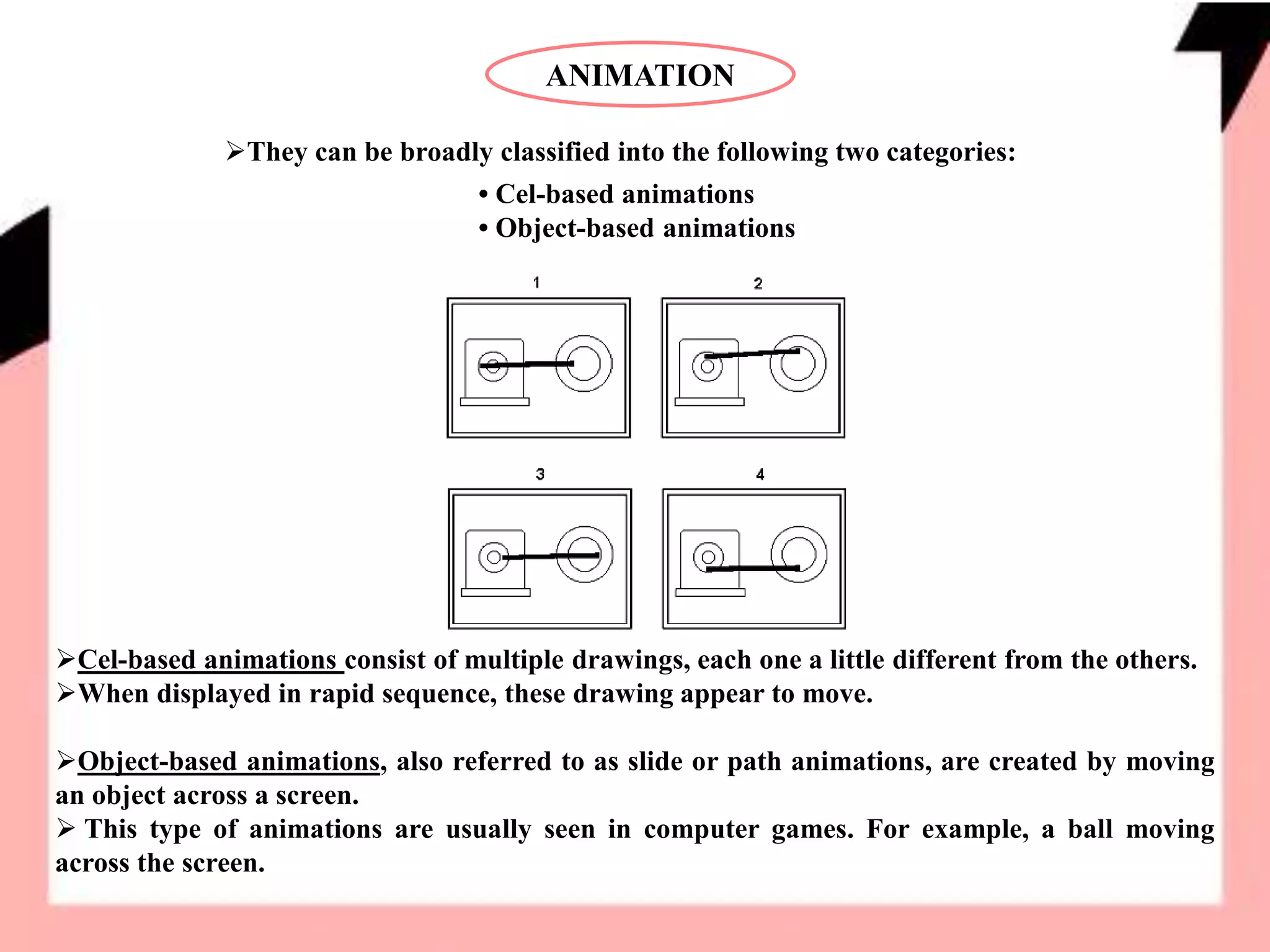
The document discusses various multimedia elements like sound, animation, and video. It describes how sound waves are converted to digital format through sampling. It explains different animation techniques like cel-based and object-based animations. Popular file formats for images, sound, and video are also outlined along with multimedia hardware and software. Inline embedding of multimedia and use of helper applications is briefly covered.